Context
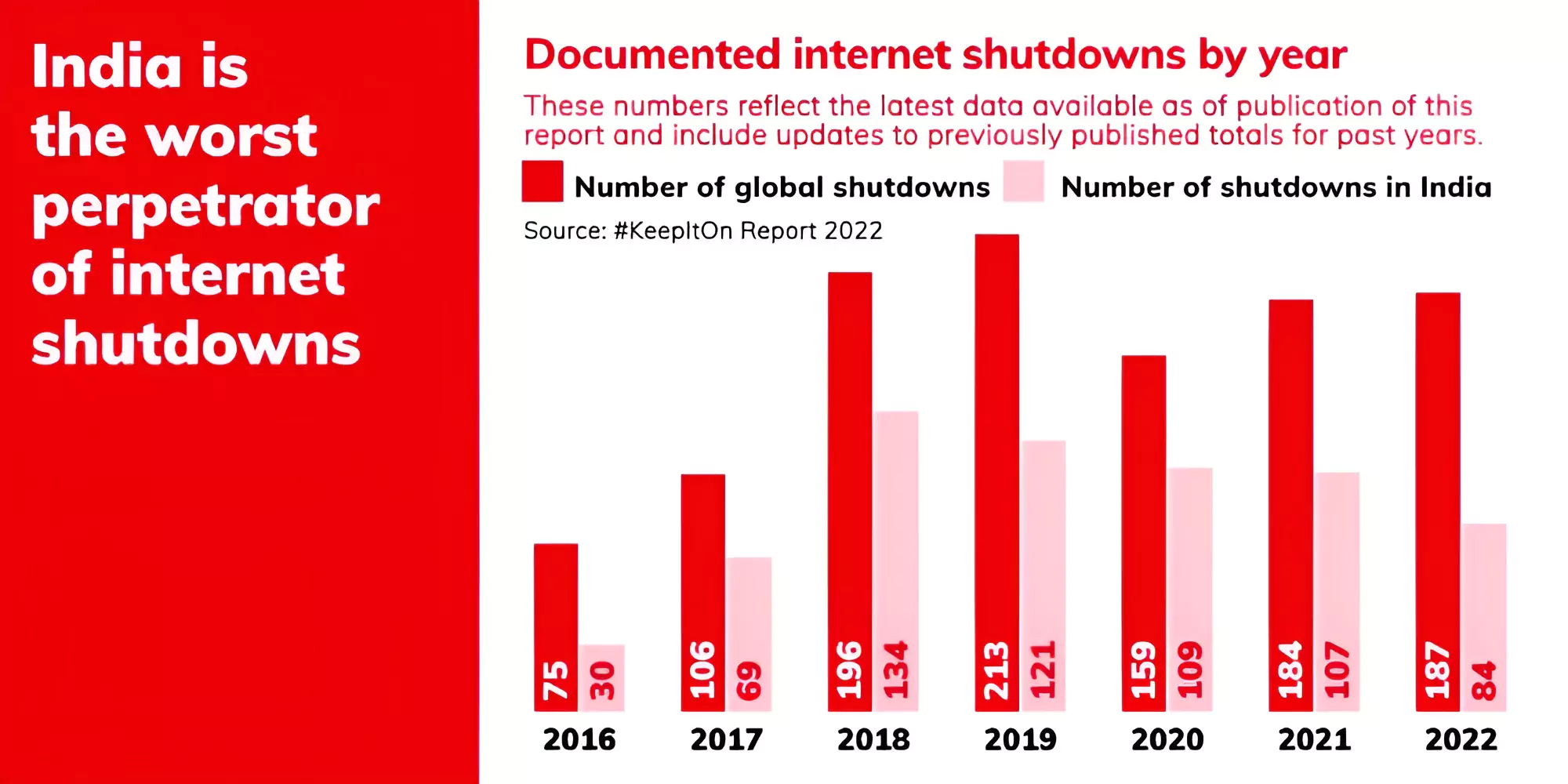
In 2023, India had the most internet shutdowns in the world for the 6th year in a row (116 out of 283 globally).
Internet Shutdowns Report
This makes up over 40% of all internet shutdowns worldwide.
- This result has been declared according to data analyzed by Access Now.
- Access now is a not-for-profit group that focuses on digital rights.
- Internet shutdown in 2016: India has had a total of 773 internet shutdowns since 2016, which is more than half (53%) of all shutdowns tracked during that time.
- There has been a significant rise in internet shutdowns globally, with a 41% increase from 2022 to 2023.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
About Internet Shutdown
A complete restriction on the use of internet services imposed by a government order.
Provisions related to internet shutdown
- Section 5(2) of the Indian Telegraph Act, 1885: This section empowers central government and state government for lawful interception in the interests of the sovereignty, and integrity of India.
- Read with Temporary Suspension of Telecom Services (Public Emergency and Public Safety) Rules, 2017: This provision allows the union or state home secretary to suspend telegraph services.
- For example: The internet service, during a public emergency or for public safety.
- The suspension of telegraph services cannot exceed 15 days.
- Section 144 of the Code of Criminal Procedure: This provision gives power to district magistrates, sub-divisional magistrates, and potentially other officials designated by the state government to issue orders to stop nuisance that creates trouble or disrupt public peace.
- The orders may include suspension of internet services in a specified region for a set amount of time.
Violation of rights due to internet shutdown
- Article 19(1)(a) and Article 19(1)(g): The shutdown of the internet violates fundamental rights of Indians.
- Freedom of Speech and Expression (Article 19(1)(a)) : In Anuradha Bhasin case, 2020, SP recognised that internet access is crucial for freedom of speech and expression.
- Right to Practice a Profession (Article 19(1)(g)): The internet plays major role for professionals so shutting down the internet can violate the right to practice a profession through the internet.
- Right to Information (Article 19) : Every Indian has the right to get information and for it, the availability of internet access is important. If the Internet is shut down, it can limit India’s ability to get information.
- Right to Internet (Article 21) : The Kerala High Court has accepted internet access as a fundamental right under the right to life and liberty.
|
- Scope and Duration
- Geographical Limitation: Can be confined to a specific area.
- Time Frame: Can be set for a specific period, time, or number of days.
- Indefinite Extension: Sometimes, the shutdown may extend indefinitely.
- Types of Internet Services Affected
- Mobile Internet: Includes internet services used on smartphones.
- Wired Broadband: Covers the broadband connections typically used on desktops.
- Combined Shutdown: Can affect both mobile internet and wired broadband simultaneously.
Key findings of the Internet Shutdowns Report

