Context
Recently, a report titled “India’s rise as the emerging services factory of the world”, has been released by Goldman Sachs.
Goldman Sachs:
- It is a leading global investment banking, securities and investment management firm that provides a wide range of financial services to a substantial and diversified client base that includes corporations, financial institutions, governments and individuals.
|
Crucial Insights of the Report On India’s Services Sector
-
Rise in India’s Service Exports:
- India’s services exports reached $340 billion in 2023.
- India has become the ‘services factory’ of the world as the country’s services exports have more than doubled in the past 18 years and are expected to touch $800 billion by 2030.
- While global services exports tripled over 18 years, India grew at twice the pace to reach nearly $340 billion last year.
- Between 2005 and 2023, Indian services exports grew from 2% to 4.6% whereas the country’s goods exports in the same period only grew to 1.8% from 1%.
- Also, India’s exports growth has been the third fastest globally since 2005, behind Singapore and Ireland.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
-
Contribution in Indian Economy:
- India’s services exports will comprise 11% of the GDP by 2030 (versus 9.7 percent of GDP in 2023), which would amount to $800 billion (compared to around $340 billion in 2023).
- It further projected that the current account deficit would be 1.1% of the GDP by 2030 “assuming no significant moves in commodity prices and goods trade balance beyond 2024”.
- Over the last 18 years, professional consulting has grown the fastest and travel services have grown the slowest, and financial services could gain if initiatives such as the GIFT City are promoted.
-
Concerns Raised:
- Domestic Concerns: The report flagged the resource stress that Bengaluru, a hub of computer services export, is facing (water crisis) and the issue of a skilled workforce for the future.
Outsourcing Success Stories- How India Became the Global Hub for Business Transformation:
- India has emerged as a cornerstone in the global outsourcing landscape by consistently delivering transformative solutions for businesses.
- Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) and Nielsen: TCS revamped Nielsen’s IT framework, enhancing its data analytics and market research capabilities.
- This collaboration exemplified India’s aptitude for revitalising intricate global processes.
- Wipro and Citibank: Wipro developed scalable core banking solutions for Citibank.
- This partnership showcased India’s strengths in the fintech domain with applications that have global relevance.
- IBM India and Bharti Airtel: IBM India was instrumental in transforming Bharti Airtel’s IT operations, enhancing customer service and operational efficiency.
- This partnership underlined the capacity of Indian tech solutions to elevate telecommunications services.
|
-
- Fall on Target: The projected growth of the services exports would still fall short of the government’s target.
- In India’s foreign trade policy unveiled in 20230, the government had set the target of $1 trillion for services exports by 2030.
- International Concerns: The report also highlighted that the exports are dependent on global demand for information and communications technology (ICT) spending and rising protectionism in destination countries could hurt export prospects.
-
Actions Required:
- A Calibrated Approach: India needs a calibrated approach that should include a hard push for global market access and opportunities for all professional services, as well as a light-touch regulatory approach to let new ideas and enterprises bloom across areas such as artificial intelligence, manufacturing-linked services, and blockchain applications.
- Need for Specific Focus: India should not take services exports for granted as services exports as per projection is seeming to fall short of the government’s target.
India’s march towards a $5 trillion economy by 2025 and role of service sector:
- India is one of the fastest growing major economies and its strengths are indicative of the potential of India to achieve a USD 5 trillion economy by 2025.
- The current structure of the economy and the emerging dynamics provide us grounds to target achieving 1 trillion dollars from agriculture and allied activities, 1 trillion from manufacturing and 3 trillion from services.
|
Service Sector in India
The service sector is also known as the tertiary sector. It is one of the three sectors of the economy, the other two being the primary sector (includes agriculture, forestry, mining, and fishing) and the secondary sector (includes manufacturing and construction).
- Includes: India’s services sector covers a wide variety of activities such as trade, hotel and restaurants, transport, storage and commun
- ication, financing, insurance, real estate, business services, community, social and personal services, and services associated with construction.
- Evolution & Development: The reforms of the 1990s have been associated with the expansion of the service sector in India.
- Midway through the 1980s, the service sector began to expand, but it took off in the 1990s when India started a series of economic reforms in response to a serious balance of payments issue. Jurisdiction:
- Union List: Telecommunications, postal, broadcasting, financial services (including insurance and banking), national highways, mining services.
- State List: Healthcare and related services, real estate services, retail, services incidental to agriculture, hunting, and forestry.
- Concurrent List: Professional services, education, printing and publishing, electricity.
