The past few years have witnessed a dramatic increase in the number of workers being deleted from MGNREGA job cards.
About MGNREGA
- The Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) stands as a cornerstone of India’s social security net.
- It provides a legal guarantee of 100 days of work per year to every rural household.
- This right, enshrined in the Act and operationalized through job cards.has been increasingly undermined by a surge in worker deletions.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
About MGNREGA Job Cards
- MGNREGA Job Cards are essential documents issued to rural households under the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA).
- These cards serve as a crucial tool for ensuring the implementation of the Act and guaranteeing the right to work for rural households.
Key Features of MGNREGA Job Cards
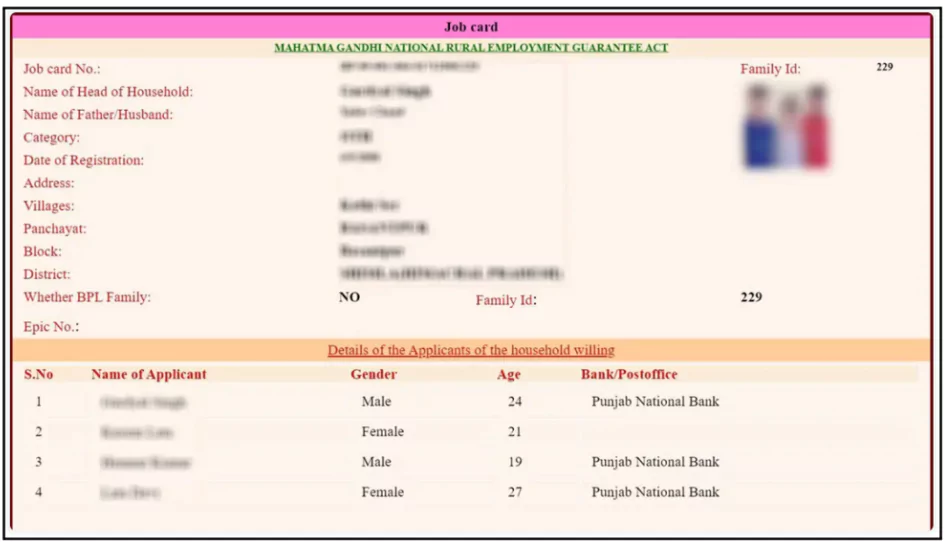
- Unique Identification: Each job card is assigned a unique identification number.
- Household Details: Contains information about all adult members of the household eligible for work.
- Work Eligibility: Entitles the cardholder to 100 days of guaranteed wage employment per year.
- Wage Disbursement: Records the work done, wages earned, and payment details.
- Monitoring Tool: Used to track work progress, monitor wage payments, and assess program implementation.
- Issued by Gram Panchayat: Local self-government bodies are responsible for issuing MGNREGA job cards to eligible households within their jurisdiction.
MGNREGA and the Right to Work as a Step Towards DPSP
- Legal Framework: MGNREGA provides a statutory right to work for rural households.
- Job Guarantee: Ensures at least 100 days of wage employment in a financial year.
- Article 41 DPSP: Right to Work, Education and Public Assistance)
- Wage Employment: Creates employment opportunities, especially during agricultural off-seasons.
- Social Security Net: Acts as a social safety net, particularly for marginalized communities. (
- Asset Creation: Contributes to rural development through the creation of public assets like roads, ponds, and irrigation canals.
- Article 43 DPSP: Living Wage, Conditions of Work.
- Empowerment of Rural Women: Encourages women’s participation in the workforce.
- Article 42 DPSP: Just and Humane Conditions of Work and Maternity Relief
|
Factors responsible for Rising Deletions
- A staggering 10.43 crore workers have been removed over the last four years, with a particularly alarming spike in 2022-23.
- Reason for deletion: The implementation of Aadhaar-based payment systems in MGNREGA has been linked to the rise in worker deletions.
- Arbitrary Deletions: In a rush to achieve 100% Aadhaar seeding, field officials resorted to shortcuts, including deleting job cards of workers who could not be immediately linked to their Aadhaar numbers.
- Lack of Transparency: The deletion process has often been marred by a lack of transparency and due process.
- Workers have been removed from job cards without proper notice or opportunity to be heard.
- Reasons cited for deletion, such as “not willing to work” or “duplicate applicant,” often seem arbitrary and unsubstantiated.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Impact on Rural Livelihoods
- This trend is deeply concerning, as it directly impacts the livelihoods of millions of rural households.
- The erosion of the right to work has severe consequences for rural livelihoods.
- Workers who are deleted from job cards are deprived of their legal entitlement to employment and social security.
- This can push vulnerable households into deeper poverty and food insecurity.
Restoring the Right to Work
- Strengthening Accountability and Transparency: Implementing robust monitoring and evaluation mechanisms to track worker deletions and ensure adherence to due process.
- Independent Audits: Conducting regular, independent audits of MGNREGA implementation to identify and rectify irregularities.
- Empowering Gram Sabhas: Empowering Gram Sabhas to play a more active role in overseeing MGNREGA implementation and protecting the rights of workers.
- Public Awareness and Grievance Redress: Raising awareness about the right to work and establishing effective grievance redress mechanisms.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: Leveraging technology and data analytics to improve MGNREGA implementation and identify trends in worker deletions.
Additional Reading: MGNREGA
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.


