Context: Recently, a new joint report “Digital Trade for Development” was released which looks into opportunities and challenges for developing economies arising from digital trade.
About the IMF Report on Digital Trade for Development
- Published by: It is a joint publication by the International Monetary Fund (IMF), the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD), the World Bank and the World Trade Organization.
Key Highlights of IMF Report on Digital Trade for Development
- Digital Transformation: The world is witnessing a paradigm shift with the advent of digital transformation.
- Today, an estimated 5.4 billion people can connect to the internet, yet one-third of the global population remains offline.
- New Opportunities: Cross-border digitally delivered services are a rapidly growing segment of international trade presenting new opportunities.
- With a nearly fourfold increase in value since 2005, digital trade outpaces goods and traditional services, comprising 54% of total services exports.
- Policy Challenges: The report explores specific policy issues, including the WTO’s moratorium on customs duties on electronic transmissions, regulation of cross-border data flows, competition policies, and consumer protection.
Must Read: OECD’s International Migration Outlook 2023
About WTO Rules and E-Commerce
- Regulation: Since 1998, the WTO Work Programme on E-commerce has considered how WTO rules apply to e-commerce, which is widely seen as being within the scope of existing WTO agreements.
- The WTO moratorium on imposition of customs duties on electronic transmissions is the only WTO provision that applies explicitly to e-commerce and has been in place since 1998.
- Problem: A majority of WTO members consider that, to respond to the changing nature of trade and to facilitate e-commerce-related activities, existing WTO rules related to digital trade need to be updated and complemented by new ones.
- Negotiations: The WTO e-commerce negotiations, through a Joint Statement Initiative (JSI), began in 2019 with 90 members trying to reach a consensus on data flows, data localization, and protection of source code by MC13.
- India’s Stand: India has opposed the plurilateral initiative and has kept away from the talks. India backs flexibility in digital policy and has concerns about the potential dominance of a handful of e-commerce players.
|
What is Digital Trade?
- Digital Trade Definition: According to the OECD, digital trade encompasses digitally-enabled transactions of trade in goods and services that can either be digitally or physically delivered, and that involve consumers, firms, and governments.
- For example:
- Purchase and physically deliver a paper book through an online marketplace.
- Purchase and digital delivery of an e-book.
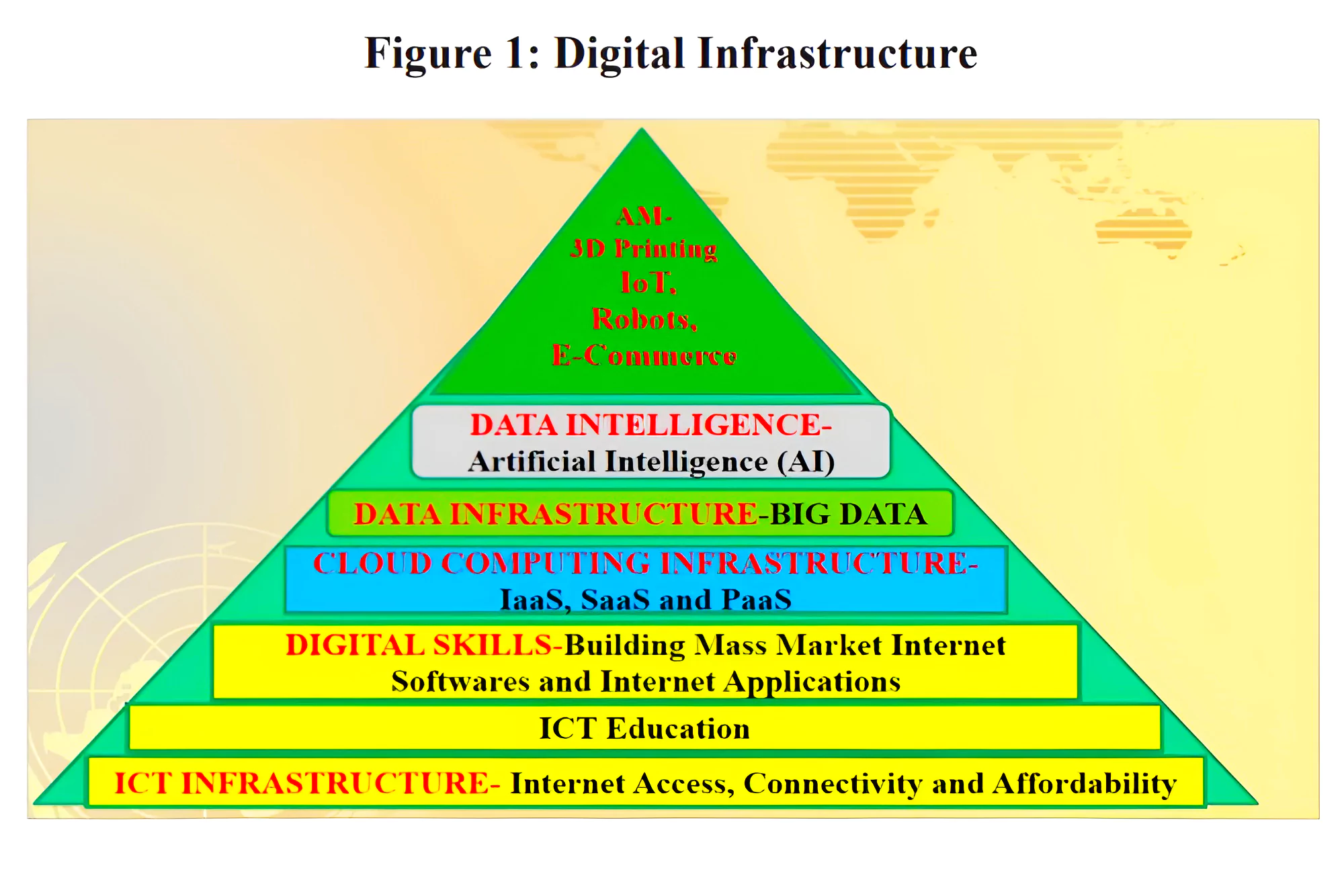 Digital Economy: Economic activities conducted or facilitated through digital technologies.