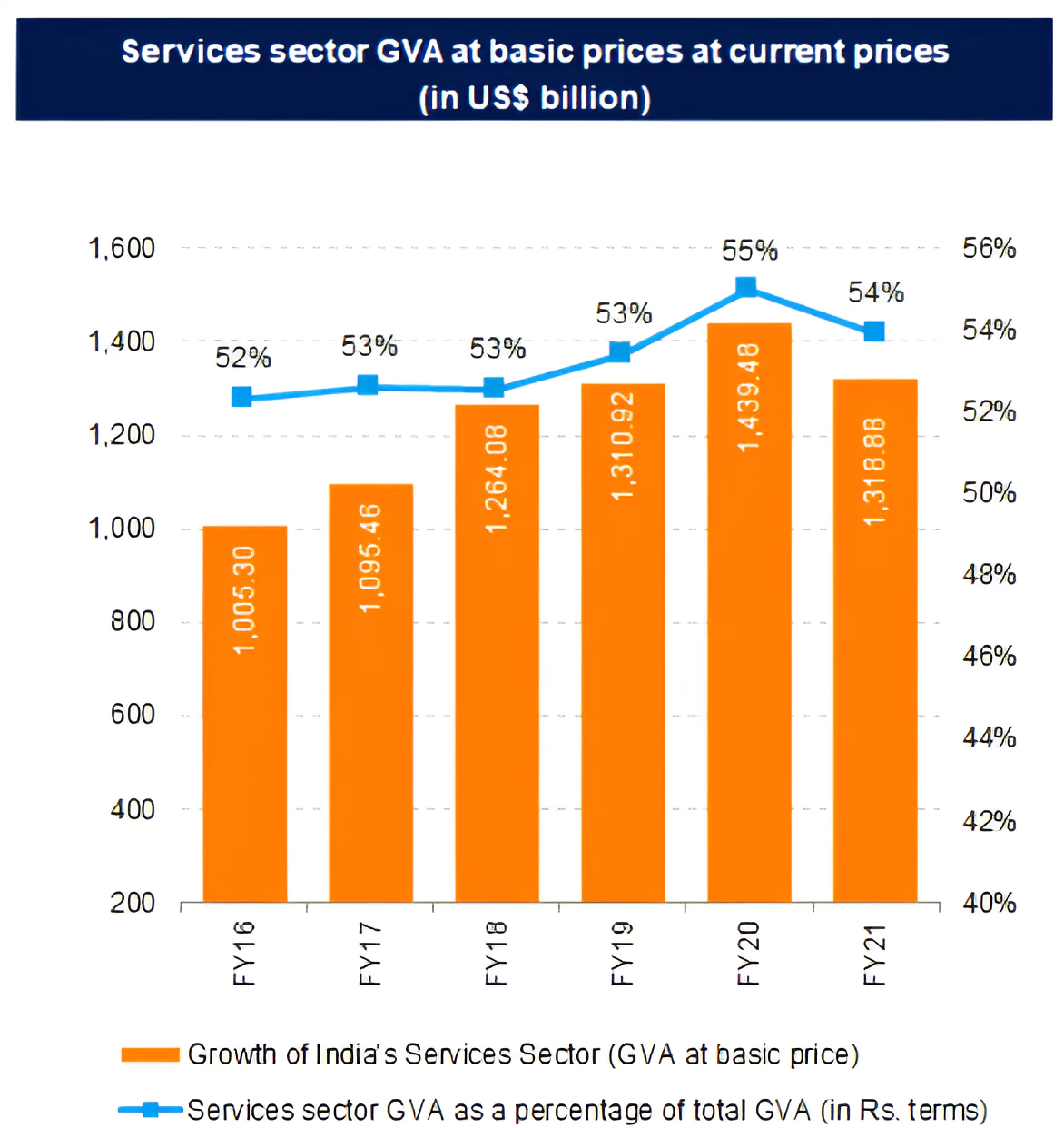 Contribution: The service sector has over 50% contribution to India’s GDP.
Contribution: The service sector has over 50% contribution to India’s GDP.
- The service sector has emerged as the highest employment generator with a 5-7% y-o-y growth in 2022.
- The share of the services sector accounted for 57% of the total Gross Value Added (GVA) in FY24 (April-September) as per advance estimates.
- As per data released by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), the services category ranked first in FDI inflows.
- India’s service exports stood at US$ 163.94 billion, whereas imports stood at US$ 88.89 billion in (April-September) 2023-24. The services trade surplus for 2023-24 (April-September) is expected to be US$ 75.05 billion.
-
Future Prospects of Service Sector in India:
- Upcoming sectors are expected to contribute to rapid expansion of services sector in India:
- By 2025, the healthcare industry is expected to reach US$ 372 billion.
