As of 2023, 440 districts in India have excessive nitrates in their groundwater, compared to 359 districts in 2017, as reported by the Central Groundwater Board (CGWB) on January 1, 2025.
- This rising contamination poses significant health risks, especially for young children, and contributes to environmental toxicity.
Key Highlights of the Report
- Districts Affected: Excessive nitrate contamination was found in 440 districts in 2023, up from 359 districts in 2017.
- 56% of India’s districts are currently affected by nitrate issues.
- Definition of Contamination: Groundwater nitrate contamination is defined as nitrate levels exceeding 45 mg per litre.
- Regions with High Contamination: States like Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, and Gujarat have consistently reported high nitrate levels since 2017.
- Central and southern regions of India exhibit increasing trends of nitrate contamination.
- States with Notable Contamination
- Maharashtra (35.74%)
- Telangana (27.48%)
- Andhra Pradesh (23.5%)
- Madhya Pradesh (22.58%)
- Seasonal Impact on Contamination: Nitrate contamination tends to increase during the monsoon season:
- Pre-monsoon contamination: 30.77%
- Post-monsoon contamination: 32.66%
- Other Chemical Contaminants: High concentrations of fluoride and uranium have been detected in states such as Rajasthan, Gujarat, Haryana, Punjab, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, and Karnataka.
- Uranium levels exceeding 30 ppb (parts per billion) are deemed unsafe for consumption.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
About Ground water Contamination
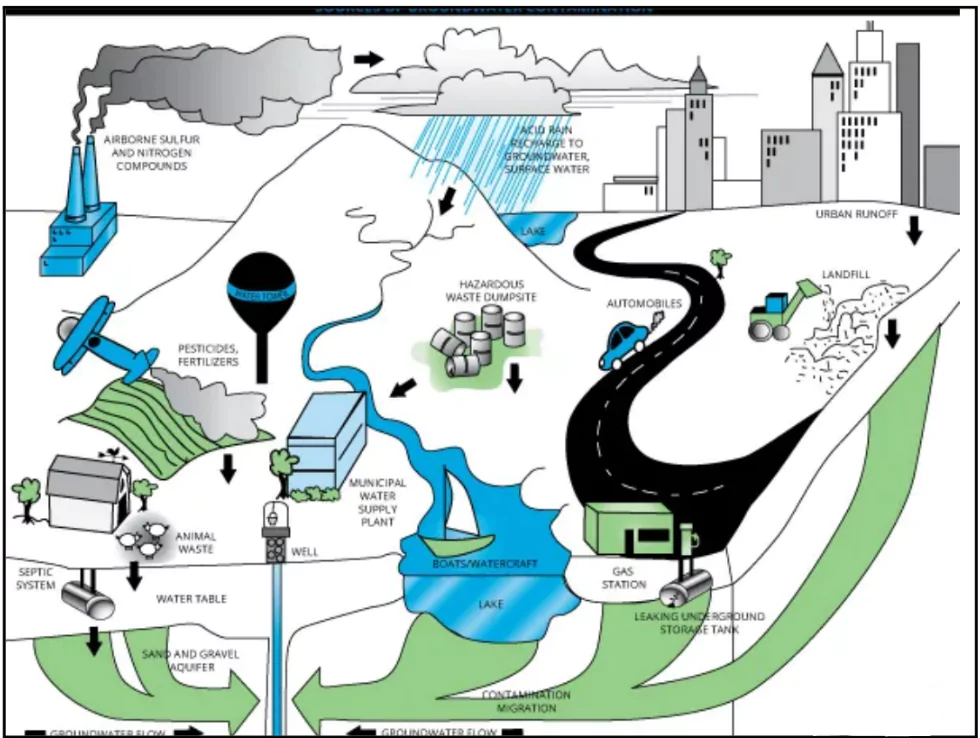
- Groundwater contamination occurs when pollutants enter the groundwater, making it unsafe for use.
- Sources of contamination:
-
- Industrial waste: Chemicals, heavy metals
- Agricultural activities: Fertilizers, pesticides
- Septic systems: Leaking tanks
- Landfills: Leaching of heavy metals into Ground water .
- Mining: Acid mine drainage
- Oil spills: Leaking underground storage tanks
State of Groundwater Extraction
- Groundwater Extraction Rate
- The Groundwater extraction rate remains at 60.4%, unchanged since 2009.
- Groundwater extraction rate refers to the proportion of groundwater withdrawn for uses such as agriculture, industry, and domestic purposes compared to the total available recharge.
- Recharge of ground water is through natural replenishment of groundwater through rainfall and other sources.
- Safety of Blocks
- 73% of groundwater blocks in India are now classified as being in the “safe zone,” where replenishment matches or exceeds extraction.
- This is an improvement from 67.4% in 2022 to 73% in 2023.
Different types of groundwater contamination, their sources, and health impacts
| Type of Contaminant |
Sources |
Health Impact |
| Nitrates |
Overuse of subsidised synthetic nitrogen fertilizers in agriculture |
- Reacts with haemoglobin to form methaemoglobin.
- It reduces oxygen-carrying capacity causing Methemoglobinemia.
- Causes Blue Baby Syndrome: Bluish discolouration of infants’ skin due to reduced oxygen in the blood.
|
| Arsenic |
- Naturally occurring in soil and water.
- Human-made forms used in agriculture, mining, and manufacturing.
- Seepage from industrial discharges, mining activities, and fly ash ponds in thermal power plants.
|
- Causes Black Foot Disease: Affects blood vessels in the limbs.
- Long-term exposure can lead to cancer and skin lesions.
|
| Fluoride |
- Naturally occurring in groundwater in some regions.
|
- Leads to neuromuscular disorders, gastrointestinal problems, and dental deformities.
- Causes skeletal fluorosis: Painful, stiff joints.
- Can cause Knock-Knee Syndrome: Outward bending of legs from the knees.
|
| Uranium |
- Found in alluvial aquifers in Rajasthan and northwestern states.
- Found in crystalline rocks (granite) in southern states like Telangana.
|
- High levels can cause kidney toxicity.
|
| Radon |
- Originates from the radioactive decay of granites and uranium.
|
- Inhalation or ingestion can damage lung tissues and increase the risk of lung cancer.
|
About Central Water Commission (CWC)
- Genesis: Established in 1945 based on the advice of Dr. B. R. Ambedkar.
- Ministry: Operates under the Ministry of Jal Shakti, specifically the Department of Water Resources, River Development, and Ganga Rejuvenation.
- Headquarters: Located in New Delhi.
- Leadership: Chaired by a Chairman who also serves as the Ex-Officio Secretary to the Government of India.
- Functions
- Deals exclusively with surface water management.
- Groundwater issues are managed by the Central Groundwater Board (CGWB).
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
About Central Groundwater Board (CGWB)
- Formation: Established in 1970 to develop groundwater policies and programs.
- Structure: A multi-disciplinary scientific organization comprising hydrogeologists, geophysicists, chemists, hydrologists, hydrometeorologists, and engineers.
- Headquarters: Located in Faridabad, Haryana.
- Central Groundwater Authority (CGWA)
-
- Constituted under Section 3(3) of the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.
- Responsible for the regulation and control of groundwater development and management in India.
![]() 2 Jan 2025
2 Jan 2025


