Context: Recently a study was published in the American Meteorological Society’s Journal of Hydrometeorology which reveals that Peninsular River basins face a higher probability of widespread flooding compared to the Ganga and Brahmaputra (transboundary rivers).
Widespread Floods in Indian Peninsular River Basins:Key Findings
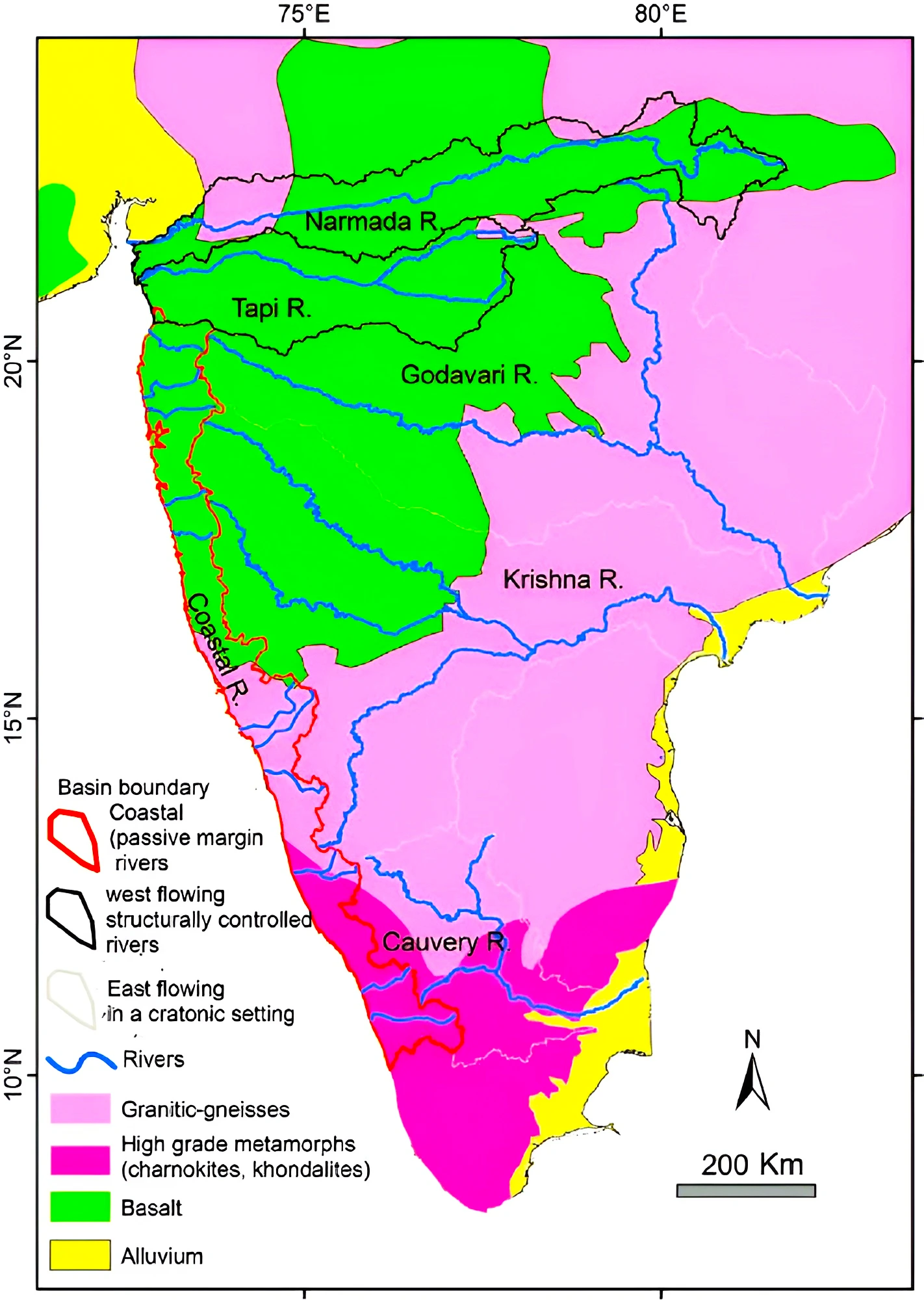
- Basis of Study: The Study is done based on the occurrence of widespread floods in seven major river basins in the Indian subcontinent, such as Ganga, Brahmaputra, Godavari, Krishna, Mahanadi, Narmada and Kaveri in 1959-2020.
Flooding Probability: Peninsular Rivers:
-
- Narmada basin (59 per cent)
- Mahanadi (50 per cent)
- Godavari (42 per cent)
- Cauvery (19 per cent)
- Transboundary Rivers
- Ganga (21 per cent )
- Brahmaputra (18 per cent)
- Flooding Events: Mahanadi and Narmada river basins witnessed 40 events of flooding.
- Krishna and Godavari basins witnessed more than 20 widespread floods.
- Seasonal Trends: Strong seasonal trends were observed in widespread flood probability in the subcontinental river basins.
- For example, during the summer monsoon season, all seven river basins, except Cauvery, experienced widespread flooding in August.
About Atmospheric Rivers
- Atmospheric rivers are long, flowing regions of the atmosphere that carry water vapor through the sky.
- Data: Atmospheric rivers caused 70% of India’s floods between 1985 and 2020.
|
- Drivers of widespread flood:
- Atmospheric rivers: Atmospheric rivers typically transport moisture from the tropics to the extratropics leading to widespread flood.
- Example:
- Floods in the lower Mississippi River in 2008, 2011, and 2015–19
- Kerala floods in 2018 and
- Floods in Pakistan in 2022
- Atmospheric circulations: The study reveals that widespread floods in India are associated with large atmospheric circulations that cause precipitation in the river basin.
|
-
- Gentler slopes: Unlike the Himalayan rivers, these rivers traverse modest valleys and have relatively gentler slopes.
- Seasonal:Many of these rivers are seasonal, relying on rainfall for their flow.
- Straight and horizontal courses:The peninsular rivers are characterized by their firm granite bed and lack of sand and silt, which limit meandering, resulting in straight, horizontal courses.
- Example: Narmada, Tapi, Godavari, Krishna, Kaveri, and Mahanadi river systems.
- Transboundary Rivers:
- Shared by two or more countries:Transboundary waters are the aquifers and lake and river basins shared by two or more countries.
- World freshwaters:Transboundary waters account for 60 percent of the world’s freshwater flows.
- Examples:
- Ganges (India – Bangladesh)
- Indus(China India Pakistan)
|
Must Read: Urban Flooding: Why Are Our Cities So Flood-Prone?
News Source: Down To Earth
![]() 22 Dec 2023
22 Dec 2023