- By 2025, India’s digital economy is estimated to reach US$ 1 trillion.
- By the end of 2023, India’s IT and business services sector is expected to reach US$ 14.3 billion with 8% growth.
- By 2035, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is expected to boost India’s annual growth rate by 1.3% .
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Reasons for Growth in Services Sector
- Structural Transformation: LPG Reforms offered more opportunities for the development of the services sector particularly in the field of Banking, Insurance, Telecommunication, Aviation, Transportation etc.
- Technological Advancements: Technical advancements have led to a shift in outsourcing, leading in the expansion of the service industry. Also, the development in the agriculture and industrial sector has increased the need for services such as transportation, storage and trade.
- Rise of Demand: There is high demand in the Indian service sector in foreign markets, rise in domestic population and also the necessity for basic services like hospitals, educational institutions, banking services, etc.
- Attractive Ecosystem: Various government policies such as Start-up India, Digital India Program, Ayushman Bharat, PM Kaushal Vikas Yojana have increased the potential for the sector in India.
- Low setup costs make this sector an attractive investment destination.
- India also has a reasonably well-developed financial market.
- Skilled Workforce: A large pool of skilled IT manpower has made India into a global outsourcing hub.
- Improved Productivity: Due to better technology and improved labor productivity there is an increase in output of manufacturing goods and agriculture with less labor.
- Global Technology Hub: India is the digital capabilities hub of the world, with the presence of about 75% of global digital talent.
- In the next five years, the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology is working to increase the contribution of the digital economy to 20% of GDP.
- The government is working to build cloud-based infrastructure for collaborative networks that can be used for the creation of innovative solutions by entrepreneurs and startups.
Some Developments in the Services Sector in India

- FDI: The Indian services sector was the largest recipient of FDI inflows worth US$ 106.70 billion between April 2000-September 2023.
- According to the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, the service sector received US$ 3.85 billion in FDI equity inflows in FY24* (April-September).
- Banking Sector: According to RBI’s Scheduled Banks’ Statement, deposits of all scheduled banks collectively surged by a whopping Rs.1.75 lakh crore as of December 1st, 2023.
- Telephone Industry: India’s telephone subscriber base stood at 1,179.21 million as of August 2023 and total broadband subscriber base stood at 876.53 million.
- Teledensity (the number of telephone connections for every 100 individuals) in India stood at 84.69%, as of August 2023.
- Startups: Since the launch of the Startup India initiative in 2016, DPIIT has recognized 98,119 entities as startups as of 30th April 2023.
- Healthcare Industry: It is growing at a Compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16% and the total public and private spending on healthcare is 4% of GDP. India’s healthcare industry is expected to grow to US$ 50 billion in size by 2025.
- The Indian healthcare industry is expected to shift to digitally enabled remote consultations via teleconsultation. The telemedicine market in India is expected to increase at a CAGR of 31% from 2020 to 2025.
- CAGR is the mean annual growth rate of an investment over a specified period of time longer than one year.
- The IT & Business Services Market: It will grow at a CAGR of 8.3% between 2021-26, reaching a US$ 20.5 billion valuation by the end of 2026.
Initiatives taken by the India to Promote Service Sector Growth
- Action Plan for Champion Sectors in Services: To give focused attention to 12 identified Champion Services Sectors.
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY): As of November 9, 2022, the number of bank accounts opened under PMJDY scheme reached 47.39 crore and deposits in Jan Dhan bank accounts totalled Rs. 1.76 lakh crore (US$ 21.59 billion).
- Production-linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme: In October 2021, the government launched a PLI scheme to boost manufacturing of telecom and networking products in India.
- Mahatma Gandhi National Fellowship (MGNF): In October 2021, the government launched phase II of MGNF to empower students and boost skill development.
- PM Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission: It was launched in October 2021 to strengthen the critical healthcare network across India in the next four to five years.
- 100% FDI: The FDI limit for insurance companies has been raised from 49% to 74% and 100% for insurance intermediates.
- Third phase of Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY): It was launched in January, 2021 tol focus on new-age and COVID-related skills.
- National Digital Health Mission (NDHM): It was launched in 2020 to provide a unique health ID to every Indian and revolutionize the healthcare industry by making it easily accessible to everyone in the country.
- Over the next 10 years, the National Digital Health Blueprint can unlock the incremental economic value of over US$ 200 billion for the healthcare industry in India.
- National Broadband Mission: The government of India has launched the National Broadband Mission to provide Broadband access to all villages by 2022.
- IGnITE Programme: It was launched in December 2020 to encourage high-quality training and technical education.
