![]() March 29, 2024
March 29, 2024
![]() 5159
5159
![]() 0
0
The banking system in India, which evolved over several decades, is well established and has been serving the credit and banking needs of the economy. The banking ecosystem is providing impetus to the economic growth and development of the country and catering to the specific and varied financial requirements of different customers and borrowers.
Banks play a crucial role in efficiently channeling resources from depositors to lenders, mutually benefiting parties and promoting economic growth by optimizing resource utilization.
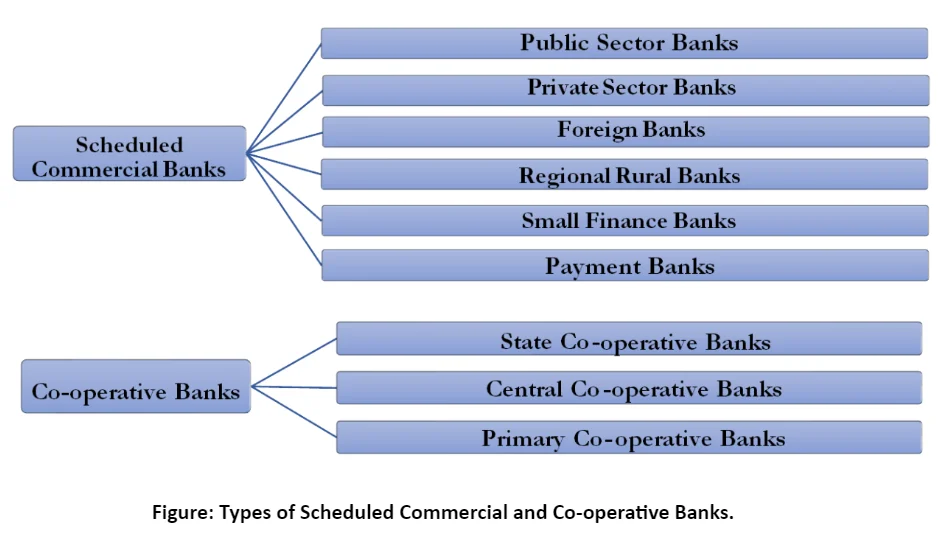
Landscape of Commercial Banks in India
Differentiated Banks
Differentiated Banking Landscape in India:
Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation
| NBFCs | Banks |
|
|
Automated Teller Machine
Digital Payment
|
Recent Status of Digital Payment in India.
Overview of Banking System and Financial Infrastructure in India
|
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Conclusion
| Related Articles | |
| Indian Economy: Evolution | Basics of Money |
| Banks in India | Financial Market |
| Indian Insurance Sector | Financial Inclusion |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
Latest Comments