![]() December 9, 2023
December 9, 2023
![]() 476
476
![]() 0
0
Trade refers to the voluntary exchange of goods and services. Two parties are needed for this exchange and it should be mutually beneficial. From the early barter system to the complexities of international trade, this practice has evolved significantly over time.
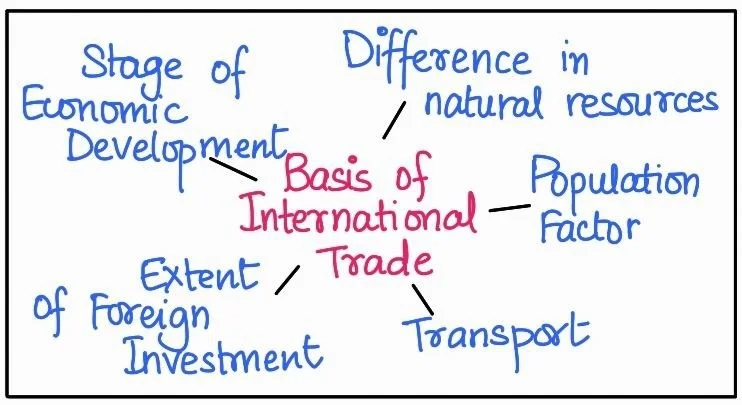
Significance of Trade: Barter to Global Prosperity
|
Dumping The practice of selling a commodity in two countries at a price that differs for reasons not related to costs is called dumping. |
|---|
Also Read: WTO (World Trade Organization): Meaning and Objectives
<div class="new-fform">
</div>

Latest Comments