Digital Economy: Economic activities conducted or facilitated through digital technologies. - Digitalisation and Changing Trade: Digitalisation increases the scale, scope and speed of trade and allows firms to bring new products and services to more digitally-connected customers across the globe.
Digital Trade in India: Status & Vision
- India’s Trillion-Dollar Digital Opportunity: It is an endeavor of the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) to present India’s Digital Vision and the potential of India to attain $1 trillion of economic value of digital economy by 2025.
- Economic Value of Digital Trade: According to the All India Management Association and the Hinrich Foundation research, the economic value of digital trade in India, including exports, has the potential to grow 14 times to $512 billion from $35 billion by 2030 if cross-border data flows and storage are fully facilitated.
Also Refer: Vision India@2047: Transforming India into a Developed Nation
Government Initiatives to Boost Digital Trade in India
- Digital India Programme: The program aims to establish better connections between citizens and the government via e-services and deliver government services in a cost-effective and transparent manner.
- For example, as per budget announcement for FY 2022-23, the 12 DTH Channels would be expanded to 200 PM e-Vidya DTH TV Channels, ensuring e-service delivery.
- AI for All Strategy: Artificial Intelligence (AI) for All is a self-learning online program designed to raise public awareness about AI which aims to demystify AI for people from all walks of life and build a ‘Digital First Mindset’.
- Digital Infrastructure Built on India Stack: India Stack consists of open Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) that unlock essential economic elements such as identity, digital payments, and data. This creates a platform for easy transactions and the delivery of goods and services.
- The Aadhaar layer provides online bio-metric-based digital identities to individuals.
- Government eMarketplace (GeM): The government has also digitized procurement of goods and services by creating a centrally managed GeM, one of the largest procurement platforms.
- GeM has surpassed ₹2 Lakh Crore in Gross Merchandise Value (GMV) within less than 8 months of the current fiscal year (2023-24), surpassing the total GMV inscribed at the end of last fiscal year.
- Pandemic Relief Services: Bringing relief to people during the COVID-19 pandemic, were driven on India’s digital public infrastructure i.e. COWIN, a technology platform created by the government to control the rollout of the world’s largest vaccination program.
Digital Trade and Associated Opportunities in India
- Increased Efficiency: Adopting digital technologies reduces manual tasks and enhances operations, leading to cost reductions, quick decision-making, and a competitive edge.
