Context:
This editorial is based on the news “How to tackle malnutrition effectively” which was published in the Hindu. This article highlights the two-way relationship between nutritional deficiencies and certain disorders and the challenges in addressing malnutrition in India.
Malnutrition in India and Iron Deficiency
- Causes: One of the many causes is iron deficiency.
- Shift of traditional dietary patterns, as from seasonal and varied foods to processed and sugar-laden alternatives, which are calorically dense but nutritionally deficient.
- Inter-relation between Deficiencies and Disorders: There is a two-way relationship between nutritional deficiencies and certain disorders.
- Deficiencies leading to Disorders: Consistent intake of food lacking in essential micronutrients can lead to iron deficiency anaemia and Vitamin A, and zinc deficiency, and impair immunity.
- Disorders leading to Deficiencies: Conditions such as celiac disease and infections like h. pylori or worm infestations can disturb the digestive system, leading to nutrient deficiencies.
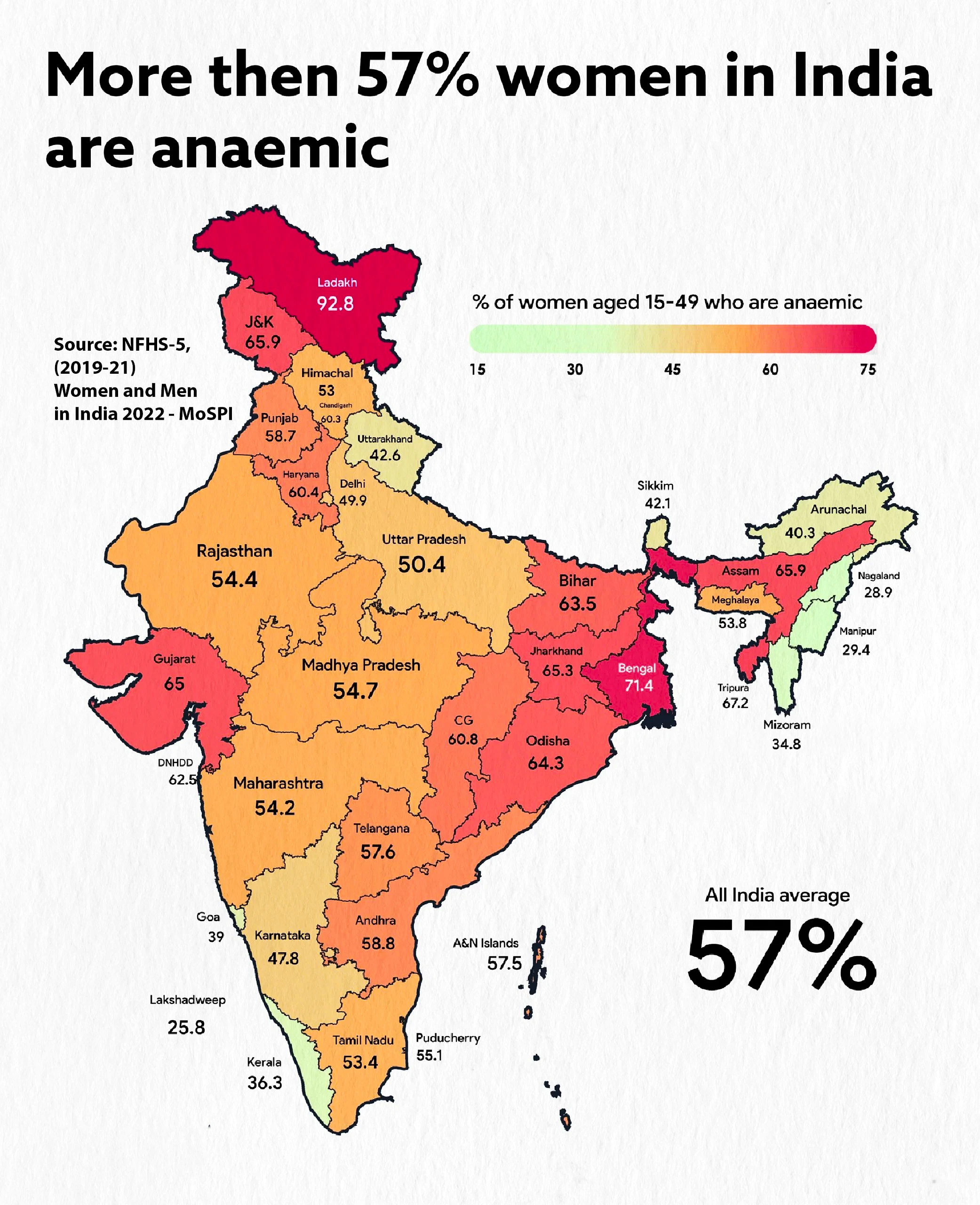
Map: Iron Deficiency Anaemia in India
Challenges Associated With Malnutrition in India
- Malnutrition primarily impacts children and women.
- Intergenerational Impacts: Malnutrition caused by micronutrient deficiency has intergenerational impacts- anaemic mothers are known to give birth to anaemic babies.
- South Asia’s Burden: As per FAO data, about 46% of South Asia’s population lacks access to an affordable balanced diet.
- India’s Concern: As per the State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World, 2023, around 74% of India’s population could not afford a healthy diet, and 39% fell short of a nutrient-adequate one.
Steps Taken by Government to Address Malnutrition in India
- Anaemia Mukt Bharat (AMB): It involves administering iron and folic acid (IFA) tablets and other prophylactic measures.
- The Mid-day Meal Scheme: It is the Scheme for school children.
- Concern: There are challenges of effective implementation of both Anaemia Mukt Bharat and Mid-day Meal Scheme.
- Food Fortification: Recent government interventions such as Large-Scale Food Fortification (LSFF) are timely. Food fortification may not be the ideal remedy. However, it is a vital first step.
- Adoption: Earlier India adopted iodised salt under the National Iodine Deficiency Disorders Control Programme in 1992. Now, India’s food fortification programme includes adding micronutrients to staples such as wheat flour, rice, edible oils, and salt.
- Concern: Many countries adopted universal food fortification several years ago. India lags behind here.
Way Forward to to Address Malnutrition in India
- Need of a Balanced Diet: Focusing on the affordability and accessibility of a balanced diet.
- Community Awareness: Multiple awareness strategies can be adopted to foster greater awareness, including utilising communication channels such as community radio, videos and door-to-door outreach.
- Dispel Misconceptions and Build Trust: Messages in vernacular languages ensure that the information is easily understood and also helps dispel misconceptions and build trust.
- Aware and Responsible Citizens: People need to recognise that reducing consumption of processed foods is a crucial step towards ensuring better health outcomes.
- Use of Large-Scale Food Fortification (LSFF): LSFF, when aligned with micronutrient supplementation programmes, diet diversity promotion and measures to induce behavioural change has immense potential to improve the efficacy of existing initiatives.
- Awareness Campaigns for Fortified Foods: Awareness is critical to the acceptance of fortified foods among the targeted beneficiaries.
- Addressing Concerns about Fortified Foods: Addressing concerns of misgiving such as appearance and texture of such fortified foods requires an intensive information, education and communication (IEC) campaign.
Conclusion
The burden of malnutrition in India is complex and needs to be addressed through multiple interventions. It requires not just adoption of healthier dietary practices at the individual and community levels but also strategies by the state such as LSFF.
Also Read: 74.1% Of Indians Unable To Afford A Healthy Diet
![]() 30 Jan 2024
30 Jan 2024

