The National Statistical Office (NSO) is considering using GST (Goods and Services Tax) data to estimate value addition in the upcoming GDP revision.
GDP Base Year Revision to 2020-21

- This would replace the MCA-21 database from the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, which is currently used for the Private Corporate Sector (PCS), accounting for 38% of GDP.
- Current and Proposed Base Year
- The current GDP base year is 2011-12.
- A revision is planned, proposing 2020-21 as the new base year.
- Most major datasets are ready, except for Census data.
About MCA-21 Database
- Background: The MCA-21 database was introduced during the last GDP revision (2011-12 base year) to improve the estimation of value addition in the Private Corporate Sector (PCS).
- Previous Methods:
- Annual Survey of Industries (ASI): Earlier, ASI was used to estimate value added by factories.
- RBI Sample: A small sample of large companies by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) was used to measure non-financial corporate output.
- Reason for the Shift:
- Limitations of ASI: ASI didn’t account for value added outside of factories within corporate entities.
- Inadequate RBI Sample: The RBI sample couldn’t capture the rapid growth in PCS.MCA-21 Benefits:
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
What is Base Year?
- It is the first year in the financial index.
- It provides a reference point for measuring changes in the economic trends and variables such as GDP, CPI, PPI.
- In addition to the above, it helps policy decision makers by providing insightful data on inflation, employment, and economic growth.
|
-
-
- The MCA-21 database is extensive.
- It provides up-to-date data on corporate annual returns and results.
- It offers a more accurate picture of corporate output.
Issues with MCA-21 Database
- Overestimation: The MCA-21 database led to overestimation of GDP growth rates, particularly in the manufacturing sector.
Impact of the 2011-12 Base Year Revision
- The 2011-12 base year led to:
- Smaller absolute GDP size but a faster growth rate.
- For 2013-14, industrial growth showed a sharp contrast: +5.4% growth in the new series versus -1.90% in the earlier series.
- This discrepancy raised concerns as other economic indicators, like bank credit growth and industrial capacity utilization, didn’t align with the revised GDP figures.
|
-
- Comparison of Estimates: Gross Value Added (GVA) and Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF) were compared between National Accounts Statistics (NAS) and Annual Survey of Industries (ASI) for the period 2012-13 to 2019-20.
- Findings:
- GVA: NAS reported an average annual growth rate of 6.2%, while ASI reported 3.2%.
- GFCF: NAS showed a growth rate of 4.5%, compared to 0.3% by ASI.
- Inconsistent Data: The data from MCA-21 did not align with other macroeconomic indicators, such as bank credit growth and industrial capacity utilization.
- Lack of Transparency: The government’s refusal to make the MCA-21 data available for independent scrutiny raised doubts about the accuracy of the estimates.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Issues with GST Data
- Unverified Data: GST data may be unverified and could contain errors or inconsistencies.
- Limited Access: The lack of public access to GST data limits its potential for independent analysis and validation.
- Methodological Challenges: Developing accurate estimation methods using GST data may be challenging, especially for specific industries and sectors.
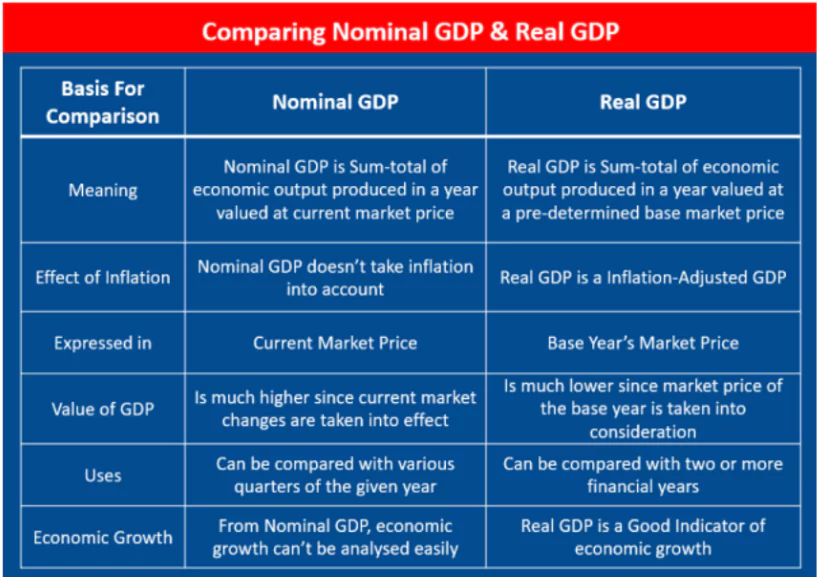
About GDP
- GDP is a monetary measure of the total market value of all final goods and services produced within a country over a specific period.
- Purpose:
- Used to assess the economic health of a country or region.
- Types of GDP:
- Nominal GDP
- Measures economic output using current prices without adjusting for inflation.
- Calculation: All goods and services are valued at their selling prices in the year they are produced.
- Usage:
- Useful for comparing output within the same year.
- Expressed in local currency or U.S. dollars at current exchange rates for international comparisons.
- Real GDP
- An inflation-adjusted measure of economic output, reflecting the actual quantity of goods and services produced.
- Real GDP is calculated using “constant” prices, removing the effect of inflation or price changes.
- Estimating Real GDP
- Base year is used to estimate real GDP and is updated every 5-10 years.
- The National Statistical Office (NSO) is responsible for revising the GDP base year to reflect changes in prices and economic output.
- Purpose:
- Allows for year-to-year comparisons by showing real growth or decline in production.
- Calculation:
- Uses a GDP price deflator to account for price changes between the current year and the base year.
- Nominal GDP is divided by the deflator to obtain real GDP.
|
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
![]() 23 Sep 2024
23 Sep 2024
