As India aims for its vision for a “developed India” by 2047, this article presents a comparison of economic growth story of India and China.
| Relevance for Prelims: Vision India@2047, Economic Indicators, and Growth Rate Dynamics: Insights From India, China.
Relevance for Mains: Relative economic growth of India and China. |
|---|
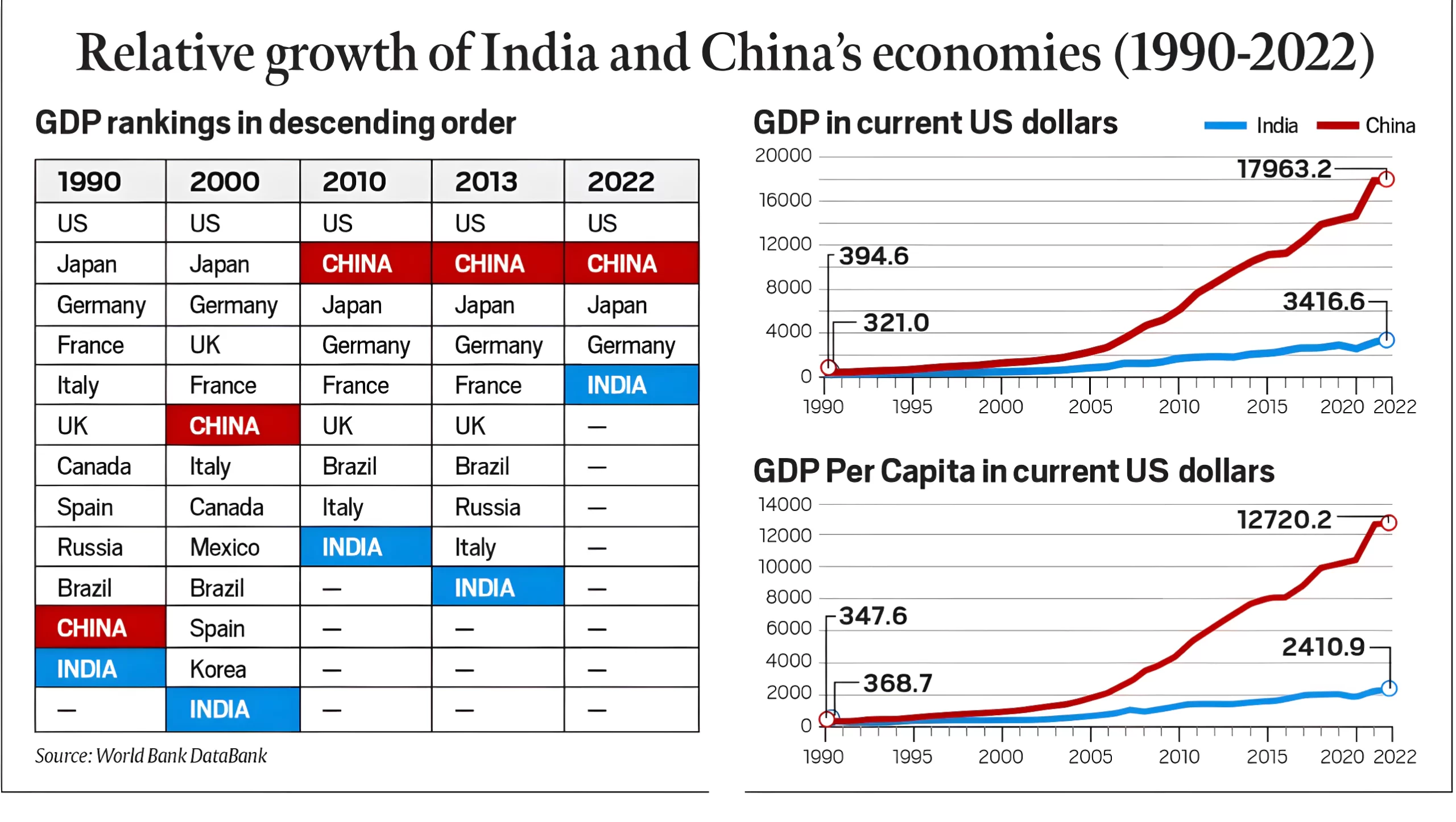
At current per capita GDP levels, India currently falls within the category of “lower-middle income” countries ($1,136 to $4,465) and China is classified as an “upper-middle income” country ($4,466 to $13,845). To reach the status of a developed country ($13,846 or higher), is a goal worth striving for.
| Prelims PYQ (2015):
A decrease in tax to GDP ratio of a country indicates which of the following? 1. Slowing economic growth rate 2. Less equitable distribution of national income Select the correct answer using the codes given below. (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 Ans: (d) |
|---|
| Mains Question: Despite India being one of the countries of Gondwanaland, its mining industry contributes much less to its Gross Domestic Products [GDP] in percentage. Discuss. [150 Words, 10 Marks] |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Vaikom Satyagraha has completed 100 years on March 30, 1924.
| Relevance for Prelims: Vaikom Satyagraha, Socio-Religious Reform Movement, and Non Cooperation Movement 1920.
