| Relevancy for Mains: Cult Of Operational Superiority, Importance of Political Relations between Countries, Role of Non-state Actors in Creating Challenges to Internal Security. |
|---|
Also Read: Hamas Attack on Israel: Lessons For India to Learn
Also Read: National Security Strategy
The Israel-Hamas conflict highlights the pitfalls of relying solely on military superiority without addressing the underlying political dimensions, emphasizing the need for India to adopt a comprehensive approach involving both military and political strategies in handling tensions with its neighbors, particularly Pakistan.
| Mains Question: Intelligence agencies are the backbone of a nation. What lessons Indian Intelligence Agencies need to learn from the recent attack of Hamas on Israel? (150 words, 10 Marks) |
|---|
| Relevancy for Prelims: National Security Strategy
Relevancy for Mains: National Security Strategy, its need and significance. |
|---|
Also Read: Chanakya Defence Dialogue 2023
The formulation of India’s National Security Strategy is crucial for addressing external and internal threats, though challenges of transparency and differing views need careful consideration, emphasizing the importance of a well-coordinated, comprehensive approach for safeguarding the nation’s interests.
| Prelims Question (2023)
With reference to Home Guards, consider the following statements: 1. Home Guards are raised under the Home Guards act and Rules of the Central Government. 2. The role of the Home Guards is to serve as an auxiliary force to the police in maintenance of internal security. 3. To prevent infiltration on the international border/coastal areas, the Border Wing Home Guards Battalions have been raised in some States. How Many of the above statements are correct? (a) Only one (b) Only two (c) All three (d) None Ans: (b) |
|---|
| Relevancy for Prelims: Net Neutrality, Regulation Code For OTT Platforms in India, and Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI).
Relevancy for Mains: Net Neutrality, arising challenges between OTTs and Telcos, and steps that need to be taken to address the issue. |
|---|
Also Read: OTT Regulation in India
It is imperative for all stakeholders to uphold the principles of net neutrality to foster a conducive environment for innovation, competition, and consumer welfare, especially in countries such as India where the Internet is going to be the carrier of all Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI).
| Mains Question: Discuss the issues related to OTT regulation in India. What are the salient features of Draft Indian Telecommunication Bill 2022? (250 words, 15 Marks) |
|---|
| Relevancy for Prelims: Deepfakes.
Relevancy for Mains: Deepfake, arising challenges and steps that need to be taken to address the issue. |
|---|
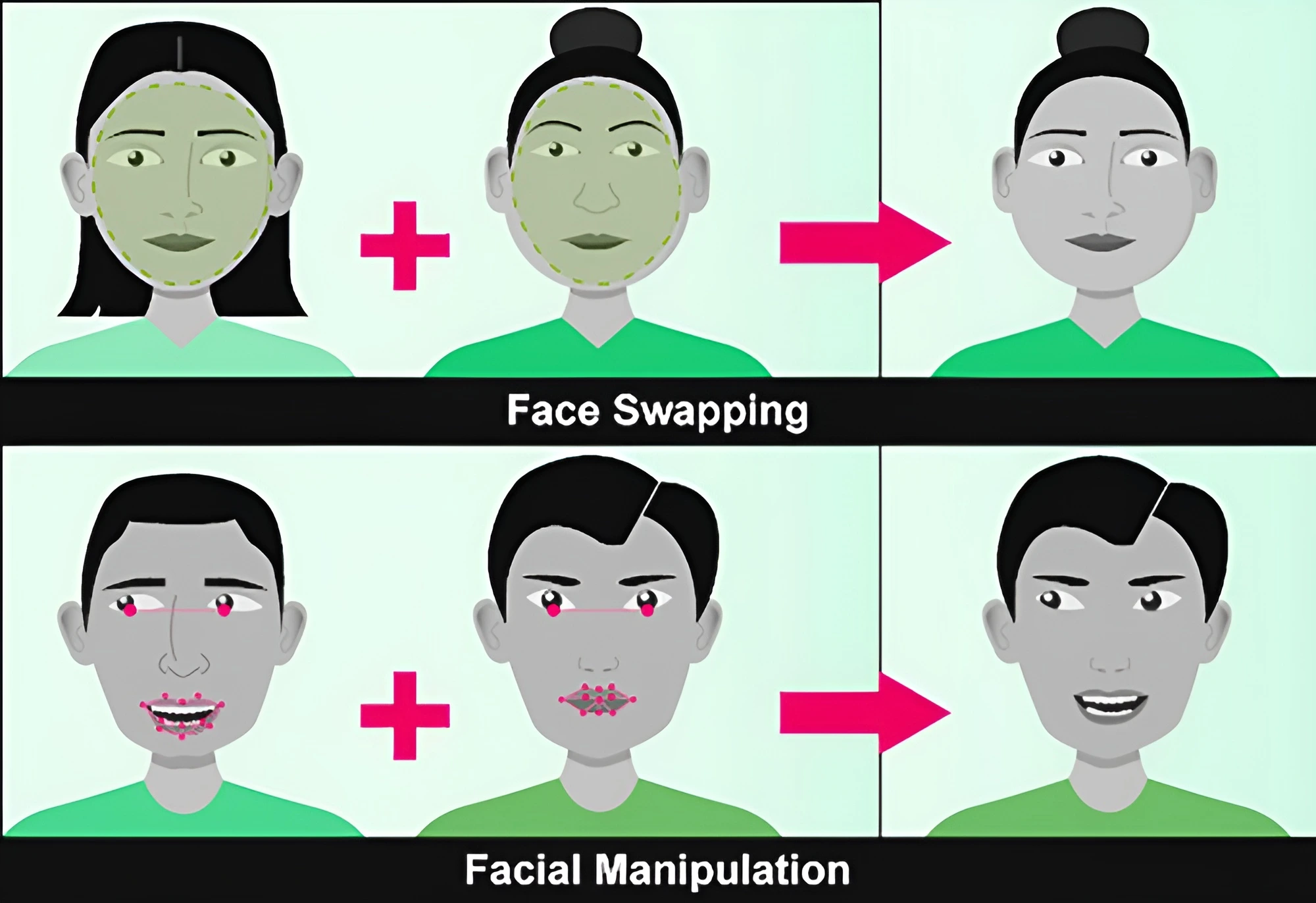
Also Read: IT Rules under scrutiny: Due to Deepfake Threats
There is a need to address the ethical, legal, and technological aspects of deepfakes in a collaboration of citizens, service providers, governments and international organizations to provide a sense of digital security to the society.
| Prelims Question (2017)
In India, it is legally mandatory for which of the following to report on cyber security incidents? 1. Service providers 2. Data centres 3. Body corporate Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1 only (b) 1 and 2 only (c) 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Ans: (d) |
|---|
| Mains Question: Examine the concept of Deepfakes, and the potential risks associated with their use. What are the solutions to mitigate the threats posed by this technology. (250 words, 15 Marks) |
|---|
Scheme for Care and Support to Victims under POCSO...
Addressing the Fatal Consequences of Illegal Hoard...
World Bee Day 2024 and Honey Production in India
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
