Context:
- This article is based on an Editorial “The G-20’s screen over ‘mazdoors’, their rights” which was published in the Hindu. Trade unions are concerned over India’s missed opportunity to protect the rights of workers and ensure their welfare. This comes after a diplomatic victory for India in the G20 Summit and the G-20’s Labour 20 (L20), a coalition of G20 leaders concerned about labour.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Migrant Workers, Forced Labour, C29, Kafala System and Sustainable Development Goals, SDG- 1, ILO, G20 Summit 2023.
Relevancy for Mains: Forced Labour and associated concerns & challenges and need to address issues for the protection and betterment of vulnerable sections. |
Forced Labour and Modern Slavery Statistics: A Critical Analysis of Workers’ Rights
- Forced Labour: As per International Labour Organization, forced or compulsory labour is all work or service which is exacted from any person under the threat of a penalty and for which the person has not offered himself or herself voluntarily.
- C29 Labour Convention: India has signed and ratified the ILO’s Forced Labour Convention known as C29.
- Indicators of Forced Labour: Restrictions on workers’ freedom of movement, withholding of wages or identity documents, physical or sexual violence, threats and intimidation or fraudulent debt from which labour cannot escape.
- Modern-day Slavery in G-20 countries: As per Walk Free Foundation, there are an estimated 27 million people trapped in modern-day slavery in G-20 countries, of whom 11 million are in India.
- Kafala System: An exploitative labour system of the Arab Gulf countries, which ties migrant workers to their employers.
- This system makes it difficult for migrant workers to leave their jobs or change employers, and it increases the risk of forced labour and modern-day slavery.
Also read: International Labour Organisation (ILO)
A Closer Look at Indian Workers Abroad
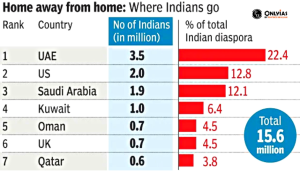
- Largest Migrant-Sending Country: India is the world’s largest migrant-sending country, with approximately 13 million workers abroad. Saudi Arabia (G-20 member) hosts 2.5 million Indian workers. Oman and the United Arab Emirates have nearly 8,00,000 and 3.5 million Indian labour respectively.
- Exploitation in the Arab Gulf: Of these, approximately nine million are working in exploitative conditions in the Arab Gulf.
- Exploitation in India: In India itself, workers in a number of industries, such as textiles, brick kilns, stone cutting, plantations, etc., face forced labour and modern-day slavery.
- In India, there are 530 million labours, of whom 430 million are in the informal sector, who are prone to different forms of exploitation, especially forced labour.
- Labour Laws: The four codes consolidated a complex web of 29 central labour laws.
- These are the Code on Wages, 2019; the Industrial Relations Code, 2020; the Occupational Safety, Health and Working Conditions Code, 2020; and the Code on Social Security, 2020.
A Call for Government Action on Migrant Workers’ Rights
- Ensure Welfare: Government need to ensure the portable insurance schemes, job creation, decent working conditions, equal pay, gender equality, the elimination of forced labour and child labour, an end to modern-day slavery, and the protection of their rights and the welfare of their families.
- Need to Counter Exploitation: Addressing forced labour and modern day slavery is important for India because the exploitation of workers would increase inequality, cause social injustice and threaten democracy.
- Conflict Resolution in Public Participation: The government should resolve the issue by talking to the trade unions, civil societies, and labour, who face a lack of decent working conditions.
- Achieving Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) Targets: If we fail to address the situation of labour, we will not be able to achieve SDG 1 (poverty eradication).
Conclusion
In the pursuit of global cooperation, India’s missed opportunity at the G20 Delhi Summit 2023 to safeguard their Overseas Workers’ rights. It is imperative for India to reassess its strategies, ensuring the protection of vulnerable labours, combating forced labour, and upholding international conventions. However, all UN countries should have a universal labour guarantee “labour rights without borders” that protects the fundamental rights of labour’, an adequate living wage, limits on hours of work and safe and healthy workplaces everywhere.
| Attempt the PY Prelims Question:
Q. In which one of the following groups are all the four countries members of G20? (2020)
(a) Argentina, Mexico, South Africa and Turkey
(b) Australia, Canada, Malaysia and New Zealand
(c) Brazil, Iran, Saudi Arabia and Vietnam
(d) Indonesia, Japan, Singapore and South Korea
Ans: (a)
Attempt the Mains Question: Explain how forced labour and modern day slavery would increase inequality, unstable social justice and threaten democracy. (150 Words, 10 Marks) |
![]() 29 Sep 2023
29 Sep 2023
