India’s legacy waste project under Swachh Bharat Mission 2.0 has remediated just 19.43% of large dump sites by mid-2024.
About Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM)
- Launch: Launched by the Central government on October 2, 2014, with the goal of eliminating open defecation and creating Open Defecation Free (ODF) villages by October 2, 2019, marking Mahatma Gandhi’s 150th birth anniversary.
|
About Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban 2.0 (SBM-U 2.0)
- Launch: Launched in 2021 as a five-year initiative to make all cities “garbage-free” by 2026.
- Aim: To maintain ODF status across 4,372 Urban Local Bodies (ULBs).
- Nodal Ministry: The Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA).
- Key Vision: Focus on 100% source segregation, door-to-door waste collection, and scientific management of all waste fractions.
- Provision for scientific landfills to safely dispose of untreated inert waste and process rejects to prevent new dumpsites.
- Under Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban 2.0, all legacy landfills are to be cleared by 2026.
- Legacy Dumpsite Remediation
- SBM-U 2.0 includes plans to remediate all legacy waste dumpsites and convert them into green zones.
- A total of ₹3,226 crore in Central Share (CS) assistance has been approved for this remediation effort.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
About Legacy Waste Dumpsites
- Definition: Legacy dumpsites are waste disposal sites that have accumulated solid waste over many years in an unscientific and uncontrolled manner.
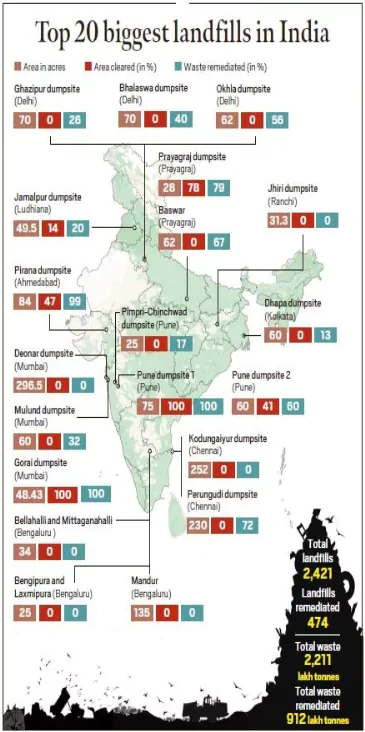
- Example: Mumbai’s Deonar dumpsite, Pirana site in Ahmedabad, Delhi’s Ghazipur and Bhalaswa sites, in Mumbai, Chennai’s Kodungaiyur site etc.
| Legacy Waste or Aged Waste refers to waste that has accumulated over time in landfills or other disposal sites and has not been processed or treated adequately. |
-
- These dumpsites have become large “garbage hills” due to the lack of proper waste management facilities.
- Components of Legacy waste: It includes a mix of organic waste, plastics, metals, and hazardous materials, posing significant environmental and health risks.
- Approaches to treat Legacy waste or Aged waste:
- Scientific Capping; Typically applied to landfills constructed scientifically (engineered landfills / sanitary landfills). It Involves covering the landfill with layers of materials to prevent leachate and gas emissions.
- Landfill Mining / Biomining: which is a technically assisted and economically managed extraction of recyclables and other revenue-generating fractions from waste materials already been disposed of by landfilling
- Biomining of dumpsites is typically aided by a process called bioremediation.
- Bioremediation: It is a microbe-mediated degradation of organic waste carried out by adding biological inoculum to the dumpsite.
- Bioremediation is effective only in dumpsites with higher organic content, typically where fresh waste is mixed with legacy waste.
Associated Data with Legacy Dumpsites
- Solid Waste Management (SWM) is a State subject.
- According to the State of India’s Environment 2023 report, Municipal solid waste generation in India is estimated to be around 1,50,000 tonnes per day.
- Dumpsites in India: India has over 3,000 legacy waste dumpsites, with 2,424 containing more than 1,000 tonnes of waste.
- Land Clearance in Major Cities: The SBM dashboard maintained by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs showed on September 27, 2024 that out of the 69 landfill sites in cities with population over 1 million, land is yet to be cleared in 35 sites.
- Buried Prime Real Estate: According to estimates of the Union Housing and Urban Affairs Ministry, approximately 15,000 acres of prime real estate is buried under nearly 16 crore tonnes of legacy waste across the country.
|
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Hazards Associated With Legacy Waste Dumpsites
- Health Hazard: Legacy waste dumpsites pose significant health risks to nearby communities and the workers involved in the Waste Management Chain.
