The theme for International Fatty Liver Day this year, an awareness initiative observed annually in June, is ‘Act Now, Screen Today‘.
Tackling the Fatty Liver Disease Epidemic
This theme resonates more urgently today than ever before. Liver diseases were predominantly associated with excessive alcohol use and this remains an important cause of advanced chronic liver disease.
- However, in recent years, we are seeing the emergence of a silently growing threat to liver health, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- As our understanding of this condition has evolved, we now know that fatty liver is closely linked to metabolic health, cardiac health, and a risk for developing cancers.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Growing Burden
The trends in fatty liver disease prevalence are alarming.
- MASH (Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis), a progressive form that causes liver inflammation and scarring, is expected to become the most common cause of chronic liver disease and the leading indication for liver transplantation.
- The global prevalence of MASLD is estimated at 25-30%.
- In 2022, a meta-analysis revealed that in India, among adults, the pooled prevalence of fatty liver was 38.6%, while among obese children, it was around 36%.
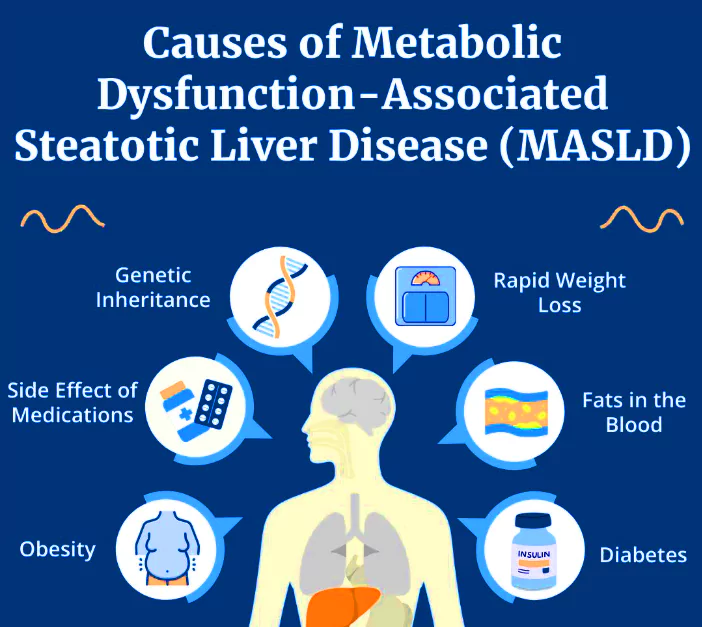
- There is a close link between fatty liver disease and metabolic syndrome, including obesity, diabetes, high blood pressure, and abnormal cholesterol levels.
- Individuals with these conditions have high MASLD prevalence rates:
- 55.5%-59.7% for diabetes.
- 64.6%-95% for obesity.
- 73% for severe metabolic syndrome.
- Consuming excessive carbohydrates, especially refined carbs and sugars, worsens these conditions by causing metabolic problems.
- When the body has too much glucose, it increases insulin production to help cells absorb the glucose.
- However, constantly eating too many carbs causes persistently high insulin levels, leading to insulin resistance, where cells become less responsive to insulin.
- Insulin resistance disrupts normal metabolism and promotes the conversion of excess glucose into fatty acids, which are then stored in the liver. The liver cells fill up with fat, leading to fatty liver.
- Over time, this continuous damage affects the liver’s ability to function properly, progressing from simple fatty liver to more severe conditions like such as steatohepatitis and cirrhosis, which are hallmarks of MASLD, and may require a liver transplant.
- Despite this growing burden of fatty liver disease, it often goes undetected as there is usually no warning or symptom in the early stages.
- Diagnosis is usually made at an advanced stage, often when significant liver damage has already occurred.
- The key to early diagnosis is simple – a comprehensive health screening that includes a thorough history, physical examination, blood tests, and an ultrasound of the abdomen.
- Physical examination will include height, weight, body mass index (BMI), abdominal girth, and waist-to-hip ratio to assess visceral fat, which is an important marker of metabolic health.
Check Out UPSC Modules From PW Store
Conclusion
Tackling fatty liver disease urgently requires early diagnosis through comprehensive health screenings and lifestyle changes to address metabolic syndrome, improving liver and overall metabolic health.
![]() 13 Jun 2024
13 Jun 2024


