Context
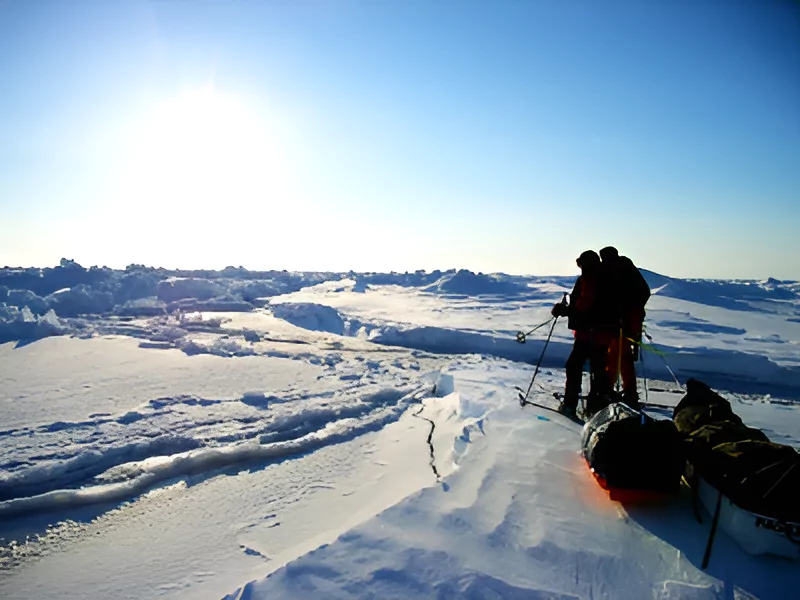
In March 2024, India completed its first-ever winter expedition successfully in the Arctic.
- Their destination was Himadri, India’s research station located in the International Arctic Research undefined at Svalbard, Norway.
- Organization to undertake winter mission to the Arctic: India’s National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR).
Winter Expedition in the Arctic Region

-
Objectives:
- To gather data on atmospheric phenomena like the aurora borealis and atmospheric electricity during polar nights.
- On polar nights, there is no sunlight for nearly 24 hours and sub-zero temperatures (as low as -15 degrees Celsius).
- To conduct space-specific studies to better understand these processes.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
-
Observations and Monitoring Process:
- During polar nights, scientists conducted atmospheric observations.
- They monitored variations in sea ice and studied the effects of precipitation and aerosols on climate change.
-
Benefits of Expedition
-
- The research is very helpful in providing insights into how the Arctic climate interacts with the Indian monsoon system.
- It will contribute to a broader understanding of the impacts of global warming.
- In winter and summer, thunderstorms and lightning create different kinds of electric fields.
- Therefore, expedition is very useful in understanding the electrical properties of thunderstorms, especially in the polar winter.
Reason for Undertaking Winter Mission to the Arctic Region
- Scientific Discoveries: Recent research revealed a faster-than-expected rate of Arctic warming.
- This warming is linked to extreme weather events impacting India’s climate, prompting policymakers to take action and gather more data through winter missions.
- Economic potential: The opening of Arctic sea routes, particularly the Northern Sea Route, can present immense opportunities to reduce shipping costs and transit times for Indian trade.
- This could benefit India by cutting down expenses for shipping companies, saving time, fuel, and improving security when transporting goods.
- Geopolitical Landscape: China’s growing Arctic investments, particularly its expanded access to the Northern Sea Route through Russia, is a matter of concern.
- Russia’s increased reliance on its nuclear deterrent in the Kola Peninsula adds to these concerns.
- This strategic concern motivated India to increase its Arctic presence, including undertaking winter missions.
- Apart from the above, India is increasing its interest in the Arctic region, largely due to the conflict between Russia and Ukraine.
- Suspension of various cooperative forums in the region has further exacerbated the situation.
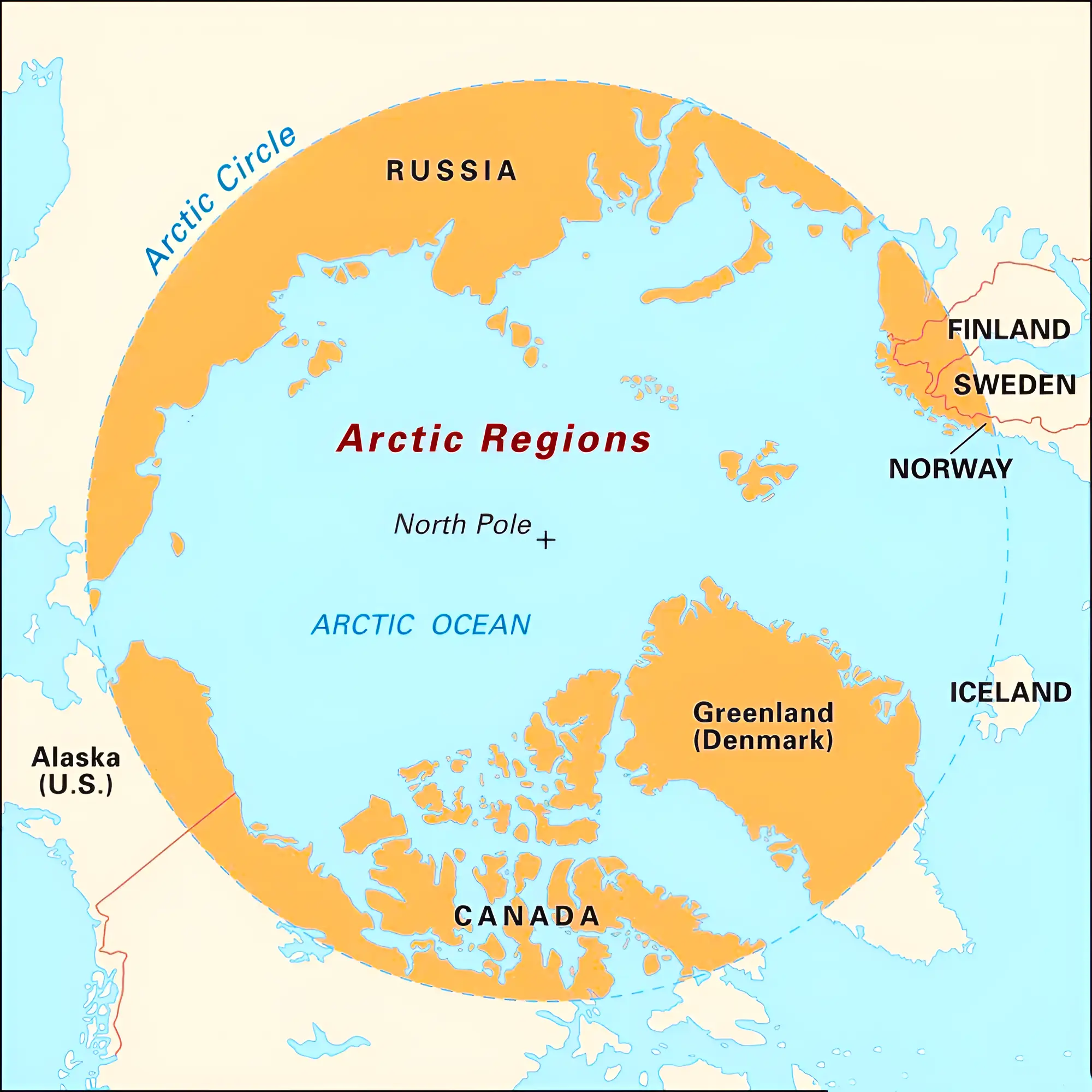
About Arctic Region
- Arctic Region is the northernmost region of Earth.
- This region is entirely covered by water, much of it frozen.
- It comprises the northern parts of Canada, the United States, Russia, Finland, Sweden, Norway, Iceland, and Greenland.
- Climatic conditions in the arctic region: cold winters and cool summers.
- Most of its precipitation falls as snow.
- Majority of the region gets less than 50 cm (20 in).
- Flora and fauna: Arctic vegetation includes dwarf shrubs, grasses, herbs, lichens, and mosses.
- It grows close to the ground, forming tundra.
- In the Arctic, trees cannot grow, but in the warmer regions, shrubs are common and can reach heights of up to 2 meters (6 feet 7 inches).
Significance of the Arctic Region
