Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), commonly known as drones, are increasingly used in military operations because they are seen as less threatening than fighter jets, but they come with both benefits and risks.
What Are UAVs?

- Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), commonly known as drones, are aircraft that operate without a human pilot on board.
- They can be controlled remotely by an operator or operate autonomously using pre-programmed flight paths and AI-based navigation systems.
Types of UAVs
- Based on Size:
- Micro and Nano UAVs: Small drones used for close-range surveillance (e.g., quadcopters).
- Tactical UAVs: Medium-sized drones for military reconnaissance and border patrol.
- Strategic/Combat UAVs: Large drones with long endurance and combat capabilities (e.g., MQ-9 Reaper, Bayraktar TB-2).
- Based on Function:
- Surveillance UAVs: Used for intelligence gathering and border security.
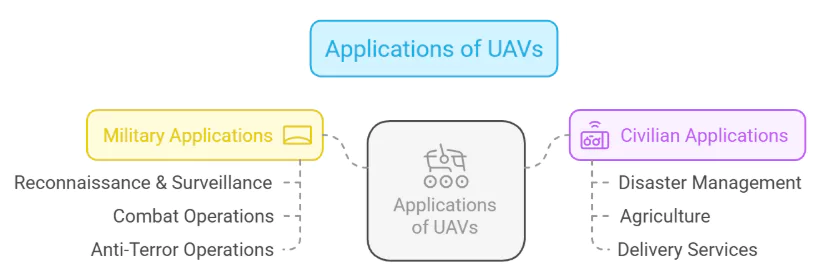
- Combat UAVs (UCAVs): Armed drones that carry missiles and bombs for military strikes.
- Logistics UAVs: Used to transport supplies, medicines, or weapons in remote areas.
- Commercial UAVs: Used for photography, agriculture, and delivery services.
- Based on Operational Range:
-
- Short-Range UAVs: Can fly within a few kilometers, used for local reconnaissance.
- Medium-Range UAVs: Operate within 100-300 km, commonly used for tactical missions.
- Long-Endurance UAVs: Can stay airborne for 24 hours or more, used for strategic operations.
Why Are UAVs Seen as Less of a Threat?
Several factors contribute to the perception that UAVs are less threatening than traditional fighter jets:
- Lower Lethality: Most UAVs are used for surveillance and reconnaissance rather than combat. Even armed UAVs are less capable than piloted fighter jets.
- No Human Risk: The absence of a human pilot reduces the stakes, as there is no risk of losing lives.
- Cost-Effective: UAVs are generally cheaper to produce and operate compared to manned aircraft. Losing a UAV is less financially burdensome than losing a fighter jet.
- Restrained Responses: When UAVs are shot down, the response from the affected country is often less severe compared to the downing of a piloted aircraft.
Recent Examples of UAV Incidents
- 2019 Iran-US Incident: Iran shot down an American surveillance drone over the Strait of Hormuz. Despite tensions, the U.S. did not retaliate militarily, highlighting the lower escalation risk associated with UAVs.
- 2023 Russia-US Incident: Russia downed an American MQ-9 Reaper UAV, but the incident did not lead to significant retaliation.
- These examples show that while UAVs can be used for high-risk missions, their loss often results in limited diplomatic or military consequences.
Risks of Using UAVs
- Encouraging Risk-Taking: The lower stakes associated with UAVs may encourage countries to take greater risks, such as infiltrating airspace or conducting surveillance in sensitive areas.
- Dual-Use Threat: Smaller UAVs can be used for illegal activities, such as transporting arms or drugs across borders, as seen in the case of Pakistan.
- Cost of Countermeasures: Using expensive missiles to shoot down cheap UAVs is not cost-effective. For example, India used a costly air-to-air missile to down a Pakistani UAV in 2019.
Challenges for India
- Border Security: Pakistan frequently uses small UAVs to transport arms and drugs across the border. India needs cost-effective ways to counter these threats without resorting to expensive missiles.
- Neighbouring UAV Deployments: Bangladesh’s deployment of Turkish Bayraktar TB-2 UAVs near the Indian border highlights the need for a strategic response to larger, more advanced drones.
- Escalation Management: India must develop protocols to address UAV incursions without escalating tensions, especially with neighbours like Pakistan and China.
Way forward for India
- Develop Cost-Effective Countermeasures: India should invest in affordable anti-drone technologies, such as jamming systems or drone interceptors.
- Enhance UAV Capabilities: India needs to expand its own UAV fleet for surveillance, reconnaissance, and combat roles.
- International Collaboration: Partnering with other nations to develop advanced UAV technologies and countermeasures can strengthen India’s position.
![]() 21 Mar 2025
21 Mar 2025



