The newly constituted European Commission (EC), the executive arm of the European Union, elected Ursula von der Leyen, the EC’s first female President, for a second term.
Background: Selection Process of the European Commission President
The selection of the European Commission (EC) President involves a two-stage process aligned with the results of the parliamentary elections:
- Proposal and Election by the European Council:
 The European Council, consisting of leaders from the EU’s 27 member countries, proposes and elects a candidate for the EC President.
The European Council, consisting of leaders from the EU’s 27 member countries, proposes and elects a candidate for the EC President.- This decision typically reflects the dominance of the top three political groups: the centre-right European People’s Party (EPP), the centre-left Socialists & Democrats (S&D), and the liberal Renew group.
- Approval by the European Parliament:
- The proposed candidate is then subjected to a secret ballot in the European Parliament.
- Controversy Over Ms. Von der Leyen’s Candidature: The decision regarding Ms. von der Leyen’s candidature was not unanimous, with Italy’s far-right Prime Minister Giorgia Meloni and her party, Brothers of Italy, opposing it.
- The European Conservatives and Reformists (ECR), briefly the third-largest group in the legislature, also objected.
- Ultimately, 25 of the 27 EU leaders backed the Council’s nominee despite opposition, resulting in Ms. von der Leyen’s re-election.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
European Union (EU): A Unified Bloc for Peace and Prosperity
- About: The European Union (EU) is a political and economic union of 27 countries located primarily in Europe.
- Founding Treaty: The EU was established by the Maastricht Treaty, which entered into force on November 1, 1993.
- Currency of Euro: The EU has its own currency, the Euro. 19 of these countries use the euro as their official currency.
- Eurozone: The Eurozone is a monetary union composed of 19 European Union member countries that have adopted the Euro as their official currency.
- The remaining nine countries (Bulgaria, Croatia, Czech Republic, Denmark, Hungary, Poland, Romania, Sweden, and the United Kingdom) do not use the euro.
- Origin Purpose: The EU was established to form a unified European political entity to prevent the conflicts that led to World War II and devastated much of the continent.
- The main goal of the EU is to promote cooperation and integration among its member states in order to enhance economic and political stability in Europe.
- Single Market: The EU has developed an internal single market through a standardised system of laws that apply in all member states in areas where they have agreed to act collectively.
- Nobel Peace Prize: In 2012, the EU was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize for its efforts in promoting peace, reconciliation, democracy, and human rights in Europe.
- Brexit: Brexit refers to the United Kingdom’s decision to leave the European Union, which was decided by a 2016 referendum.
- The United Kingdom (UK) officially exited the EU on January 31, 2020.
European Union (EU) Governance
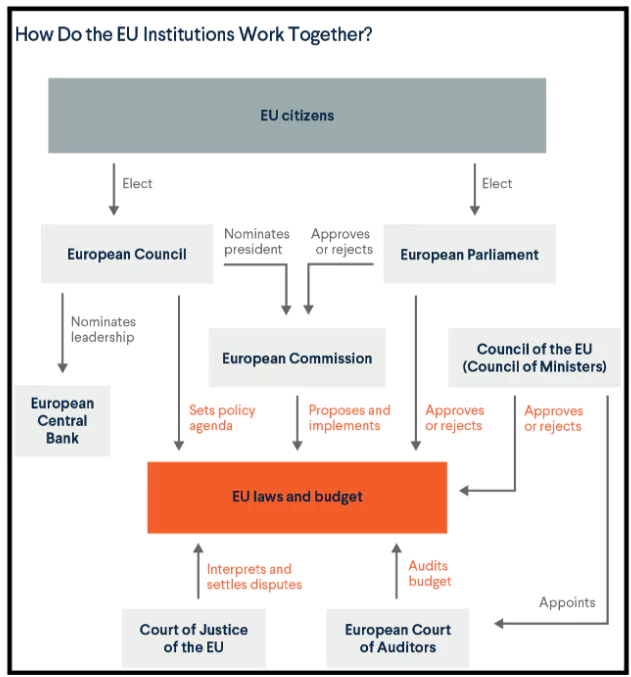
There are 4 main decision-making institutions which lead the EU’s administration. These institutions collectively provide the EU with policy direction and play different roles in the law-making process:
- The European Commission (Brussels/Luxembourg/Representations across the EU)
- The European Parliament (Brussels/Strasbourg/Luxembourg)
- The European Council (Brussels)
- The Council of the European Union (Brussels/Luxembourg)
Their work is complemented by other institutions and bodies, which include:
- The Court of Justice of the European Union (Luxembourg)
- The European Central Bank (Frankfurt)
- The European Court of Auditors (Luxembourg)
European Commission (EC)
- About: It is an executive body of the European Union, responsible for proposing legislation, implementing decisions, upholding the EU treaties and managing the day-to-day business of the EU.