- Observer Status in the Arctic Council: India is one of thirteen countries with Observer status in the Arctic Council, showing its importance in Arctic affairs.
- Abundance of Resources: The Arctic region is rich in natural resources and has both mineral and animal resources.
- Minerals include iron ore, copper, nickle, zinc phosphates and diamonds and oil, making it valuable.
- Abundant fisheries are the living resources of the Arctic .
- Importance of Shipping Routes: Many shipping routes pass through the Arctic, which is important for global trade.
- Adverse Impact of Climate Change: Climate change is not only affecting the availability of minerals and oil in the Arctic, but it’s also changing the routes that ships take around the world.
India’s Science History in the Arctic Region
India has been involved in Arctic affairs since 1920, starting with the signing of the Svalbard Treaty in Paris.
-
Research Initiatives:
- Since 2007, India has conducted various research missions in the Arctic, focusing on microbiology, atmospheric sciences, and geology.
- In 2013, India gained Observer status in the Arctic Council.
- Subsequently, India established research infrastructure, including a multi-sensor moored observatory and an atmospheric laboratory in Svalbard.
-
India-Norway Collaboration in the Arctic Region:
- Since the late 1980s, India and Norway have collaborated on Arctic and Antarctic research, focusing on their impact on South Asia.
- A partnership with Norway would mainly focus on scientific research and protecting the environment from climate change.
- These areas are two of the six key aspects of India’s Arctic Policy, which also includes
- economic and human development
- transportation and connectivity
- governance and international cooperation
- national capacity building
- Norway could assist India in developing a sustainable policy that balances the interests of the scientific community and industry.
- Partnering with Norway could greatly benefit India by increasing its involvement in the Arctic Council’s working groups, addressing issues such as the blue economy, connectivity, maritime transportation, investment, infrastructure, and responsible resource development.
-
India’s Arctic Policy
-
- Collaboration with Arctic nations: India’s current policy aims to collaborate with Arctic nations in promoting green energy and sustainable industries to enhance its reputation as a responsible stakeholder.
- Collaborations with Denmark and Finland focus on areas like waste management, pollution control, renewable energy, and green technology.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Key Provisions of India’s Arctic Policy
This policy lays down six central pillars
- Strengthening India’s scientific research and cooperation
- Climate and environmental protection
- Economic and human development
- Transportation and connectivity
- Governance and international cooperation
- National capacity building in the Arctic region.
- Objective : It aims to Strengthening national capabilities and competencies in science and exploration.
- In addition to above, it aims to Enhance understanding of the impact of climate change in the Arctic on India’s climate
- It also aims to Contribute better analysis, prediction, and coordinated policymaking on the implications of ice melting in the Arctic
- Studying linkages between polar regions and the Himalayas.
- Deepen cooperation between India and countries of the Arctic region
- Increase India’s participation in the Arctic Council
|
Also Read: Changes in the Arctic Region: How India Can Help Save the Arctic Region
![]() 16 Apr 2024
16 Apr 2024

