Context: The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW) released the updated regulations under Schedule M of the Drugs and Cosmetics Rules, 1945.
Schedule M
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP)
|
|---|
News Source: Business Standard
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: According to the report analysis by Respirer Living Sciences and Climate Trends, only 27 out of 49 cities showed a decline in PM 2.5 level over five years despite the effort put forth by the National Clean Air Programme (NCAP).
About the National Clean Air Programme (NCAP)
|
|---|
Also Refer: Mumbai’s Air Pollution Is The Second Highest In The World
News Source: The Hindu
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: Tata Memorial Hospital (TMH), Mumbai, is addressing the shortage of cancer specialists through AI in cancer detection.
About the Department of Biotechnology
About National Cancer Grid (NCG)
|
|---|
Definition: It is a compilation of radiology and pathology images linked to clinical information, outcome statistics, treatment specifics, and additional metadata.
Mechanism: It employs Biosensing with light to generate non-invasive visual representations of biological processes in cells, tissues, and anatomy for more accurate diagnosis and treatment.
| Biosensing: is the detection of target molecules based on the principles used by a living system such as an immune system.
Bioimaging: It includes methods for visualising fixed biological material for observation. |
|---|
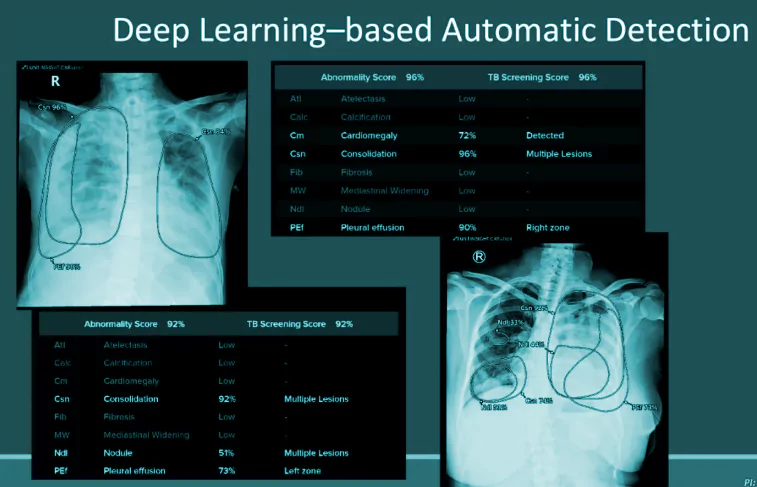
| Use of AI in the future in treating Cancers and Tumours
Personalised Treatment: AI is expected to customise treatment approaches according to individual patient profiles, enhancing therapeutic results. Facilitating Diagnosis: AI has the potential to enable doctors to diagnose intricate cancers seamlessly with just a single click, elevating the precision of cancer treatments. Continuous Learning: As AI undergoes continuous learning and improvement, it provides increasingly precise cancer diagnoses, leading to better patient outcomes and supporting healthcare professionals. |
|---|
Also Refer: Casgevy Therapy – A Gene Therapy For Sickle Cell Disease
Artificial intelligence (AI) in treating cancer has great potential to change how we approach healthcare however, all the challenges, like biased data, rules, and insufficient infrastructure, need to be solved for AI to be used fairly and effectively in healthcare.
News Source: Indian Express
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: Recently, the Indian Defence Minister visited the United Kingdom for bilateral talks.
India and the U.K. are both trying to carve out their new identities on the global stage and their strategic convergence has allowed for the possibility of reimagining the future of their partnership.
News Source: The Hindu
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: Recently, the renowned Hindustani classical singer- Ustad Rashid Khan passed away in Kolkata.

About Mian Tansen
Also Refer: Tansen Samaroh Or Tansen Music Festival 2023 |
|---|
Indian Classical Music:
|
|---|
Must Read: Sahitya Akademi Award 2023
News Source: PIB
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: The Ministry of Commerce and Industry has set up a task force to identify and resolve trade barriers being faced by foreign exporters to provide greater market access to domestic goods.
Barriers Faced by India’s Exports
|
|---|
Also Refer: Meaning And Reasons For International Trade
News Source: Business Outlook
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: Recently, the Union Minister laid the foundation stone for the Modernisation of Paradip Fishing Harbour.
