India, Italy to Negotiate Defence Industrial Roadmap
Context: India and Italy will negotiate a defence industrial roadmap, ensure classified information protection, and enhance maritime and port sector cooperation under the Joint Strategic Action Plan 2025-29.
India-Italy Defence Cooperation Highlights
- Defence Industrial Roadmap:
- Promotion of an MoU between the Society of Indian Defence Manufacturers (SIDM) and the Italian Industries Federation for Aerospace, Defence, and Security (AIAD).
- Military Exchanges:
- Increased interactions between Armed Forces to enhance interoperability, especially in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Historic maritime exercise with carrier strike groups, including INS Vikramaditya and ITS Cavour, showcasing naval collaboration.
- Technology Collaboration: Focus on co-production, co-development, and technology sharing for defence platforms and equipment.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Carrier Strike Groups (CSG) exercise
- About Carrier Strike Groups: A CSG is a flexible naval force that can operate in all weather conditions, at any time of day, and in both open ocean and confined waters.
- Ships: CSGs are led by aircraft carriers, and also include cruisers, destroyers, submarines, and support ships.
- The first-ever Carrier Strike Groups (CSG) exercise between India and Italy took place from October 1–6, 2024 off the coast of Goa.
- Carriers: The Indian Navy’s INS Vikramaditya and the Italian Navy’s ITS Cavour led the sea phase of the exercise.
- The exercise was a significant step in enhancing interoperability and strengthening naval ties between the two countries.
|
Key Highlights of India-Italy Joint Strategic Action Plan 2025-2029
- Political Dialogue
- Regular meetings and visits between Heads of Government and Ministers.
- Annual Foreign Office Consultations at the Senior Officials’ level.
- Enhanced interaction between ministries for sectoral cooperation.
- Economic Cooperation and Investments
- Boost bilateral trade and investment in sectors like transportation, food processing, green technologies, and pharmaceuticals.
- Connectivity
- Collaborate on sustainable transport and maritime infrastructure under the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEEC).
- Agreement on maritime and port sector cooperation.
- Science, Technology, and Innovation
- Expand collaboration in critical technologies like AI, telecom, and digitalization.
- Joint initiatives in Industry 4.0, clean energy, and critical mineral refining.
- Launch of the Indo-Italian Innovation and Incubation Exchange Programme.
- Space Sector
- Strengthen Italian Space Agency (ASI) – Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) cooperation in Earth observation, heliophysics, and lunar science.
- Organise an Italian space industry delegation visit to India in 2025.
- Energy Transition
- Collaboration in green hydrogen, biofuels, and renewable energy.
- Promote the Global Biofuels Alliance and International Solar Alliance.
- Share best practices in energy efficiency and grid development.
- Defence Cooperation
- Annual Joint Defence Consultative (JDC) meetings and Joint Staff Talks (JST).
- Develop a Defence Industrial Roadmap and facilitate co-development of platforms.
- Security Cooperation
- Annual Joint Working Group meetings on international terrorism and crime.
- Migration and Mobility
- Promote safe and legal migration pathways and training for Indian health professionals for employment in Italy.
- Culture, Academic, and People-to-People Exchanges
- Strengthen university collaborations and vocational education exchanges.
SANYUKT VIMOCHAN 2024′
Context: Recently, The Indian Army successfully organised an exercise, ‘Sanyukt Vimochan 2024’ at Ahmedabad and Porbandar, Gujarat.
About Exercise Sanyukt Vimochan
- It is a multilateral annual joint Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) Exercise.
- The exercise was conducted by the Konark Corps of Southern Command of the Indian Army.
- Objective:
-
- To improve India’s ability to respond effectively to natural disasters by enhancing preparedness and readiness.
Key Highlights of the Exercise
- About Table Top Exercise on Cyclone Management
- Location: Ahmedabad
- Theme: ‘Cyclone in Coastal Region of Gujarat’
- A Tabletop Exercise (TTX) simulated a cyclone affecting the Okha-Porbandar coastline, focusing on disaster relief strategies.
- Key aim: Identify gaps in inter-agency cooperation and establish mechanisms for a swift, coordinated disaster response.
- About Multi-Agency Capability Demonstration
- The day featured a live simulation of disaster management in a cyclone scenario.
Green World Awards 2024
Context: Coal India Limited (CIL), under the Ministry of Coal, received the Green World Environment Award 2024 in the Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) category.
More on the news
- This international award has been given to CIL for exemplary work in the field of CSR i.e Thalassemia Bal Sewa Yojna.
- The company was also honoured with the title of Green World Ambassador for its contributions to environmental sustainability and social responsibility.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
About The Green Organization.
- Established: 1994.
- Headquarter: East Amherst, New York, United States.
- It is an independent non-political, non-profit group.
|
- Award Ceremony
-
- The award was presented by The Green Organization.
- The ceremony took place at The Orangery, Kensington Palace, London.
About Thalassemia Bal Sewa Yojna
- It offers curative treatment for Thalassemia patients through stem cell transplant called Bone Marrow Transplant (BMT).
- Achievements of the Scheme:
-
- Over 600 patients have received permanent treatment under the program.
- Financial assistance of up to ₹10 lakh is provided as per BMT procedure.
- The initiative partners with 17 leading hospitals across India.
About Coal India Limited (CIL)
- It is a state-owned coal mining corporate.
- Established: 1975
- Classification: classified as a ‘Maharatna’ enterprise under the Ministry of Coal, Government of India.
- Headquarters- Kolkata
Indira Gandhi Peace Prize
Context: Recently, the Indira Gandhi Prize for Peace, Disarmament, and Development 2023 was given.
Event Details
- Award Recipients
- Daniel Barenboim: He is Argentine-born distinguished classical pianist and conductor.
- Recognized for promoting peace through musical and cultural dialogue.
- Ali Abu Awwad: Palestinian peace activist honoured for his non-violent advocacy and dialogue efforts through his organisation, Roots an outfit that he started after spending time in an Israeli jail.
About Indira Gandhi Peace Prize
- The Indira Gandhi Prize, also known as the Indira Gandhi Peace Prize, is an annual award presented by the Indira Gandhi Memorial Trust.
- Location: New Delhi
- First awarded: 1986
- Naming: After former Prime Minister Smt. Indira Gandhi.
- Eligibility and Criteria
- It honours individuals or organisations for their exceptional contributions in
- Promoting international peace and development.
- Advocating for a new international economic order.
- Ensuring scientific discoveries benefit humanity.
- Expanding the scope of freedom.
- Award Components
- The prize includes:
- A cash award of 2.5 million Indian rupees.
- A citation recognizing the recipient’s contributions.
African Penguins
Context: The African Penguin was recently listed as critically endangered by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
About African Penguins
- They are also known as Cape penguin or South African penguin, as they are confined to southern African waters.
- Scientific name: Spheniscus demersus
- Present Status: Less than 10,000 breeding pairs are left globally, mainly concentrated in South Africa, down from 42,500 in 1991
- African Penguins are feared to go extinct in the wild by 2035.
- IUCN Status: Critically Endangered.
- Habitat: Large colonies of penguins are found along the southwestern rocky coast of Africa from Namibia to Port Elizabeth, and many of the surrounding islands.
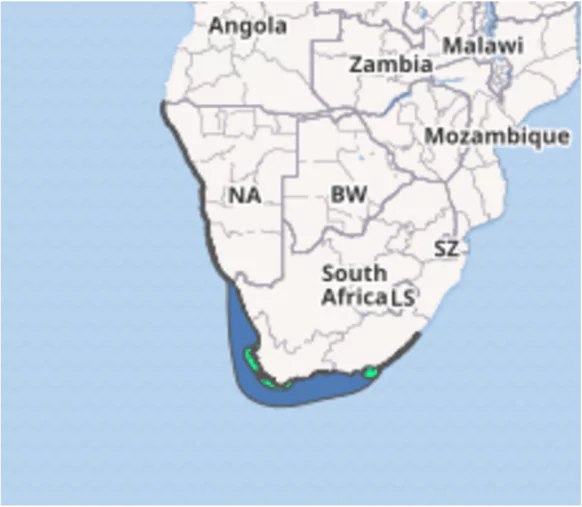 The largest colony is located on Dyer Island.
The largest colony is located on Dyer Island.
- Prey: The preferred prey of the penguins are sardines or anchovies, capelin, and night smelt as well as squid and crustaceans.
- Features:
- Size: The African penguin is one of the smallest penguin species.
- Appearance: They are covered in a black, white, and gray dense, waterproof feathers. They also have a distinct, sharply pointed beak and black feet.
- Flecks: They have a number of dot-like markings flecked across their white chests which are unique to each penguin.
- Communication: Penguins communicate with each other through vocalisations and body language.
- Cause of Decline:
- Lack of Nutrition and Food: When Penguins starve and don’t eat enough they tend to abandon breeding.
- Other Causes: Climate change, disturbances, predators, disease, oil spills etc.
- Threats:
- Tourism: Each year thousands of people visit the penguin colonies making them susceptible.
- Industrial Fishing: Direct competition for their primary food source with the industry is resulting in a lack of food affecting their breeding behaviour.
- Climate Change: Climate Change induced global warming is altering their habitat and ecosystem.
- Conservation:
- No Fishing Zones: A commercial fishing ban has been imposed around six penguin colonies for 10 years.
- Artificial Nests and New Colonies are being made up to support breeding.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
India-Japan MOI for Co-development of UNICORN Masts
Context: India and Japan have signed a Memorandum of Implementation (MoI) for the “co-development” of UNICORN (Unified Complex Radio Antenna) Nora-50 integrated mast for Indian Naval Warships.
