The Consortium of International Agricultural Research Centres (CGIAR) has launched the Global Strategy for Resilient Drylands (GSRD) 2030 in Cop 16 UNCCCD Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Organisations Involved
- About Consultative Group of International Agricultural Research (CGIAR): CGIAR is the world’s largest publicly-funded group of agrifood systems research centers, focusing on transforming food, land, and water systems in response to the climate crisis.
- About International Center for Agricultural Research in Dry Areas (ICARDA)
- It focuses on agricultural research for development in climate-vulnerable regions of North Africa, Central and West Asia, and the Middle East.
- About International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT)
- It is a premier drylands agricultural research institute, dedicated to uplifting smallholder farmers and ensuring food security in semi-arid tropics
- It was established under a Memorandum of Agreement between the Government of India and the CGIAR on the 28 March 1972
|
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
About Drylands
- Definition: According to the UN Environment Programme (UNEP), ‘’Drylands are lands with an aridity index of less than 0.65.’’(Aridity index is the ratio between average annual precipitation and potential evapotranspiration).
- These areas include deserts, semi-arid regions, etc. and they typically experience harsh climates with extreme temperatures and limited vegetation.
- Drylands are home to one in every three of the world’s people, nearly half of the livestock and 44 percent of food systems.
- Degradation of Drylands: When land degradation occurs in the drylands, it is called desertification.
- Drylands are degraded across continents due to over-cultivation, overgrazing, deforestation, poor irrigation and rising temperatures.
- Around 20-35 percent of the Drylands are degraded.
- Significance: Traditionally viewed as fragile ecosystems, these areas hold immense potential for climate-smart agricultural innovation that can be scaled globally.
About Global Strategy for Resilient Drylands (GSRD) 2030
- The 2030 Global Strategy for Resilient Drylands (GSRD) is a transformative initiative by CGIAR to address the challenges faced by drylands, leveraging 50 years of research on dryland ecosystems.
- The Vision aims to provide a roadmap to enhance food security, conserve biodiversity and build resilient livelihoods for the 2.7 billion people inhabiting drylands, particularly in Asia and Africa.
- The strategy reframes drylands not as areas of scarcity but as hubs of untapped potential for resilience.
- Developed by: The GSRD is collaboratively developed by CGIAR institutes under the leadership of ICARDA (International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas) and ICRISAT (International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics).
- Launched at: It is launched at the 16th Conference of Parties to the UNCCD in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
- Key Focus Areas of the GSRD: The strategy emphasizes five critical areas:
- Adapting agrifood systems to climate change.
- Conserving biodiversity.
- Sustainable management of soil and water resources.
- Promoting healthy diets.
- Fostering inclusive development.
- Key Innovations under GSRD:
- Climate-Smart Agriculture (CSA):
- Introduction of drought-resistant crops like barley, lentils, chickpeas, and cacti.
- Advanced agroforestry techniques to integrate trees with agriculture.
- Sustainable Resource Management:
- Solar-powered agri voltaics for energy-efficient farming.
- Improved livestock feeding practices to enhance productivity.
- Technology Integration: Pioneering solutions to address water scarcity, land degradation, and desertification.
Significance of Global Strategy for Resilient Drylands (GSRD)
- Climate Change Impact on Drylands: Drylands are experiencing warming at rates 20-40% higher than other regions, making them highly vulnerable to climate change.
- Addressing Global Food Insecurity: 70% of the world’s hungry live in environmentally fragile and conflict-affected areas, highlighting the urgent need to transform dryland agriculture to tackle global food insecurity.
- Collaborative Effort for Transformation: Developed through collaboration between national research organizations, governments, and the private sector, GSRD is a collective response to dryland challenges.
- Global Relevance: As drylands expand due to climate change, the solutions from the GSRD offer hope for sustainable agricultural practices, benefiting both dryland regions and the global community facing environmental changes.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Drylands In India
- In India, drylands are mostly located in areas with the annual rainfall between 500-1,100 mm with no regular irrigation facilities like canal and groundwater, although these lands may get one or two supplementary irrigation from water harvest structures like check dams, farm ponds.