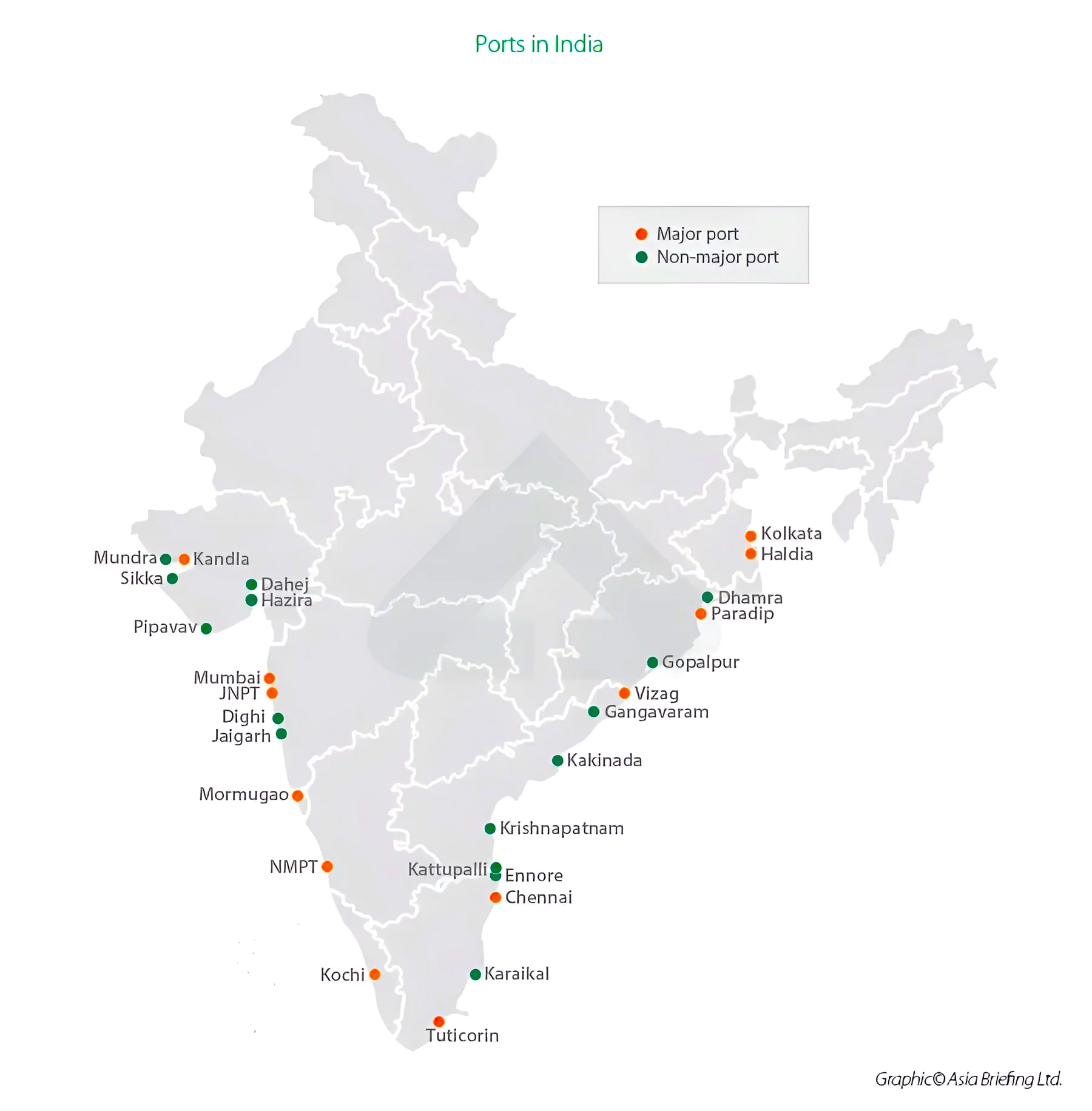
About PM Matsya Sampada Yojna (PMMSY)
Must Refer: Harnessing the Potential of Fisheries Sector in the Marine States |
|---|
| Major port | Minor port |
|---|---|
| Managed by Union Ministry of Shipping | Managed by State Government |
| Handles international trade | Handles coastal and fishing trade |
Also Read: Indian Ports Hold The Key To Growth & Employment
Additional Reading: Major Ports in India
News Source: PIB
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: Ocean surface waves caused by tropical cyclones have increased over time as per the research published in the journal Nature Communications.