- Legacy dumpsites can attract pests and vermin, leading to public health concerns.
- Example: Respiratory issues, skin diseases, and other chronic health problems.
- Environmental Hazard: These dumpsites can lead to soil and water pollution, affecting local ecosystems. Toxic leachates can contaminate groundwater sources, harming plants and animals.
- Air quality may deteriorate due to the release of harmful gases from decomposing waste, contributing to air pollution and climate change.
- Economic Impact: Legacy waste dumps can lower property values in nearby areas, negatively affecting real estate markets.
- Remediation Efforts undertaken by the Governments can be expensive requiring diversion of funds from essential services.
- Space Constraints: Growing urban populations lead to a scarcity of available land, and legacy dumpsites occupy valuable space that could be used for housing, parks, or commercial purposes.
- Fire Hazard: These Dumpsites pose fire hazards, as decomposing organic waste can create conditions conducive for spontaneous combustion.
- Example: Ghazipur landfill, Delhi. Fires often break out here, mostly because of the methane generated as the waste decomposes.
Key Concerns on Legacy Waste Remediation
- Inefficient Bioremediation Methods: Bioremediation may not work effectively for all types of legacy waste, especially in older landfills where the waste composition has changed significantly over time.
- The success of bioremediation can vary significantly based on site-specific conditions, including microbial population, moisture levels, and oxygen availability. This inconsistency can lead to unpredictable outcomes.
- It can be a slow process, often requiring years to achieve desired results
- Poor waste segregation at source leads to mixed waste at landfills, making bioremediation more complex and less efficient.
- Simultaneous Dumping of Fresh Waste: Many dumpsites undergoing remediation continue to receive fresh waste, undermining the progress of clearing legacy waste and prolonging the process indefinitely.
- Both legacy and fresh waste management must be complementary activities.
- Contamination Risks in Generated Material: Fine soil-like material produced from the remediation process may contain heavy metals, raising concerns about its use as compost, potentially leading to environmental and health hazards.
- Limited Alternative Waste Processing Facilities: The lack of designated locations to process fresh waste forces continued dumping at the same sites, complicating the remediation efforts.
|
Possible Call of Action for Legacy Waste Management
- Enhanced Understanding of Waste Composition: There is a need to conduct detailed analysis of legacy waste to understand its composition. This knowledge can guide effective bioremediation strategies and recycling efforts.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Successful Examples of Legacy Waste Management in India:
- Indore: Indore has been recognized as one of the cleanest cities in India due to its effective waste management strategies. It has successfully remediated its landfill through bio-mining.
- Delhi: It has developed waste-to-energy plants to convert municipal solid waste into energy, reducing the volume of waste sent to landfills. Legacy waste treatment and sorting is being carried out in the Okhla dumpsite
- Kerala’s Kudumbashree Mission: It empowers local self-governments to manage solid waste through community participation, focusing on source segregation and decentralised waste processing.
|
- Infrastructure Development for Waste Management
- Collection and Sorting Centers: Establish designated facilities for efficient waste collection and sorting, streamlining the waste management process.
- Material Recovery Facilities (MRFs): Invest in MRFs to recover valuable materials from waste, enhancing recycling efforts and minimising landfill usage.
- Wet and Dry Waste Processing Facilities: Implement separate facilities for composting organic waste and recycling dry waste to further reduce reliance on landfills.
- Focus on Organic Waste Treatment: Promote the treatment of organic waste through composting and bio-methanation to convert waste into fuel, reducing landfill pressure.
- Strict Implementation of Waste Management Rules: Enforce regulations like the “Polluter Pays Principle” to hold waste generators accountable and incentivize responsible waste practices.
- 4 R’s Principle: Encourage individuals to adopt the principles of Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, and Recover (4 R’s) at home and work to reduce waste generation effectively.
- Utilisation of Scrap: Implement systems to recover scrap polymeric and combustible materials (4-19% of legacy waste) for producing refuse-derived fuel (RDF) for electricity generation.
- Explore using the fine fraction of decomposed organic waste, combined with silt and construction and demolition (C&D) waste, as soil cover in engineered landfills.
- Integration of Informal Waste Workers in Waste Management Chain: Mechanisms must be established that guarantee fair wages, access to benefits etc to the Informal Workers.
- Additionally, training programs should be provided to enhance their skills in waste sorting, recycling, and safe handling practices, improving overall waste management efficiency.
![]() 4 Oct 2024
4 Oct 2024

