Context:
Late last month, the Indian Prime Minister launched ‘Urea Gold’ fertilizer, developed by Rashtriya Chemicals and Fertilizers Ltd (RCF) with an aim to address soil deficiencies, improve nitrogen use efficiency (NUE), and reduce fertilizer consumption.
Current Status in India:
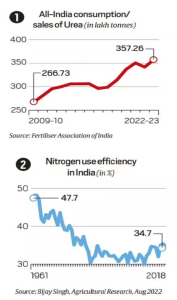
- Widely Used: Consumption of Urea is increased from 26.7 mt to 35.7 mt (2009-10 to 2022-23).
- Facing Challenges:
- Rising imports
- Low NUE (only 35% utilized)
- Increased fertilization for the same yield
About Urea Gold:
- Fortified Urea: Urea Gold is urea fortified with Sulphur (S).
- Composition: Containing 37% Nitrogen (N) and 17% Sulphur.
Significance of Urea Gold:
- Delivering Sulphur Along with Nitrogen:
- Indian soils lack sulphur, crucial for oilseeds and pulses.
- Oilseeds and pulses require sulphur for optimal growth and yield.
- Enhancing Nitrogen Use Efficiency (NUE):
- Coating urea with sulphur leads to gradual nitrogen release.
- Prolongs urea action, keeping plants greener for longer.
- Farmers can reduce fertilizer application frequency.
- Extended greener period enables reduced urea use for paddy or wheat.
About Fertilizer:
- Nutrient Provider for Growth: It is defined as any organic or inorganic substance, natural or artificial supplying one or more of the chemical elements/nutrients required for plant growth.
- Understanding Fertilizer Numbers:
- Nitrogen (N): For plant color and growth
- Phosphorus (P): For fruit & flowers
- Potassium (K): For strong roots
- Required Composition for N:P:K is 4:2:1
- Types of Nutrients:
- Primary (Macro) Nutrients: Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), and Potassium (K), Calcium (Ca), Magnesium (Mg), Sulphur (S)
- Secondary (Micro) Nutrients: Boron (B), Chlorine (CI), Copper (Cu), Iron (Fe), Zinc (Zn), etc.
|
Fortification as a Solution:
- Micronutrient Coating for Enhanced Efficiency:
- Coating urea/DAP with secondary nutrients (Sulphur, Calcium, Magnesium) and micronutrients (Zinc, Boron, etc.).
- Improves nutrient use efficiency and controlled release.
- Example: Yara’s ‘Procote’ technology coats fertilizers with micronutrients.
- Benefits of Fortification:
- Yara’s field trials: Zincated urea increases paddy yields, sulphur-coated urea boosts wheat yields and nitrogen efficiency.
- Example: Zincated urea leads to increased paddy yields from 24-25 to 26-27 quintals per acre.
The Path Ahead:
- Factory-Level Coating:
- Coating should occur at the factory for uniform distribution of micronutrients.
- Farmers saved from mixing hassles.
- Free Maximum Retail Prices (MRPs) for Coated Fertilizers:
- Government can remove MRPs for coated fertilizers.
- Coated fertilizers should not have an excessive premium over regular fertilizers.
- Affordability at the ground level with adequate quality is a need of the hour. Government can achieve desired results by inclusion of the local level participation and by raising awareness.
News Source: The Indian Express
![]() 14 Aug 2023
14 Aug 2023