Economic and Social Impact of Internet Shutdowns in India
- Economic Impact: Internet shutdowns have a significant negative impact on the Indian economy.
- The report estimates that shutdowns in the first half of 2023 alone cost the country $1.9 billion and resulted in a loss of $118 million in foreign investment.
- Job Losses: A single-day internet shutdown can lead to unemployment for up to 379 people, according to the report’s citation of the Internet Society’s NetLoss Calculator.
- Impact of shutdown: In India, many shutdowns affected large areas. 64 shutdowns impacted more than one district in 2023.
 The high number of multi-district shutdowns in March can be attributed to two specific events:
The high number of multi-district shutdowns in March can be attributed to two specific events:
- The state-wide shutdown in Punjab.
- The frequent, recurring shutdowns in Manipur (47 instances).
- A particularly severe case was Manipur, which experienced a 212-day internet shutdown (with a brief interruption) from May to December 2023.
- Impact on Women: The report highlights that internet shutdowns disproportionately affect women.
- Limited internet access makes it harder for women to document human rights abuses, including violence against them, hindering efforts to hold perpetrators accountable.
Geographic Scope and Trends of Internet Shutdowns

- Increased Frequency and Duration: Internet shutdowns in India became more frequent and longer-lasting in 2023.
- The number of states experiencing more than five shutdowns rose from 3 to 7, and the percentage of shutdowns lasting over five days jumped from 15% to 41%.
- Wider Geographic Impact: Local or statewide internet shutdowns occurred in 13 Indian states in 2023, highlighting a broader geographic reach compared to previous years.
- Global Comparison: While India leads in internet shutdowns, other countries were also affected.
- Myanmar (37) and Iran (34) had the second and third highest numbers of shutdowns in 2023. A total of 39 countries experienced internet restrictions.
- External Actors and Conflict: The report raised concerns about external actors using internet shutdowns as a tool during conflicts.
- Palestine and Ukraine, facing border conflicts, witnessed shutdowns imposed by external parties, unlike other countries where the government itself ordered restrictions.
Reasons for Internet Shutdowns and Platform Blocking
- Reasons for Shutdowns: The report has identified various reasons for internet shutdowns across the globe including India:
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
| Reason for internet shutdown |
Count |
| Conflicts (across 9 countries) |
74 |
| Protests (across 15 countries) |
63 |
| Exam Cheating (across 6 countries) |
12 |
| Natural Disasters (across 4 countries) |
4 |
-
- Conflicts (74 instances across 9 countries, including India)Protests (63 instances across 15 countries)
- Preventing cheating in exams (12 instances across 6 countries, including India)
- Emerging reasons like natural disasters (4 instances across 4 countries)
- Internet Shutdowns and Human Rights Abuses: The report reveals a concerning link between internet shutdowns and human rights violations.
- At least 51 shutdowns in 11 countries (including Iran, Palestine, Ukraine, Russia, and Sudan) coincided with documented human rights abuses.
Global Platform Blocking Trends
- Increase in Platform Blocking: The report indicated a rise in platform blocking globally.
- The number of blocked platforms increased by 35.6%, from 39 blocks in 29 countries (2022) to 53 blocks in 25 countries (2023).
- Facebook Most Blocked Platform: Facebook was the most blocked platform globally in 2023, with restrictions occurring 23 times across 11 countries.
- Grindr Second Most Blocked: Grindr, a messaging platform primarily used by the LGBTQ+ community, was the second most blocked platform, facing restrictions in all 12 countries where data was available.
- Other Blocked Platforms: Other major platforms like Twitter (21 times in 10 countries), WhatsApp (19 times in 9 countries), and YouTube (17 times in 7 countries) were also subject to blocking by governments.
- Undercounting of Blocked Platforms: The report acknowledges limitations in capturing the full picture of platform blocking. Factors like localized platform preferences, limited data in countries with smaller user bases, inconsistent government implementation, and the use of VPNs can contribute to undercounting.
![]() 17 May 2024
17 May 2024


 The high number of multi-district shutdowns in March can be attributed to two specific events:
The high number of multi-district shutdowns in March can be attributed to two specific events:
