M-sand
Context: Rajasthan has launched the M-Sand Policy 2024 to promote sustainable construction and infrastructure.
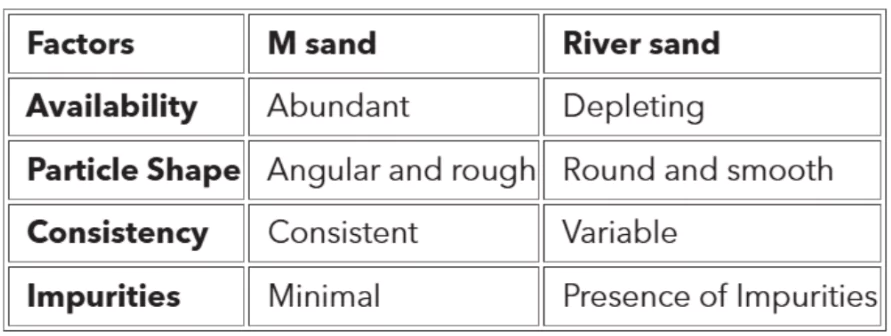
What is M – sand?
- M-Sand refers to Manufactured Sand
- It is an Artificial sand produced by crushing hard stones using a VSI (Vertical Shaft Impact) machine.
- It was Developed to address the shortage of natural river sand for construction purposes.
- Initially introduced in Tamil Nadu and Kerala to meet increasing construction demands and reduce environmental impact.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Benefits of Manufactured Sand (M-Sand)
- Cost-Effective: Lower production costs make M-Sand more affordable than natural sand.
- Quality Consistency: Uniform grain size and shape make it ideal for construction projects.
- Environmental Benefits: Reduces dependency on natural sand mining, protecting ecosystems.
- Reuses overburden from coal mines, converting waste into usable material.
- Reduced Water Consumption: Does not require washing which saves water during construction.
- Enhanced Mine Safety: Useful for sand stowing in underground mines, improving safety and conservation.
- Reduction in River Sand Extraction:
- Prevents riverbed erosion.
- Protects aquatic habitats and maintains ecological balance.
Fighter Jets Generation
Context: Unconfirmed images of a Chinese sixth-generation fighter jet are circulating online.
- Baidi White Emperor ‘B Type Fighter Jet’: In November, China’s Aviation Industry Corporation (AVIC) showcased its sixth-generation fighter jet concept at the Zhuhai Airshow 2024.
What Are Fighter Jets?
- Fighter Jets are advanced military aircraft designed for air-to-air combat and air-to-ground attacks.
- Their primary role is to dominate the skies by engaging enemy aircraft, protecting airspace, and supporting ground forces.
First to Fifth Generations
- First Generation (1940s-1950s): Early jet engines, subsonic speeds, and basic radar systems. Examples – Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-15
- Second Generation (1950s-1960s): Supersonic speeds, radar-guided missiles, and improved maneuverability. Examples – Lockheed F-104 Starfighter and MiG-21.
- Third Generation (1960s-1970s): Multi-role aircraft with better avionics and enhanced firepower. Examples- MiG-23, Hawker Siddeley Harrier, and McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom.
- Fourth Generation (1970s-1990s): Advanced radars, fly-by-wire controls, and focus on agility and stealth. Examples – MiG-29 (Russia), Tejas MK-1 (India).
- Fifth Generation (2000s-Present):
-
- Features: Stealth technology, advanced avionics, integrated sensors, and data fusion.
- Examples: F-22 Raptor (USA), Chengdu J-20 (China).
Sixth Generation (Future)
- Hypothetical Features:
- Artificial intelligence (AI) integration.
- Network-centric warfare capabilities.
- Hypersonic weapons.
- Enhanced stealth with adaptive materials.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
What Does “Generation” Mean in Fighter Aircraft?
- Fighter jet “generations” refer to different stages of technological advancement and design improvements over time.
Plantation History of Coffee Tree at Idukki Church
Context: The article focuses on the Historic Coffee Plant at CSI Church, Pallikkunnu.
About Coffee plantation in Idukki
- Location: Near Kuttikkanam in Idukki district.
- The British planted coffee on the church grounds over 150 years ago during the early plantation period in Peerumade.
- Historical Context of Coffee Plantations in Idukki
- Early Industry: Initially, coffee plants were the primary crop in Idukki.
- Shift to Tea: In 1875, a leaf disease damaged coffee plants, leading planters to switch to tea cultivation.
- Significant Yield: Thengakal near Peerumade achieved the highest coffee yield in southern India, producing two tonnes of cured coffee per acre.
Exercise Surya Kiran
Context: A contingent of 334 Indian Army personnel has departed for Nepal to participate in the 18th edition of the Battalion-Level Joint Military Exercise SURYA KIRAN.
- The exercise will take place in Saljhandi, Nepal, from 31st December 2024 to 13th January 2025.
About Exercise Surya Kiran
- Nature of Exercise: A joint military exercise between the Indian Army and the Nepal Army.
- Frequency: Conducted annually and hosted alternately by both countries.
- Objective:
- To enhance interoperability in jungle warfare and counter-terrorism operations in mountainous terrains.
- To conduct Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) under the framework of the United Nations Charter.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
About Humanitarian Assistance Disaster Relief (HADR)
- HADR is a critical response to emergencies like natural disasters (earthquakes, floods) or conflicts.
- Established in the aftermath of World War II, its primary objective is to save lives, alleviate suffering, and maintain human dignity during and after crises.
- HADR encompasses a wide range of activities, including providing food, water, shelter, medical care, and protection to those affected.
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.