- It is responsible for drawing up proposals for new European legislation, and it implements the decisions of the European Parliament and the Council of the EU.
- Appointment of President: For appointing the President of the European Commission, the candidate is put forward by national leaders in the European Council, taking account of the results of the European Parliament elections.
- He or she needs the support of a majority of members of the European Parliament in order to be elected.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
European Parliament
- About: It is the only parliamentary institution of the European Union (EU) that is directly elected by EU citizens aged 18 years or older.
- Functions: Together with the Council of the European Union(also known as the ‘Council’), it exercises the legislative function of the European Union (EU).
- Powers: The EP also approves the EU budget and votes on international agreements and enlargements of the bloc.
- It also has the power to approve or reject the appointment of the European Commission president
- Unlike national parliaments, the EP does not have the right to propose laws but can only negotiate those proposed by the executive European Commission.
European Council
- About: It is a collective body that defines the European Union’s overall political direction and priorities.
- Composition: It comprises the heads of state or government of the European Union (EU) member states, along with the President of the European Council and the President of the European Commission.
- Founding Treaty: Established as an informal summit in 1975, the European Council was formalised as an institution in 2009 upon the entry into force of the Treaty of Lisbon.
- Treaty of Lisbon: The Treaty of Lisbon, signed in 2007 and effective from 2009, reformed the institutional structure of the European Union to enhance efficiency and democratic legitimacy.
- It introduced changes such as a more powerful European Parliament, a long-term President of the European Council, and the High Representative for Foreign Affairs.
- Consensus Based Decisions: The decisions of its summits are adopted by consensus.
Council of the European Union
- About: The Council of the European Union, part of the essentially bicameral EU legislature alongside the European Parliament, represents the executive governments of the EU member states.
- In the Council, government ministers from each EU country meet to discuss, amend, and adopt laws, and coordinate policies.
- These ministers have the authority to commit their governments to the actions agreed upon in the meetings.
The Court of Justice of the European Union (Luxembourg)
- About: The Court ensures that EU law is followed, and that the Treaties are correctly interpreted and applied.
- Functions: It reviews the legality of the acts of the EU institutions, ensures that EU countries comply with their obligations under the Treaties, and interprets EU law at the request of national courts.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
The European Central Bank (ECB)
- About: It is the central bank for the euro and administers monetary policy within the Eurozone, which comprises 19 member states of the European Union.
- Aim: One of the main tasks is to maintain price stability.
European Court of Auditors (ECA)
- About: The European Court of Auditors is tasked with evaluating the economy, efficiency, and legality of EU actions to ensure proper financial management.
- Through independent audits, it aims to improve accountability and transparency within the EU, thereby strengthening citizens’ trust and addressing both current and future challenges.
- It investigates the proper management of finances within both the EU entities and EU funding provided to its member states.
- It can refer unresolved issues to the European Court of Justice to arbitrate on any alleged irregularities.
India-EU Relation
- Financial Relations: The EU is one of India’s third-largest trading partners. EU foreign direct investment (FDI) in India reached €87 billion in 2020.
- The European Investment Bank (EIB) has invested over €3 billion in infrastructure, energy, and climate projects in India.
- Strategic Partnerships: EU-India Joint Declarations have been adopted to bolster efforts on
- connectivity, water, and resource efficiency, employing a circular economy approach.
- In 2023, the EU and India also launched a Trade and Technology Council focusing on digital transformation and green technologies.
- Neighbourhood, Development and International Cooperation: Under the Neighbourhood, Development and International Cooperation Instrument (NDICI-Global Europe), India is set to receive €90 million in grant funding for the period 2021-2027.
- Additionally, India is a beneficiary of various multi-country EU programmes.
- Cultural and educational exchange: The EU and India have a number of cultural and educational exchange programs, including the Erasmus+ program, which allows Indian students to study in the EU and vice versa.
- Research and Innovation: The EU and India have cooperated on scientific research and innovation, including through the EU’s Horizon 2020 program
- Free Trade Agreement India-EU: Indian and EU does not have a Free Trade Agreement yet.
- India and the EU had launched talks for having a Free Trade Agreement (FTA), called Bilateral Trade and Investment Agreement (BTIA), in 2007.
- The talks stalled in 2013 over differences in market access and the movement of professionals.
- However, India and the EU relaunched Free Trade Agreement negotiations after 9 years in 2021.
|
![]() 2 Aug 2024
2 Aug 2024
 The European Council, consisting of leaders from the EU’s 27 member countries, proposes and elects a candidate for the EC President.
The European Council, consisting of leaders from the EU’s 27 member countries, proposes and elects a candidate for the EC President.