![]() 21 Feb 2024
21 Feb 2024
English
हिन्दी
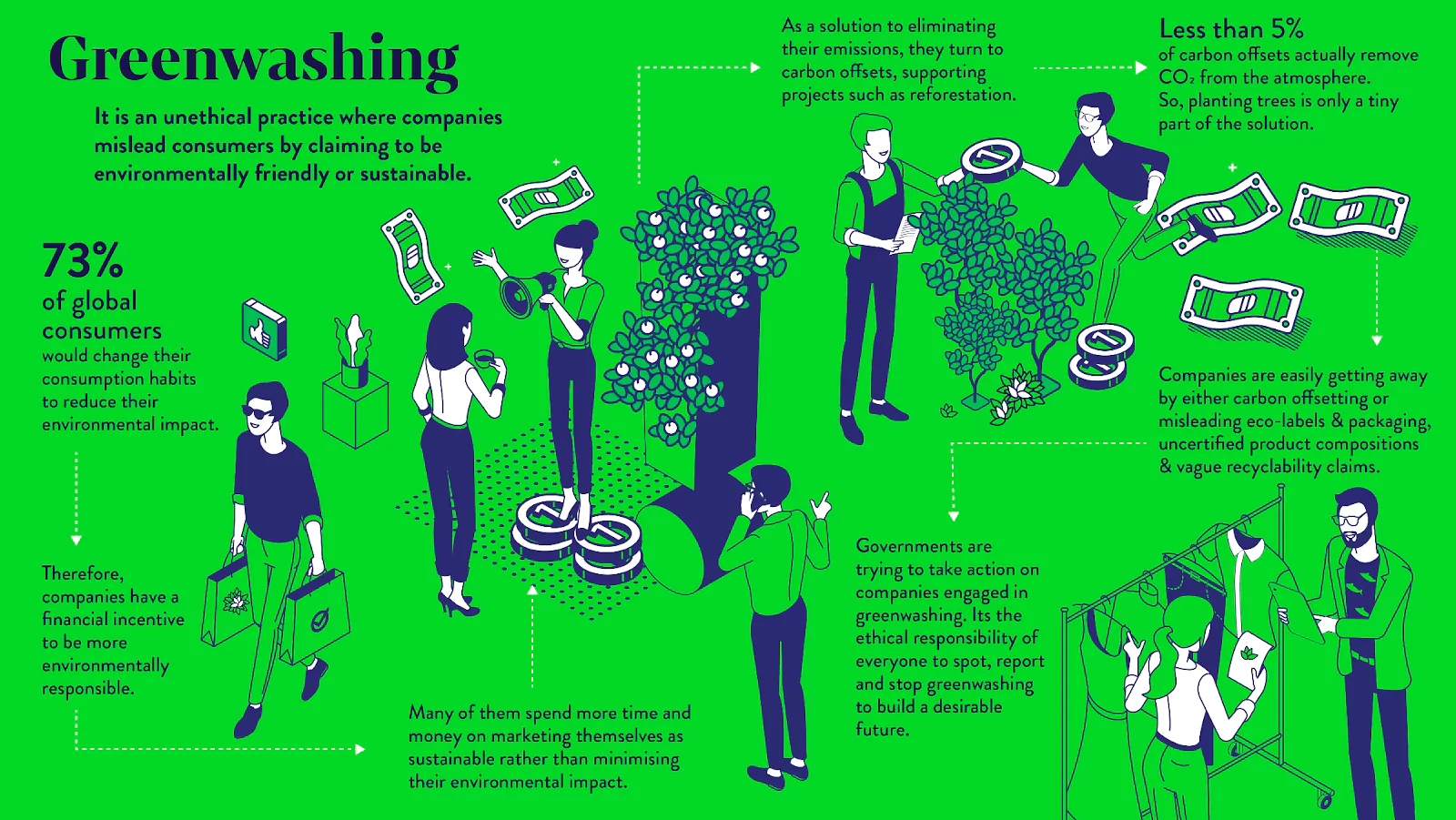
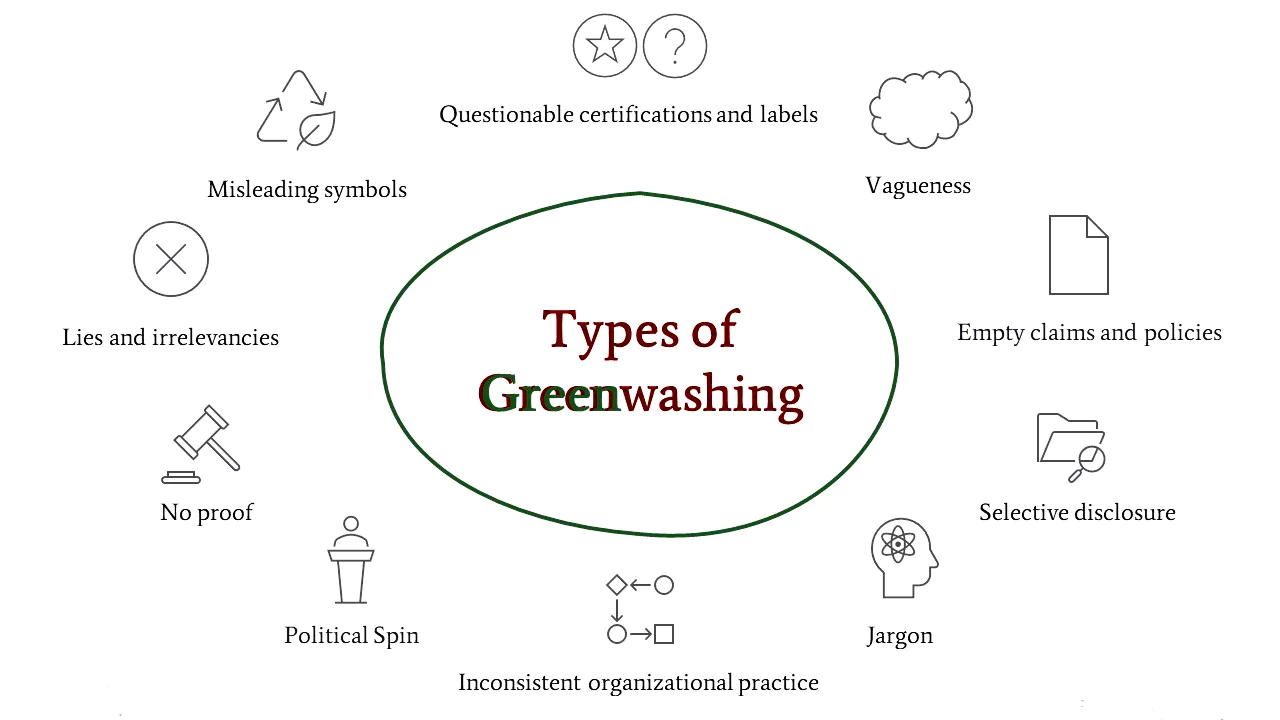
The Central Consumer Protection Authority has recently sought public comments on Draft Guidelines for the Prevention and Regulation of Greenwashing.
Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA)
|
|---|
News Source: AIR
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>