About ERA5
|
|---|
What are Ocean Surface Waves?
Hazards of Ocean Surface Waves
|
|---|
About Tropical Cyclone
|
|---|
To Read More: Tropical Cyclones
News Source: DTE
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
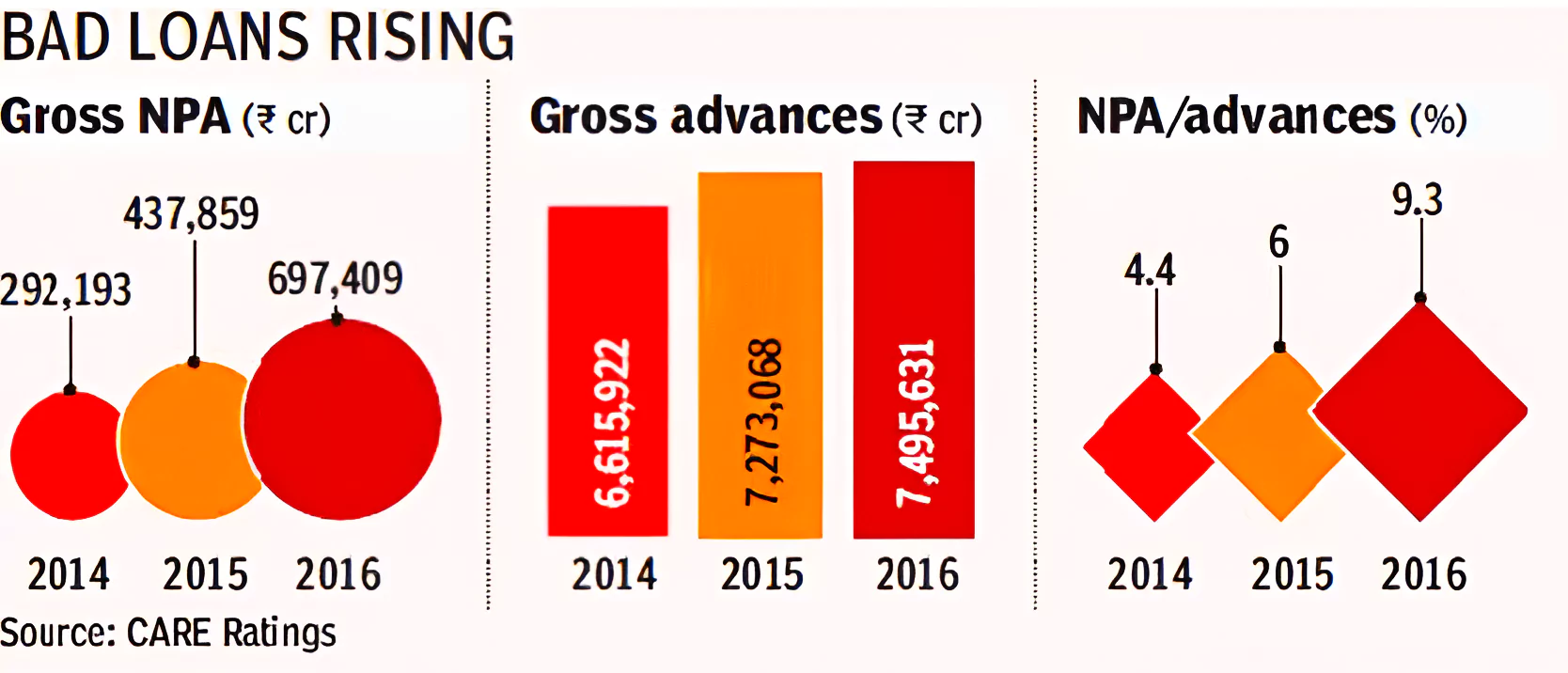
Context: This article is based on the news “It is time for a full-scale overhaul of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code” which was published in the Hindu. The Financial Stability Report (FSR) released by the Reserve Bank of India reveals the challenges faced and the need for the full-scale overhaul of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC), 2016.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Financial Stability Report (FSR), RBI, National Company Law Tribunals (NCLTs), Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs), and Non-Performing Assets (NPAs).