Types of Drylands In India
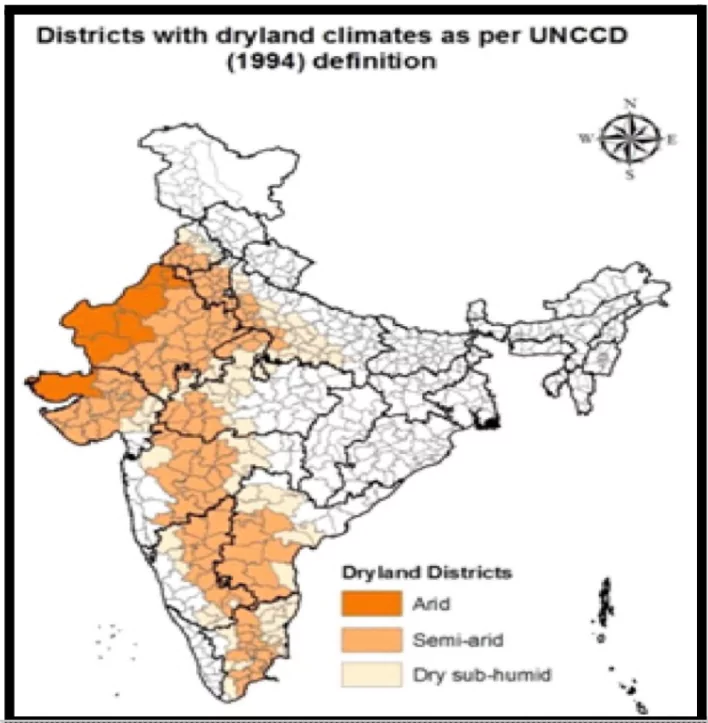
- Arid Regions: These include desert areas like Rajasthan, Gujarat, and parts of Haryana and Punjab, where annual rainfall is less than 250 mm.
- These areas are typically characterized by extreme temperatures and very low vegetation cover.
- Semi-Arid Regions: These are areas that receive between 250 mm and 500 mm of rainfall annually.
- They include regions such as parts of Maharashtra, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana. Semi-arid areas are more suitable for agriculture but face challenges like soil erosion and declining water tables.
- Dry Sub-Humid Regions: These regions receive rainfall between 500 mm and 750 mm annually and include parts of Tamil Nadu, Uttarakhand, and Madhya Pradesh.
- They have a more varied ecosystem, but agricultural productivity remains vulnerable due to erratic rainfall patterns.
Challenges Faced by Drylands
- Water Scarcity: Water is a scarce resource in drylands, limiting agricultural and livestock productivity.
- Over-extraction of groundwater for irrigation, reduced rainfall, and increased evaporation rates due to high temperatures make water management a major issue.
- Land Degradation: Over-cultivation, deforestation, and poor soil management practices have led to widespread land degradation in many dryland areas.
- The desertification of once fertile regions has become a critical environmental concern, threatening food security and biodiversity.
- Climate Change Impact: Drylands are warming at a faster rate than other regions, making them more vulnerable to droughts and extreme weather events.
- The variability of rainfall patterns and rising temperatures increase the risk of crop failures and impact livelihoods.
- Soil Erosion: Due to the lack of vegetation cover and frequent droughts, drylands in India are prone to soil erosion.
- Biodiversity Loss: Dryland ecosystems are rich in biodiversity, but they are under threat from overgrazing, habitat destruction, and climate change.
- This leads to a decline in native flora and fauna, disrupting the ecological balance.
Check Out UPSC Modules From PW Store
Government Initiatives for Dryland Development
- India became a signatory to the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD): India became a signatory to the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD) in 1994 and ratified it in 1996.
- Land Degradation Neutrality (LDN): India is committed to restore 26 million hectares of degraded land by 2030 to achieve Land Degradation Neutrality (LDN), as part of global commitments, in alignment with Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 15.3.
- National Action Programme for Combating Desertification (NAPCD): Launched by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, this program aims to combat desertification and land degradation, particularly in arid and semi-arid regions of India.
- Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY): PMKSY focuses on providing irrigation solutions in water-scarce regions, especially in dryland areas. The program aims to improve water-use efficiency and ensure that water reaches every field, boosting agricultural productivity.
Land Degradation Neutrality (LDN)
- A state whereby the amount and quality of land resources necessary to support ecosystem functions and services to enhance food security remain stable, or increase, within specified temporal and spatial scales and ecosystems.
|
- Integrated Watershed Management Programme (IWMP): This program focuses on sustainable water management in drylands, including rainwater harvesting, building check dams, and soil moisture conservation to increase agricultural productivity.
Way Forward
- Optimizing Agrifood Systems: Develop climate-smart crops and utilize innovative breeding technology for climate resilience in crops, livestock, and aquatic systems.
- Conserving and Using Biodiversity: Promote mixed cropping, farming system diversification, and leverage Indigenous and women’s knowledge to enhance ecosystem resilience.
- Managing Soil, Land, and Water: Adopt regenerative agriculture, restore rangelands, and implement solar-powered agri-voltaics and drip irrigation for efficient water use.
- Community Involvement: Empower local communities through training and participation in decision-making to ensure sustainable farming practices.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Conclusion
The effective implementation of the Global Strategy for Resilient Drylands can drive the transformation of drylands into resilient hubs for agriculture and biodiversity through sustainable practices and innovative solutions.
![]() 9 Dec 2024
9 Dec 2024

