According to a statement by National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI), C-Edge Technologies Ltd which is a technology service provider to co-operative and regional rural banks was “possibly” hit by a ransomware attack
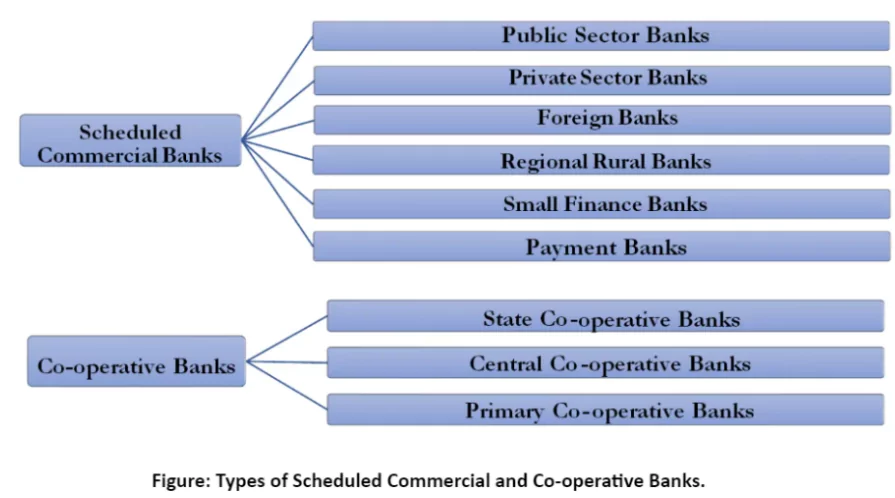
Regional Rural Banks (RRBs)
- Established on recommendations of the Narasimham Working Group (1975),
- Established under the Regional Rural Banks Act of 1976;
- The aim is to ensure sufficient institutional credit for agriculture and other rural sectors.
- The area of operation of RRBs is limited to the area notified by the Central Government.
- Ownership: 50% by the Central Government, 35% by the Sponsor Bank, and 15% by the State Government.
Cooperative Banks
- It refers to those financial institutions under the Banking System in India that operate on the principles of cooperation and mutual benefit for their members.
- Cooperative Banking in India is divided into two distinct segments- Rural and Urban.
- Four Distinct Tiers:
- Central Cooperative Banks: Operate at the district level, providing loans primarily to affiliated primary societies.
- State Cooperative Banks: Operate at state level.
- Primary Cooperative Banks: Serve urban and semi-urban areas, focusing on non-agricultural businesses.
- Land Development Banks: Cater specifically to farmers’ needs, offering credit for development purposes. Comprise three tiers: Primary, State, and Central.
- Regulatory Authority: Recently came under the regulatory purview of the National Bank for Agricultural and Rural Development (NABARD) instead of just RBI and state governments.
- Urban Cooperative banks: After the Banking Regulation (Amendment) Act 2020 was passed, all the powers were transferred to RBI from the Registrars of the cooperative societies.
- Even some powers are left with the registrar but RBI powers will override them.
- RBI allows cooperative banks to raise funds through the issuance of equity shares, preference shares and debt instruments; Large cooperative banks with paid-up share capital and reserves of Rs.1 lakh were brought under the purview of the Banking Regulation Act 1949 with effect from 1st March 1966.
|
About Ransomware
- Ransomware is a form of malware designed to encrypt files on a device, rendering any files and the systems that rely on them unusable.
- Malicious actors then demand ransom in exchange for decryption.
- Given the challenge in tracing the victim, attackers typically demand payment through cryptocurrency.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
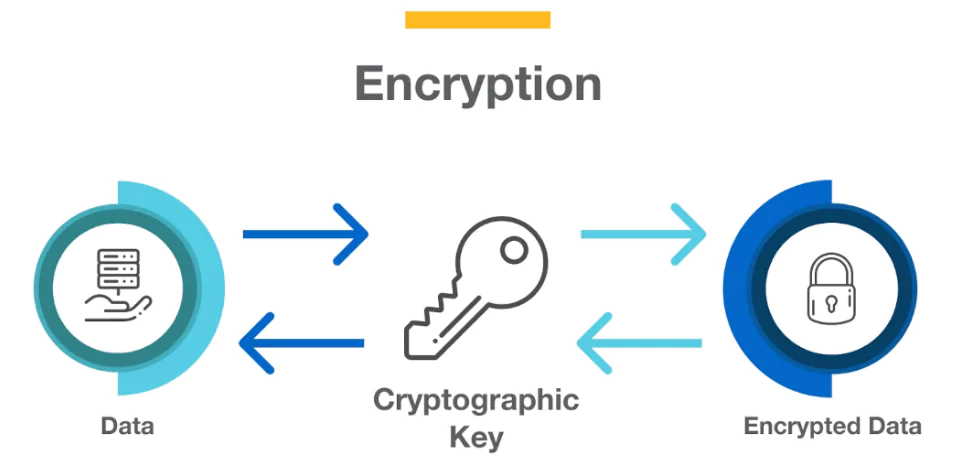
Encrypting the Data
- It means converting the data into a coded format that is unreadable without a decryption key.
- When ransomware encrypts files, it uses complex algorithms to transform the original data into an encrypted version, making it inaccessible to the user.
- The attacker then demands a ransom in exchange for the decryption key, which is needed to revert the data back to its original, readable form.
|
![]() 6 Aug 2024
6 Aug 2024