Relevancy for Mains: Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC): Objectives, Significance, Concerns and Institutional Framework for the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Resolution. |
|---|
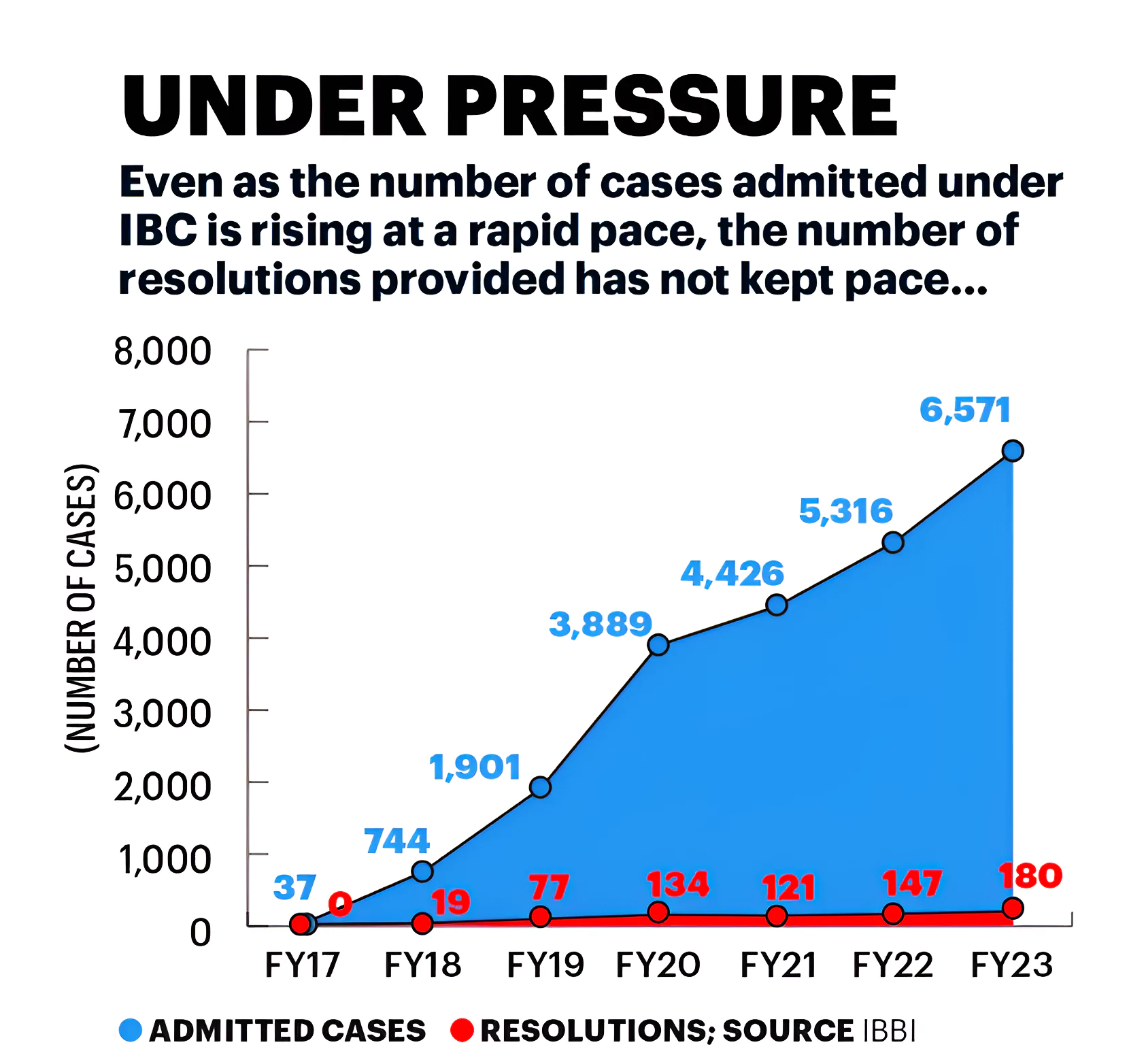
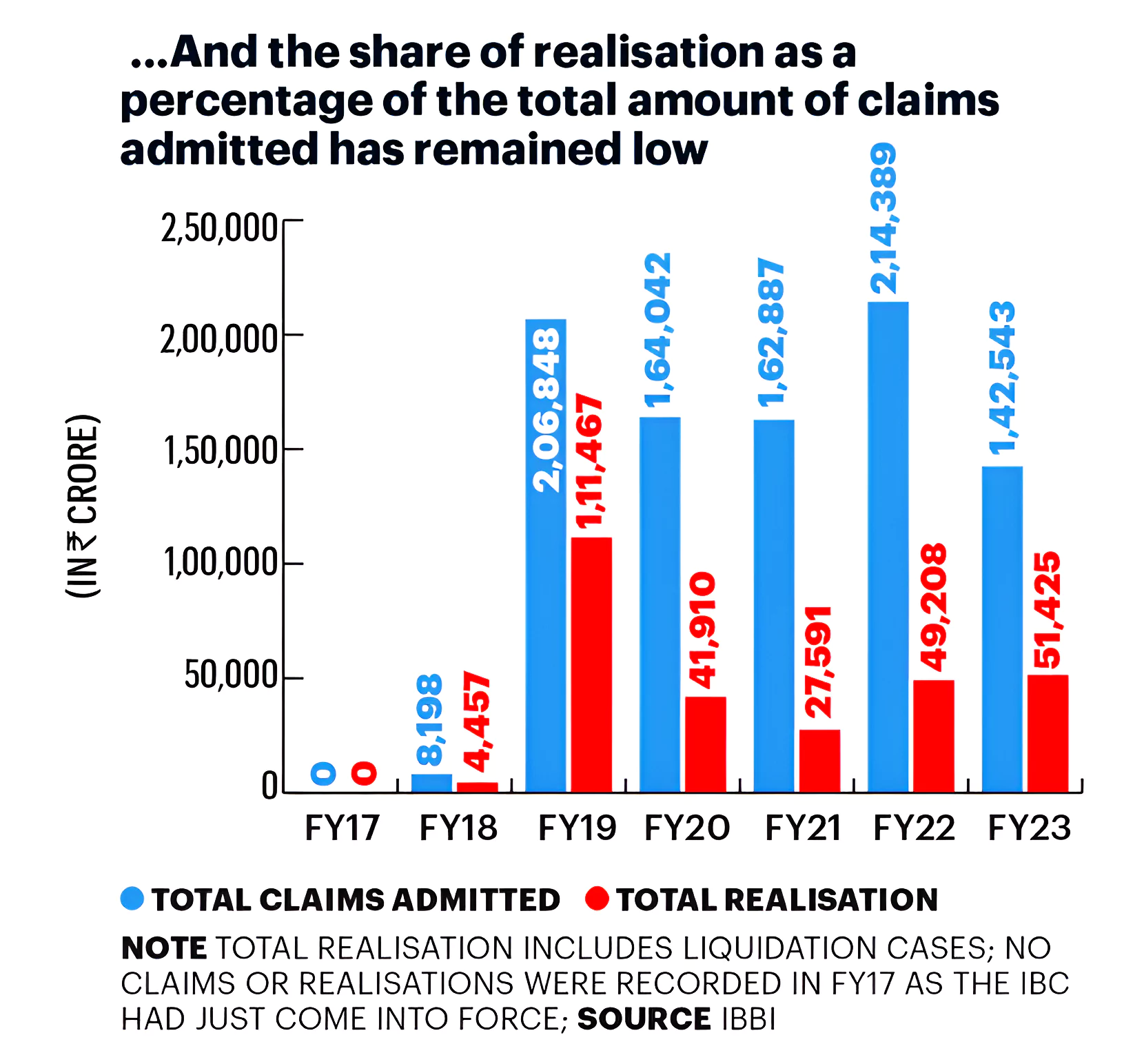
Must Read: Asset quality of Indian banks improves to decadal high: RBI
About Financial Stability Report (FSR)
|
|---|
Securitization and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest Act (SARFAESI), 2002:
|
|---|
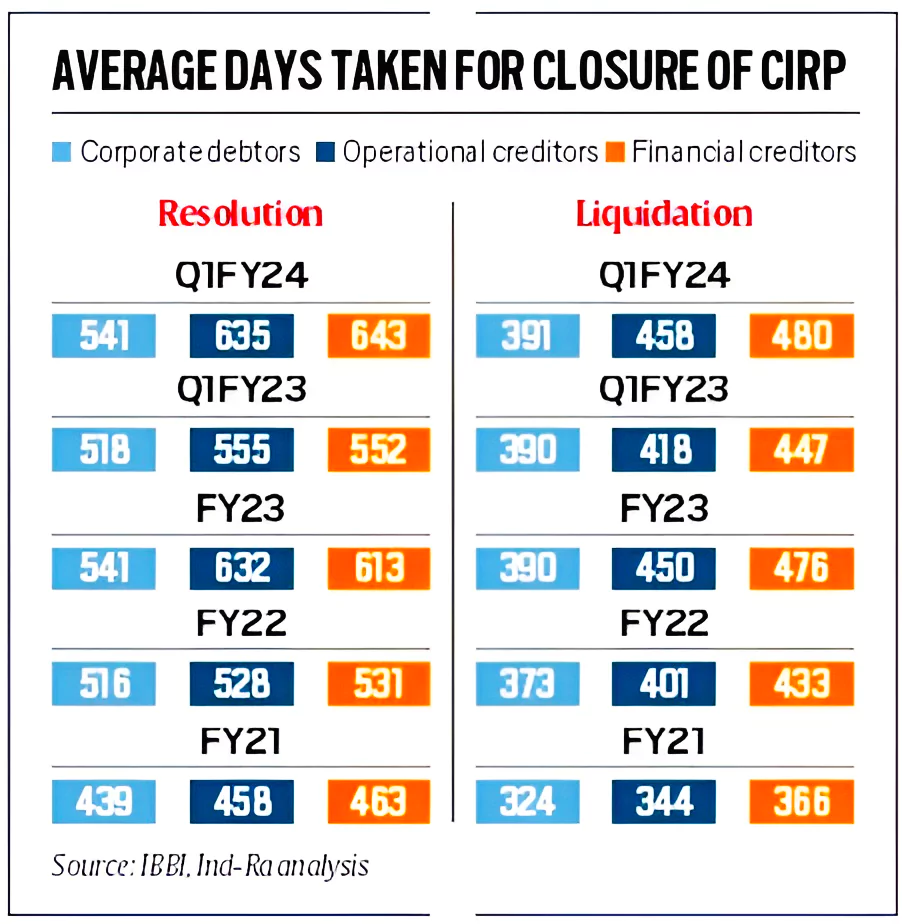 Delay in Resolution Process: While the time taken under Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code is lower than what it used to take before Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, it continues to exceed the expected timelines.