Relevance for Mains: Caste system and social Hierarchy present during colonial times |
|---|
In November 1936, the Maharaja of Travancore signed the Temple Entry Proclamation which removed the age-old ban on the entry of marginalized castes into the temples of the state, was the great success of the Vaikom satyagraha.
| Prelims PYQ (2016):
The ‘Swadeshi’ and ‘Boycott’ were adopted as methods of struggle for the first time during the (a) Agitation against the Partition of Bengal (b) Home Rule Movement (c) Non-Cooperation Movement (d) Visit of the Simon Commission to India Ans: (a) |
|---|
| Mains Question: Discuss the pivotal roles of the Vaikom Satyagraha of 1924 and the Self Respect Movement in shaping modern Indian history. (10 M, 150 Words) |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, about 5,000 Indians are trapped in Cambodia with 250 people having been rescued, and the foreign ministry is working with Interpol to rescue the remaining individuals.
| Relevance for Prelims: Growing Cyber Crimes, China’s Belt And Road Initiative, and NCRB Data On Cyber Crime In India.
Relevance for Mains: Issues Related to Organised Crimes, and Cyber frauds. |
|---|
Common Fraud Techniques
|
|---|
While governments of other countries often remain helpless against these mafias, India should focus on creating a basic awareness campaign to protect people from fake job scams.
| Mains Question: Enumerate different types of cyber-crimes affecting individuals and organisations. What preventive measures should be taken? (10 Marks, 150 Words) |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA), 2002, is being scrutinized because it expanded beyond its primary focus on combating drug money laundering.
| Relevance for Prelims: Money Laundering, Enforcement Directorate (ED), Central Vigilance Commission (CVC), and The Authority Of ED And Usage Of PMLA.
Relevance for Mains: Issues in PMLA legislation, Money Laundering and Impact |
|---|
| Aspect | PMLA Cases | Normal Criminal Cases |
| Reverse Burden of Proof | In certain circumstances, the accused has to prove that alleged proceeds of crime were legally earned. | The burden of proof is always on the prosecution to prove the guilt of the accused. |
| Bail | Bail is an exception, jail is the rule under Section 45 of PMLA. Accused has to prove prima facie innocence to get bail, which is a tough condition. | Bail is the rule, jail is an exception. If prosecution fails to establish a prima facie case, bail can be granted. |
| Burden of Proof for Bail | Accused has to prove prima facie innocence to get bail, contrary to general principles where the burden of proof is on the prosecution. | Prosecution has to establish a prima facie case against the accused for denial of bail. |
| Property Attachment | Authorities can attach suspected proceeds of crime without trial or conviction under strict provisions. | Attachment of property usually happens after conviction or with more due process. |
| Recording of Statements | Statements recorded before the investigating officer can be used as evidence in court, which is not allowed in normal criminal trials. | Statements recorded by police are not admissible as evidence unless certain conditions are met. |
Denying bail takes away personal freedom, a fundamental right under Article 21 of our constitution. The power to deny bail is a significant responsibility for the courts, to be exercised with serious consideration for its impact on both the individual and society.
| Prelims PYQ (2021):
Which one of the following effects of creation of black money in India has been the main cause of worry to the Government of India? (a) Diversion of resources to the purchase of real estate and investment in luxury housing (b) Investment in unproductive activities and purchase of previous stones, jewellery, gold, etc. (c) Large donations to political parties and growth of regionalism (d) Loss of revenue to the State Exchequer due to tax evasion Ans: (d) |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Shifting Dynamics in West Asia: US Foreign Policy,...
FICCI’s Report on Illicit Trade in India
Spam Calls, Policy Initiatives, Regulatory Challen...
Suicides and Entrance Examinations, Prioritizing M...
India Must Avoid Confrontation with Five Eyes Inte...
Chief Justice’s Call for Transformation unde...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
