Recently, India voted in favor of a United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) resolution titled “Peaceful Settlement of the Question of Palestine” .
Key Highlights of the Resolution
- Overwhelming Support for the Resolution: The resolution was adopted with 157 votes in favor, showcasing broad international support.
- Eight nations, including the United States and Israel, voted against the resolution.
- India’s Position: India supported the resolution, reaffirming its historical commitment to the Palestinian cause and the two-state solution.
- Abstentions: Seven countries, including Cameroon, Czech Republic, Ecuador, Georgia, Paraguay, Ukraine, and Uruguay, abstained from voting.
- Objective of the Resolution:
- The withdrawal of Israel from territories occupied since 1967, including East Jerusalem.
- Recognition of the Palestinian people’s inalienable rights, such as the right to self-determination and an independent state.
- A commitment to the two-state solution based on pre-1967 borders.
- Gaza Strip: Recognition of Gaza as an integral part of the Palestinian state and rejection of any actions altering Gaza’s territorial integrity.
- End to Unlawful Actions: A demand for Israel to halt all settlement activities, repeal laws enabling illegal settlements, and evacuate settlers.
- India’s Broader Stance: India’s vote reflects its consistent support for peaceful resolutions and adherence to international law while balancing strategic relationships in the region
- India’s Abstention on ICJ-Linked Resolution: India abstained from a resolution urging Israel to vacate Palestinian territories and imposing punitive sanctions, citing concerns about punitive measures not included in the ICJ opinion.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
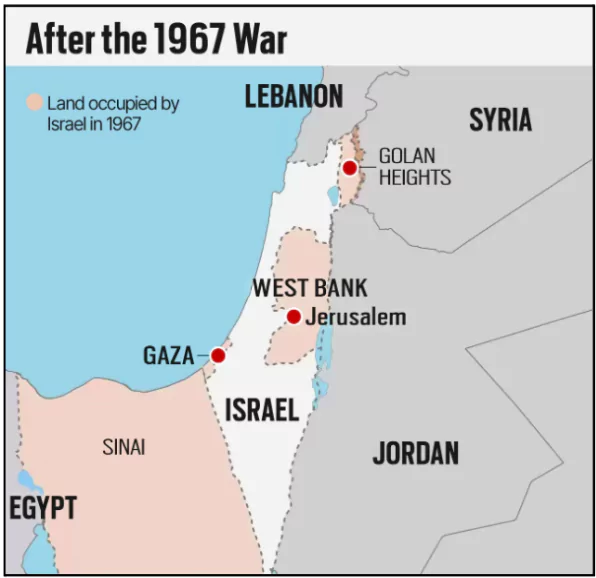
Background of Israeli Occupation
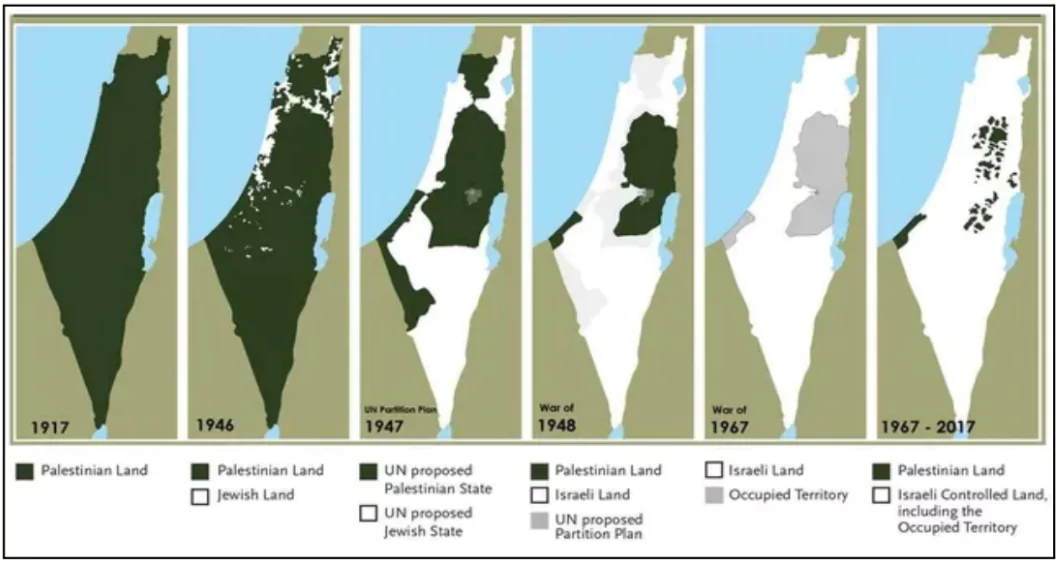
- The Israeli occupation began after the Six-Day War of 1967, where Israel captured several territories, including the West Bank, Gaza Strip, East Jerusalem, and the Golan Heights.