- For instance, adopting advanced technologies, such as AI, Machine learning, blockchain, and cloud computing, will improve the efficiency of Indian businesses, making them globally competitive.
- Innovation and Competitiveness: Digital trade enables firms to use new and innovative digital tools to overcome barriers to growth, helping facilitate payments, enabling collaboration, avoiding investment in fixed assets through cloud-based services, and using alternative funding mechanisms such as crowdfunding.
- Elevated Customer Experience: Digital transformation enables businesses to tailor services to customer needs, offering personalized experiences and constant digital support, bolstering customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Insightful Data Analysis: The extensive data generated by digital means provides critical insights into consumer preferences and market movements, aiding data-driven decisions and fostering business growth.
- For instance, personalised advertisement by using technology and data, retailers are in a position to show the right product to the right person, at the right time, in the right place.
- Expanded Global Reach: Digital transformation offers access to international markets, allowing businesses to extend their reach and explore new revenue streams and global opportunities.
Challenges Associated with Digital Trade in India
- Global Disparities in Digital Preparedness: Developed countries dominate trade in digitally deliverable services. By contrast, the shares of least developed countries (LDCs) and landlocked developing countries (LLDCs) of digitally deliverable services trade are much lower than for services in general.
- For instance, in 2022, high-income economies were responsible for over 82% of global exports of digitally delivered services, meanwhile, 17% of digitally delivered services exports originated from middle-income economies, with China and India accounting for 6% and 5%, respectively.
- Domestic Regulatory Environment: India’s evolving data governance framework is informed by multiple policy concerns including building indigenous data storage, boosting domestic digital investments, enhancing governmental control over data, etc. This complex framework makes it more cumbersome and costly for firms to engage in digital trade.
- For instance, digital trade is where some of the biggest U.S. tech companies including Amazon, Google, Meta, Intel, etc. have flagged multiple policy barriers to trading with India in a note titled “Key threats to digital trade 2023”.
- Digital Divide: There is a grave digital divide in India wherein gaps exist in internet usage and access to digital infrastructure and a significant portion of the population lacks internet access.
- According to the Internet in India Report 2022, the digital divide between states, with Bihar (32%) having less than half the level of internet penetration than the leading state, Goa (70%).
Way Forward to the Digital Trade
- Facilitating Regulatory Environment: Policies and regulations should enable remote transactions, enhance trust in digital markets, promote affordable access, and support cross-border deliveries.
- A predictable and interoperable environment that provides appropriate safeguards related to online transactions (such as data privacy, consumer protection and cybersecurity) is essential for the digital trade ecosystem to thrive.
- Estimates suggest that improved digital connectivity is twice as effective at lowering trade costs in the middle- and low-income economies with an enabling regulatory environment for digitally delivered services.
- Bridging the Digital Divide: International financial and technical support is needed to build the capacity of developing economies like India to improve connectivity and skills and regulate areas relevant to digital trade.
- For instance, initiatives like the WTO-led Aid for Trade, the UNCTAD-led eTrade for all and the World Bank-led Digital Advisory and Trade Assistance (DATA) Fund can help.
- Digital connectivity is one of the three priority areas in the WTO Aid for Trade work program for 2023-24, and recent Aid for Trade commitments to the ICT sector stand at US$ 2.16 billion in 2021-22.
- International Cooperation in Digital Trade: International cooperation is increasingly addressing rules on digital trade, with progress mainly observed in bilateral and regional trade agreements.
-
- For instance, the WTO Work Programme on E-commerce, initiated in 1998, underscores the need to update existing rules to accommodate the evolving nature of digital trade.
- Regulatory Issues Beyond Trade: Cooperation on balanced global data governance, effective regulation of market power in digital markets, and robust consumer protection frameworks are vital.
- Global solutions are required for regulatory issues like cross-border data flows, competition, and consumer protection.
- Maximising Positive Impact of Digital Trade: According to the ‘Data Opportunity: The Promise of Digital Trade’ report, to maximize the positive impact, issues such as red tape on digital enterprises, restricting cross-border data flows, and providing imbalanced copyright and intermediate liability regulations, need to be addressed.
Also Read: India To Be A $ 7 Trillion Economy By 2030: CEA

 Digital Economy: Economic activities conducted or facilitated through digital technologies.
Digital Economy: Economic activities conducted or facilitated through digital technologies. 