Delay in Resolution Process: While the time taken under Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code is lower than what it used to take before Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, it continues to exceed the expected timelines. Resolution Professionals (RPs)
|
|---|
Also Refer: India’s Forex Reserves Up by $2.54 bn
Improving operational infrastructure, providing clarity in legal interpretation, streamlining procedures, developing a robust insolvency ecosystem, and enhancing mechanisms for cross-border insolvency are crucial steps in ensuring the effective implementation of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code.
| Prelims Question (2017)
Which of the following statements best describes the term ‘Scheme for Sustainable Structuring of Stressed Assets (S4A)’, recently seen in the news? (a) It is a procedure for considering ecological costs developmental schemes formulated by the Government. (b) It is a scheme of RBI for reworking the financial structure of big corporate entities facing genuine difficulties. (c) It is a disinvestment plan of the Government regarding Central Public Sector Undertakings. (d) It is an important provision in ‘The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code’ recently implemented Ans: (b) |
|---|
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: Recently, a new joint report “Digital Trade for Development” was released which looks into opportunities and challenges for developing economies arising from digital trade.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Digital Economy, WTO, International Monetary Fund (IMF), and Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
Relevancy for Mains: IMF Report on Digital Trade, Digital Trade in India: Status, Vision, Opportunities, Challenges, Government Initiatives and Way Forward. |
|---|
Must Read: OECD’s International Migration Outlook 2023
About WTO Rules and E-Commerce
|
|---|