- These territories have since been at the heart of the Israel-Palestine conflict, with demands for a Palestinian state and Israel’s withdrawal remaining unresolved.
- The Israeli settlement construction in these territories has been widely criticized as a violation of international law, including the Fourth Geneva Convention which protects civilians during wartime, ensuring humane treatment and basic rights.
- Two-State Solution Framework: A two-state solution envisions Israel and Palestine coexisting peacefully as independent states within the borders established before 1967.
- The international community largely supports this framework as the basis for lasting peace in the region.
- Resolution on Syrian Golan Heights: The resolution demanded that Israel withdraw from the Syrian Golan Heights to the pre-June 1967 line, in accordance with relevant Security Council directives.
- It declared Israel’s 1981 decision to impose its laws, jurisdiction, and administration on the Golan Heights as null and void.
India’s Arguments for Voting Decisions
- Support for Palestine and Syrian Golan Resolutions
- India reaffirmed its longstanding support for a two-state solution as the basis for peace between Israel and Palestine.
- India emphasized the need for adherence to international law, including the cessation of settlement activities and the recognition of Palestinians’ right to self-determination.
- Abstention on ICJ Resolution
- India clarified that its abstention was based on concerns over punitive sanctions, arguing that such measures were outside the scope of the ICJ advisory opinion.
- India emphasized the importance of focusing on efforts to bridge differences between the two sides, rather than actions that may deepen divides.
About UNGA Resolutions
- A UNGA resolution is a formal expression of the opinions or decisions adopted by the General Assembly.
- While being non-binding, resolutions carry significant political and moral weight as they represent the collective will of the international community.
- Types of Resolutions:
- Declarations: Statements of principles or intent.
- Recommendations: Suggestions for actions by member states or UN bodies.
- Decisions: Relate to procedural or administrative matters.
Process of Voting on UNGA Resolutions
- Drafting: Draft resolutions are prepared by member states, committees, or UN bodies.
- They can be proposed by individual nations, regional groups, or UN entities.
- Deliberation: The draft resolution is debated in the relevant committee or in the General Assembly.
- Voting: The UNGA typically employs the following voting methods:
- Show of Hands: A simple and quick method, often used for routine decisions.
- Recorded Vote: A more formal method where each member state’s vote is recorded individually.
- Roll-Call Vote: A detailed method where each member state’s vote is called out in alphabetical order.
- Majority Requirements for Different Resolutions:
- Simple Majority: Most decisions in the UNGA are made by a simple majority of members present and voting. This means that more than 50% of the votes cast must be in favor of the resolution.
- Two-Thirds Majority: Certain important issues require a two-thirds majority of members present and voting. These issues typically relate to:
- Recommendations on peace and security
- Budgetary matters
- Election of UN officials
- Admission, suspension, or expulsion of member states
- Adoption: Resolutions adopted by the UNGA become official documents of the United Nations.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Implications of UNGA Resolutions
- Political Impact: Resolutions reflect the consensus or division among the global community on key issues.
- They can influence international opinion and policy-making.
- Moral Authority: Though non-binding, they carry moral and political weight, urging member states to act in accordance with international law and shared values.
- Support for Multilateralism: UNGA resolutions reaffirm the commitment of the international community to resolve issues through dialogue and cooperation.
- Precedent for Further Action: Resolutions often serve as a basis for subsequent legally binding agreements or Security Council actions.
- Economic and Social Development: Resolutions support global initiatives in areas like sustainable development, human rights, and poverty eradication.
- Conflict Resolution: They provide frameworks for peacebuilding and conflict resolution, even though their implementation depends on political will and practical feasibility.
Additional Reading: UN
![]() 5 Dec 2024
5 Dec 2024


