U.S. scientist John Hopfield and British-Canadian Geoffrey Hinton won the 2024 Nobel Prize in Physics for discoveries and inventions that laid the foundation for machine learning.
John Hopfield and Geoffrey Hinton Work
- Work: Developing computer algorithms that mimic the functioning of the human brain in performing common tasks.
- Hopfield’s revolutionary work in the 1980s: Built an artificial neural network (ANN) resembling the network of nerve cells in the human brain, that allowed computer systems to ‘remember’ and ‘learn’
- Hopfield’s network: Processed information using the entire network structure, and not its individual constituents.
- Traditional computing: Information is stored or processed in the smallest bits
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
About Nobel Prize
- The Nobel Prizes in Science recognize outstanding achievements in Physics, Chemistry, and Physiology or Medicine.
- Each year, laureates are honoured for groundbreaking discoveries and advancements that have significantly impacted their respective fields.
- Winners are celebrated globally for their contributions to understanding the universe, developing new technologies, and improving human health.
- The Nobel Prizes in Science are awarded by various committees based on the specific field:
- Physics: Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences.
- Chemistry: Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences.
- Physiology or Medicine: Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute in Sweden.
- These institutions evaluate nominations, conduct rigorous reviews of candidates’ work, and select the laureates based on their contributions to their respective fields.
|
- Hinton took forward the work of Hopfield and developed artificial networks that could perform much more complex tasks.
- Hopfield networks could recognise simple patterns of shape or sound
- Hinton’s advanced models could understand voices and pictures.
- Neural networks could be strengthened, and their accuracy at pattern recognition enhanced through repeated inputs of data, called training.
- Hinton developed a method called backpropagation that enabled the artificial neural networks to learn from previous mistakes and improve itself.
About Machine Learning
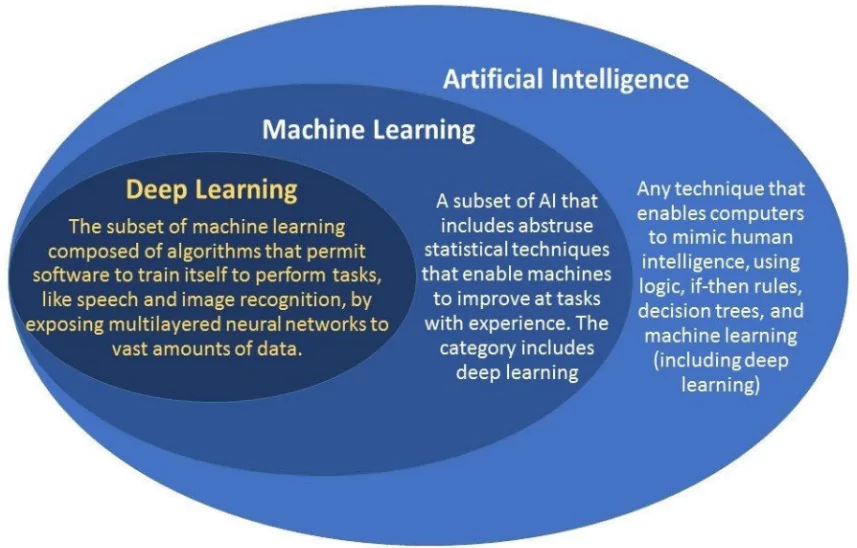
- Subset of artificial intelligence (AI), it focuses on the development of algorithms that enable computers to learn from and make decisions based on data, without being explicitly programmed for specific tasks.
- Essence of machine learning is recognizing patterns within data and making predictions or decisions based on those patterns.
- How it works
- ML systems learn by processing data and optimising internal variables, or model parameters, to reflect the data.
- The learning algorithm then updates the parameter values as it learns, allowing the model to make predictions and decisions based on the data.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
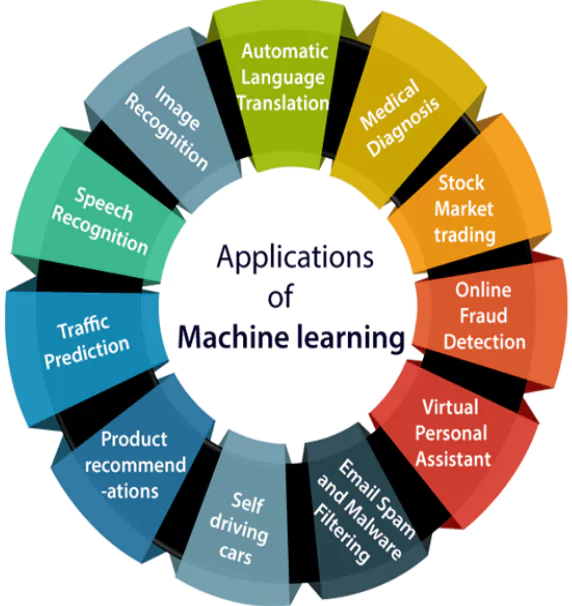
Examples of machine learning
- Spam filtering: Uses patterns in data to identify spam emails
- Natural language processing: Enables computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language.
- Neural networks: Inspired by the human brain’s neural connections, these models are used in machine learning.
- Overfitting and Underfitting: Overfitting occurs when a model performs well on training data but poorly on new data. Underfitting happens when a model is too simplistic, failing to capture underlying patterns.
![]() 9 Oct 2024
9 Oct 2024