- The agreement will be implemented under the framework of the India-Japan Defence Technology Cooperation 2015 and will be the first export case of defence technology from Japan to India.
About the UNICORN (Unified Complex Radio Antenna) Mast
- The Mast is a conical structure housing antennas and integrated communication systems atop Naval Platforms increasing their stealth characteristics.
- Built by: It is a result of collaboration between three Japanese companies ie. NEC Corporation, Sampa Kogyo K.K, and The Yokohama Rubber Co., Ltd
- Indian Partner: For the Indian Warships the UNICORN Mast will be co-developed by Bharat Electronics Limited in India with Japanese collaboration.
- The Indian Navy currently uses the BEL-supplied Advanced Composite Communication System (ACCS).
- Key Features:
- Radome: It consolidates multiple communication antennas into a single, state-of-the-art radar dome, known as a radome minimising electronic signatures and enhancing stealth.
- TACAN (Tactical Air Navigation System): UNICORN is an improvement on the TACAN antenna design framework.
- The TACAN system constitutes a mobile transmitting unit. The airborne unit, in conjunction with the Naval platform, processes the transmitted signals to a visual presentation of both azimuth and distance information
- Wider Detection Range: The UNICORN system can detect the movement of missiles and drones from afar by sensing radio waves over a wide area.
India- Japan Defence Collaboration
- Tarang Shakti Exercise 2024: It is the first multilateral exercise hosted by the Indian Air Force and Japan participation marked the first air visit by Japanese fighters to India
- Veer Guardian 2023: It is the maiden edition of the bilateral fighter exercise between the Japan Air Self Defence Force (JASDF) and the Indian Air Force (IAF).
- The Indian Navy and JMSDF interact bilaterally during JIMEX every year in addition to meeting in Multilateral settings of exercises MALABAR and MILAN.
- Development of the Andaman and Nicobar Island: Japan has aided India with 4.02 billion yen ($31 million) to develop the islands. This was the first time that India accepted foreign assistance for development on the island
Fossil Fuel Non-Proliferation Treaty Initiative
Context: Tzeporah Berman, Chair and Founder of the Fossil Fuel Non-Proliferation Treaty Initiative, recently, spelt out the latest threats to the planet at COP29 in Baku.
About Fossil Fuel Non-Proliferation Treaty Initiative
- Launched: The idea was conceptualised in 2016 and officially launched in 2019 through a Climate Breakthrough award.
- Endorsed by: The treaty is endorsed by 14 nations-states comprising,
- Vanuatu, Tuvalu, Tonga, Fiji, the Solomon Islands, Niue, Antigua and Barbuda, Timor-Leste, Palau, Colombia, Samoa, Nauru, the Marshall Islands, and the Federated States of Micronesia
- First Ministerial Meeting: The Fossil Fuel Non-Proliferation Treaty Initiative convened its first meeting in May 2024 in Antigua and Barbuda.
- Objective: The FF-NPT desires to make it legally binding on the nations to end fossil fuel extraction and phase down existing production, and manage a just transition to renewable energy.
- Pillars:
- Non-Proliferation: It is a global cooperation model to end the expansion of coal, oil and gas production
- Fair Phase-Out: A fair and equitable plan to shut down existing fossil fuel production by inculcating the Common yet Differentiated Responsibility Principle.
- Just Transition: To fast-track the adoption of renewable energy and economic diversification away from fossil fuels universally.
- Aligned with Paris Agreement Goals: The Treaty aims to support the work of Paris Agreement through,
- Implementing the New Collective Quantified Goal: It aims to establish a new financial target to assist developing countries in their climate actions post-2025.
- Through Nationally Determined Contributions (the climate action plans submitted by countries) and Just Transition Work Programmes
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Salil Chowdhury 100th Birth Anniversary
Context: Artistes in West Bengal celebrated the centennial of Salil Chowdhury, whose body of works spans across various genres of Indian music.
About Salil Chowdhary
- Birth and Background: Born on November 19, 1925, in West Bengal, India.
- Musical Training: He was deeply rooted in Hindustani classical music, skillfully blending diverse musical styles in his compositions.
- IPTA Membership: He was an cctive member of the Indian People’s Theatre Association (IPTA), composing revolutionary songs during his tenure.
Contributuions of Salil Chowdhary
- Film Contributions: Created music for 100+ films across multiple languages, including Bengali, Hindi, Malayalam, Tamil, Assamese, and others.
- Chemmeen (1965): A groundbreaking project that combined Bengali folk music with Western orchestration to portray Kerala’s coastal culture.
- Revolutionised music in Indian cinema, particularly Malayalam, through unique blending of Hindustani classical, Western classical, and folk styles.
- Legacy: Pioneered a melody-first approach to film music, now a standard in Malayalam cinema.
- In Melody First Approach the composition of music is done before writing the Lyrics.
![]() 21 Nov 2024
21 Nov 2024

 The largest colony is located on Dyer Island.
The largest colony is located on Dyer Island.