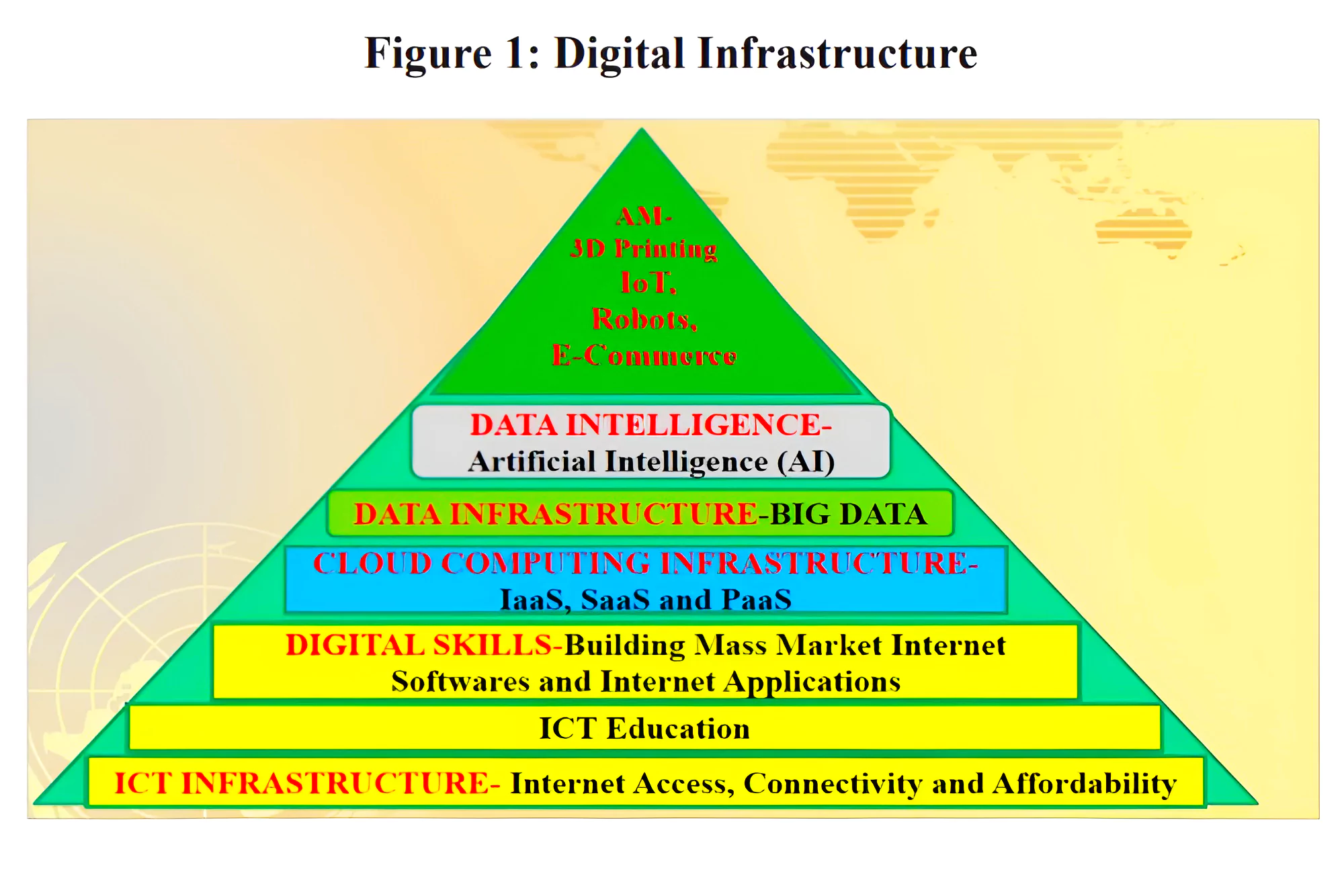 Digital Economy: Economic activities conducted or facilitated through digital technologies.
Digital Economy: Economic activities conducted or facilitated through digital technologies. Also Refer: Vision India@2047: Transforming India into a Developed Nation
Also Read: India To Be A $ 7 Trillion Economy By 2030: CEA
| Mains Question: What is the status of digitalization in the Indian economy? Examine the problems faced in this regard and suggest improvements. (150 words, 10 Marks) |
|---|
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Maharashtra Withdraws GRs on Hindi as Third Langua...
Statistical Report on Value of Output from Agricul...
Skills for the Future: Transforming India’s Work...
National Turmeric Board HQ Inaugurated in Nizamaba...
ECI Moves to De-List 345 Inactive Registered Unrec...
MNRE Issues Revised Biomass Guidelines Under Natio...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>