- ‘IGnITE’ aims to develop highly trained technicians based on the German Dual Vocational Educational Training (DVET) model. By 2024, this programme aims to upskill about 40,000 employees.
- Germany’s dual vocational education and training system is highly regarded worldwide for its emphasis on practical training and close collaboration between industry and educational institutions.
- To enhance India’s commercial services exports, share in the global services market from 3.3% and permit a multi-fold expansion in the GDP, the government is also making significant efforts in this direction.
- PM Gati Shakti: National Master Plan for multimodal connectivity infrastructure project.
- Bharatmala Project: To Improve connectivity in North East India.
- Start-up India: To catalyze Startup culture in India.
Significance of the Service Sector in India
- Economic Growth & Development: The service sector accounts for most of the country’s economic output, over 50% to India’s GDP.
- The services sector is not only the dominant sector in India’s GDP but has also attracted significant foreign investment, has contributed significantly to exports and has provided large-scale employment.
- Employment Generation: The service sector is a major source of employment in India. It provides jobs to about 30.7% of the Indian population.
- Foreign Exchange: Services like IT, business process outsourcing (BPO), and medical tourism have generated substantial foreign exchange earnings for India.
- Global Outsourcing Hub: India is a global outsourcing hub, particularly for IT, BPO, and knowledge-based services.
- Knowledge-Based Economy: India produces many highly skilled professionals, including software engineers, doctors, engineers, and business analysts.
- E-commerce and Retail Growth: These sub-sectors have experienced significant growth, driven by increasing consumer spending and digital transformation.
- Tourism and Cultural Exchange: The tourism and hospitality sector contributes to cultural exchange and the growth of India’s reputation as a global tourist destination.
Challenges Faced by the Services Sector in India
- Lack of Government Incentives: Many experts feel that the Government has not provided incentives to the services sector on the same lines as the manufacturing sector.
- Trade Restrictions: Services sector is hampered by restrictions placed by foreign governments like restrictions on movement of service professionals, domestic certification requirements for foreign service providers, tax on offshore income of Indian service firms etc. These restrictions limit the export potential of India’s Services Sector.
- As highlighted by the Surjit Bhalla Committee on Free Trade Agreements (FTAs), India has failed to capitalize on its strengths in the services sector to boost exports to FTA partner countries.
- Access to Finance: Many small services firms lack access to affordable finance that hampers access to technology, up-skilling of people, up-gradation of systems and processes that impacts their competitiveness.
- Complex Regulations: Complex and frequently changing regulations can create hurdles for growth in the service sector.
- Infrastructure Challenge: Inadequate infrastructure, such as transportation and logistics, can hinder the efficient delivery of services.
- Shortage of Skilled Labor: While India produces a large number of graduates and skilled professionals, there can be a disconnect between the skills possessed by the workforce and the demands of certain service sectors.
- Technology Advancements: While India has made significant progress in the IT and software services sector, many other service industries lag behind in adopting technology for efficiency and competitiveness.
- Data Privacy and Security: In the digital age, these concerns of data have become more pronounced.
Way Forward to Indian Services Sector
- Policy Interventions: The Services Sector in India requires structured policy interventions by the Government. The Government should launch a ‘Services from India’ initiative on the lines of Make in India.
- Government should consider greater tax incentives, and PLI-like schemes for the Services Sector to support an increase in services exports.
- Action on Priority Basis: The Services Sector needs to be accorded a greater priority in trade negotiations. Focus of India’s FTA has been on merchandise trade.
- Setting of Standards: India should push for setting standards for global data governance. There is a need to resolve data and privacy barriers.
- Comprehensive Roadmap: The Government should make a comprehensive roadmap for further diversification of the services sector. Sub-Sectors like Healthcare, Tourism, Banking/Financial Services, Telecommunication need to be supported for further expansion.
- Cultivating Soft-Skills: There is a need to impart such generic courses among peoples that can offer a holistic blend of technical proficiency, soft skills, and industry-specific knowledge essential for success in service-centric roles.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Conclusion
India is a unique emerging market in the globe due to its unique skills and competitive advantage created by knowledge-based services. The Indian services industry is supported by numerous government initiatives like smart Cities, clean India and digital India that is fostering an environment that is strengthening the services sector. The sector has the potential to open up a multi-trillion-dollar opportunity that might stimulate symbiotic growth for all nations.
Also Read: India Skills Report 2024: Key Highlights From The Report
![]() 2 May 2024
2 May 2024


 Contribution: The service sector has over 50% contribution to India’s GDP.
Contribution: The service sector has over 50% contribution to India’s GDP.

