| Relevancy for Prelims: Indian Port Sector, Major Ports in India, Ancient Indian Ports, Special Economic Zones, Sagarmala scheme,
Relevancy for Mains: Indian Ports and Economic Development, Historical Significance of Indian Ports, Multifaceted Role of Ports, Government Reforms. |
|---|
Also read: MISSION SAGAR: Indian Ocean Diplomacy and India’s Strategic Outreach
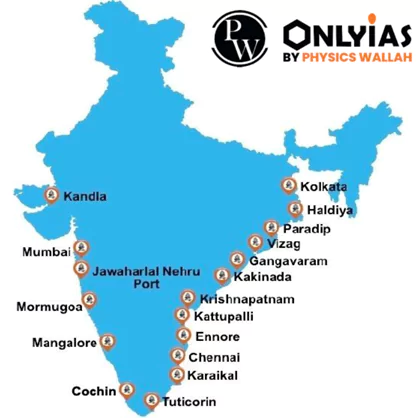
Indian ports, with their rich historical legacy and modern strategic importance, serve as vital catalysts for economic growth, global trade, and extensive employment opportunities. Thus, the Indian port sector has the potential to play an important role in India’s journey toward becoming a $5 trillion economy.
| Prelims Question (2022)
Which one of the following statements best describes the ‘Polar Code’? (a) It is the international code of safety for ships operating in polar waters. (b) It is the agreement of the countries around the North Pole regarding the demarcation of their territories in the polar region. (c) It is a set of norms to be followed by the countries whose scientists undertake research studies in the North Pole and South Pole. (d) It is a trade and security agreement of the member countries of the Arctic Council. Ans: (a) |
|---|
| Mains Question: Examine the future potential of ports in India. What are the challenges faced by the Indian port sector? (250 words, 15 Marks) |
|---|
| Relevancy for Prelims: Land Degradation and Desertification, Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS), and Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY).
Relevancy for Mains: UNCCD Reports on Land Degradation and Desrtification, Causes of Land Degradation and Desertification, Impacts of Land Degradation and Desertification, Government Measures to Combat Land Degradation and Desertification |
|---|

Also read: Climate Smart Agriculture (CSA)
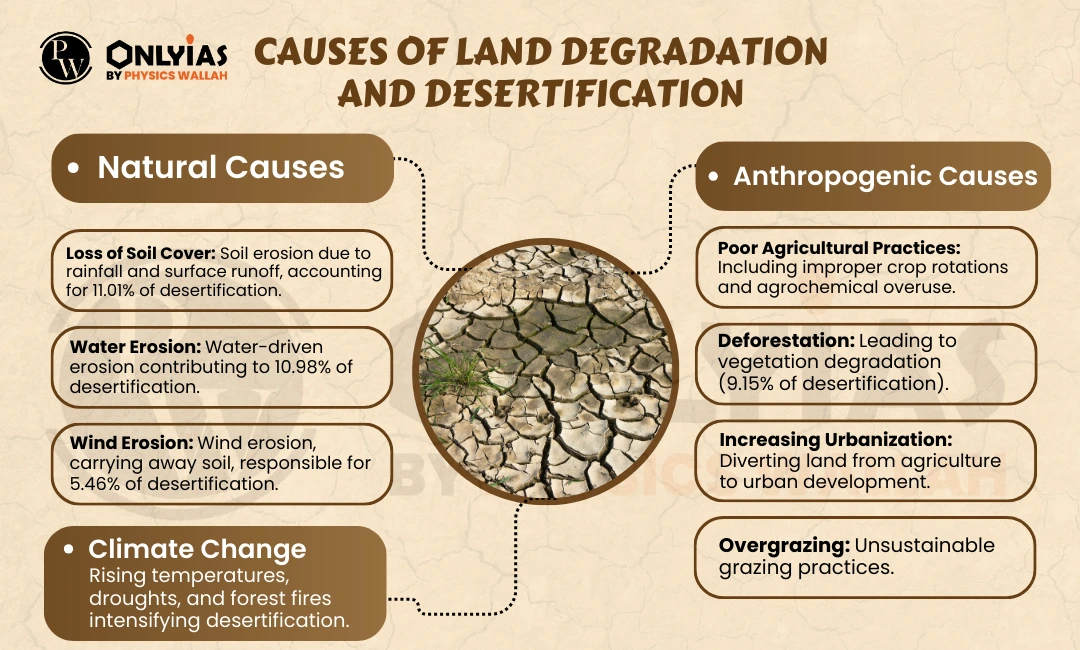
UNCCD’s Data Dashboard reveals a concerning reality for India, with the nation losing more than 30 million hectares of healthy land—highlighting a serious problem of land degradation and desertification that needs urgent attention and action.
| Prelims Question (2016)
What is/are the importance/ importances of the ‘United Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD)’? 1. It aims to promote effective action through innovative national programmes and supportive international partnerships 2. It has a special/particular focus on South Asia and North Africa regions, and its Secretariat facilitates the allocation of major portion of financial resources to these regions. 3. It is committed to bottom-up approach, encouraging the participation of local people in combating the desertification. Select the correct answer using the code given below. (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Ans: (c) |
|---|
| Relevancy for Prelims: Birth Rate in Italy, Fertility Rate, Dependency Ratio, and Population Replacement Rate.
Relevancy for Mains: Declining Birth Rate in Italy, and Aging Population, Demographic Dividend, and Migration. |
|---|
Italy’s Aging Population
|
|---|
In 2022, there were 147,000 more departures than arrivals due to following reasons:
Challenges in Utilizing Potential Demographic Dividend
|
Also read: India-Italy Bilateral Relations
The alarming decline in the birth rate in Italy necessitates urgent and comprehensive measures to address demographic challenges and ensure a sustainable future for the country.
| Prelims Question (2019)
In the context of anycountry, which one of the following would be considered as part of its social capital? (a) The proportion of literates in the population (b) The stock of its buildings, other infrastructure and machines (c) The size of population in the working are group (d) The level of mutual trust and harmony in the society Ans: (d) |
|---|
| Mains Question: Discuss the concept of depopulation, a recent focal point of discussions. What has been India’s position within global population trends? (250 words, 15 Marks) |
|---|
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
