Context:
| Relevancy for Prelims: Climate-Smart Agriculture.
Relevancy for Mains: Climate Smart Agriculture and its Significance for India and the World. |
Climate Change Impacts on Agriculture and Food Supply
- Impact of Climate Change: Heat waves, flash floods, droughts, and cyclones, are negatively influencing lives and livelihoods.
- Contributing Factors to Food Insecurity: The demand for food is increasing due to population expansion and dietary changes.
- Challenges in Agriculture: As a result of climate change, traditional farming practices are becoming less productive, hence becoming concerns for farmers.
- Future Food Demand: The need for agricultural production to rise by 60% by 2050 in order to fulfill food demand.
- Holistic Strategy for Climate Change: Climate Smart Agriculture emerges as an imperative component for a comprehensive approach to combat the challenges posed by climate change.
What is Climate Smart Agriculture (CSA)?
- A Sustainable Approach: As per the Food and Agriculture Organization (2019), Climate Smart Agriculture is an approach to transforming food and agriculture systems to support sustainable development and safeguard food security under climate change.
- Climate Smart Agriculture Objectives: CSA comprises three pillars or objectives:
- Sustainably increase agricultural productivity and incomes,
- Adapt and build resilience to climate change,
- Reduce/remove Greenhouse gas emissions, where possible.

- Dimensions: CSA includes water-smart, weather-smart, energy-smart and carbon-smart practices.
- A Step towards Sustainable Development Goals: The United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals aim to end hunger and enhance environmental management and CSA’s foundation is in achieving these goals through sustainable agriculture and rural development.
- Examples: Improvements in agroforestry, sustainable water management, and precision agriculture.
What is the significance of Climate Smart Agriculture (CSA)?
- A Holistic Framework: Climate Smart Agriculture (CSA) improves productivity, deals with land degradation and improves soil health.
- Community-Supported Agriculture Efforts: These efforts are made to create a resilient and environmentally friendly agricultural system.
- Collaborative Efforts: Various public and private sector entities such as farmer-producer organizations and NGOs are also working towards the adoption of CSA.
- Lessen Disruptive Effects of Climate Change: CSA promotes crop diversification, increases water efficiency, and integrates drought-resistant crop types.
- Profit with Sustainability: Climate Smart Agriculture has the ability to increase agricultural output (hence increasing profit for farmers) while maintaining ecological stability, which is essential for long-term food security and sustainable resource usage.
- Biodiversity Conservation: CSA’s ecosystem-based approach and different crop varieties help cropland and wild regions coexist together and also mitigate the effects of habitat degradation.
- Climate Smart Agriculture implementation is crucial for lowering GHG emissions and protecting biodiversity.
- Flexibility: CSA is more of a flexible concept with a wide range of potential applications.
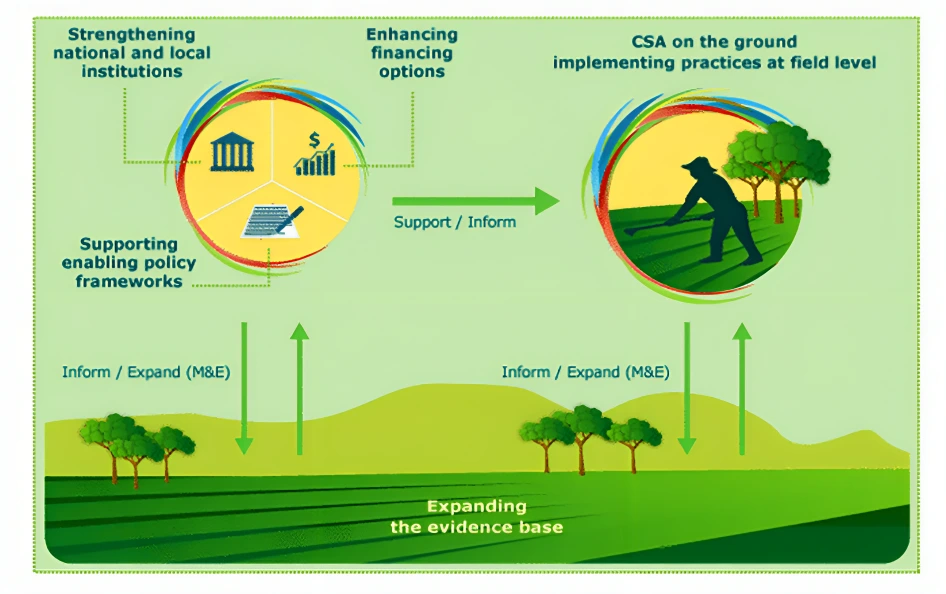
Why is there a need for Climate Smart Agriculture in India?
- Facing the Challenge of Climate Change: In India, crop yield decline owing to climate change (between 2010 and 2039) could be as high as 9%. Hence, a radical agricultural reform is a must.
- Empowering Small and Marginal Farmers: The majority of Indian farmers are small or marginal. Therefore, Climate Smart Agriculture can play a significant role in helping them increase their profits.
- Unique Juncture: The intersection of climate vulnerability and agricultural importance places India at a unique juncture where CSA adoption is essential.
- Government Initiatives for Climate Smart Agriculture (CSA):
- The National Adaptation Fund for Climate Change, National Innovation on Climate Resilient Agriculture, Soil Health Mission, Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana, Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana, Biotech-KISAN, and Climate Smart Village.
Also Read: World Food India 2023
Conclusion:
Climate Smart Agriculture (CSA) has the potential to assure food security, empower farmers, and protect our delicate ecosystems by merging innovation, resilience, and sustainability. To achieve its full potential, investment in capacity-building programmes and providing practical CSA tools and knowledge is essential.
| Prelims Question (2017)
Which of the following statements can help in water conservation in agriculture?
1. Reduced or zero tillage of the land
2. Applying gypsum before irrigating the field
3. Allowing crop residue to remain in the field
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c) |
![]() 25 Nov 2023
25 Nov 2023


