Context:
| Relevancy for Prelims: Green Revolution, Natural Farming and MS Swaminathan, Norman Borlaug, Minimum Support Price (MSP), etc.
Relevancy for Mains: Green Revolution, its significance and challenges and contribution of MS Swaminathan in agriculture, economy and India’s growth. |
What was the contribution of MS Swaminathan in the Green Revolution?
- Development of High Yielding Varieties of Seeds: During the 1960s, Swaminathan collaborated with fellow scientist Norman Borlaug and others to develop high-yielding varieties of wheat and rice.
- Made India Self-Sufficient: His efforts helped the country to double the total crop yield of wheat from 12 million tons to 23 million tons in four crop seasons and ended our dependence on grain imports.
What is Green Revolution?
Green Revolution refers to the new agricultural technology developed during the 1950s and 1960s by a team of agricultural experts at the International Centre for Maize and Wheat Improvement in Mexico and at the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) in the Philippines.
- Its Main Focus Areas:
- Farm Mechanization by substituting the use of cattle with modern tractors and other machinery.
- Use of hybrid varieties of seeds for better yield.
- Irrigation using the new dams constructed post-independence for better irrigation.
What were the success of the Green Revolution?
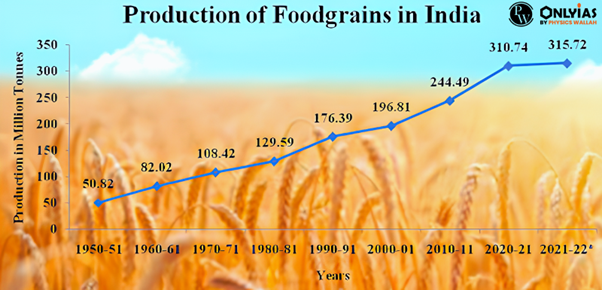
- Self-Reliant: With the help of this technology, India has achieved self-reliance in the production of food grains in the last several decades and is inching towards self-reliance in pulse production.
- Current Position: Today, India is the world’s largest sugar-producing country and holds the second position in rice production only after China. India is also the second largest producer of wheat with a share of around 14.14 percent of the world’s total production in 2020.
Also read: Sugarcane Production In India
Positive Impacts of the Green Revolution
- Increase in production and productivity of food grains
- Increase in farmer’s income
- Rural development
- Reduction in poverty due to increased income for farmers and agricultural labor.
Negative Impacts Of the Green Revolution
- Environmental Challenges:
- Decline in Soil Fertility due to the overuse of chemical fertilizers and pesticides.
- Depletion of Groundwater Resources due to significant increase in water consumption for irrigation.
- Reduction of Biodiversity and Ecosystem due to its focus on a few high-yielding varieties of crops, especially monocropping of wheat and rice.
- Economy challenges
- Debt trap due to the high cost of inputs such as seeds, fertilizers, and pesticides.
- High production costs as the Green Revolution has made agriculture more capital-intensive.
- Regional disparities as benefits mainly concentrated in Punjab, Haryana and Western UP regions.
- Rise in Inequality as small and marginal farmers have not been able to compete with large farmers who have access to more resources.
- Social Challenges:
- Health: The overuse of chemical fertilizers and pesticides has led to health problems for farmers and consumers.
- Farmers’ suicide: The debt burden and other challenges faced by farmers have led to a high rate of suicide in many areas.
- Drug abuse in Punjab: Many farmers turned to drugs to cope with the stress and challenges of modern agriculture.
ALSO READ: POVERTY AND DEVELOPMENT ISSUES
What are the current challenges of the Green Revolution?
- Shrinking Land holdings: At present, the per capita available land is only about 0.10 hectares. This is much below the world average of about 4.50 hectares.
- Water Scarcity: India uses a little over 90 percent of water resources for cultivation.
- Minimum Support Price (MSP): A survey by the government showed that less than 6%, or over nine crore agricultural households, are the direct beneficiaries. Further, only 19% of farmer families sold paddy under MSP, whereas only 9.7% of wheat farmers benefited from MSP.
- Climate Change: Agriculture in India is highly vulnerable to climate change and variability and the frequency of climatic extremes has increased in recent years resulting in increased risks to agricultural production and food security.
Way Forward
- Need for Evergreen Revolution which is based on an appropriate blend of different approaches to sustainable agriculture such as organic farming, green agriculture, eco-agriculture, etc.
- Green Revolution 2.0 can help to improve productivity in dry-farming areas, which can grow pulses, oilseeds and other high-value crops that require less water.
- Natural Farming is desirable and required for cost-effective and ecologically compatible alternatives that can help achieve the Sustainable Development Goals.
- Cooperative Farming is required to make cost-effective usage of new technology on small and marginal-size holdings.
- Green Revolution to Gene Revolution: GM seeds are considered to be more productive, more pest-resistant and more suitable to all categories of farms and all the agricultural regions.
What is an Eveegreen Revolution?
MS Swaminathan proposed the concept of an “Evergreen Revolution” as an alternative to the Green Revolution in 1990. It refers to long-term productivity growth without causing environmental and social harm. This practice incorporating ecological principles into the creation and adoption of technology.
- Key Pillars of the “evergreen revolution”:
- Long-Term Detriments Acknowledgment
- Balancing Productivity and Ecology.
- Efficient irrigation methods
- Watershed management
- Drought-tolerant crop development,
- Sustainable Agricultural Practices.
- Mitigating Ecological Perils.
- Preserving Indigenous Crop Varieties.
- Productivity in Perpetuity.
- Shift Towards Sustainable Agriculture.
Conclusion
The green revolution technology, in spite of its severe criticism on the issues related to equity, ecology and environment, made a remarkable contribution in transforming Indian Agriculture.
| Attempt the PY Prelims Question:
Consider the following statements : (2023)
- The Government of India provides Minimum Support Price for niger · ( Guizotia aoyssinica) seeds.
- Niger is cultivated as a Kharif crop.
- Some tribal people in India use niger seed oil for cooking.
How many of the above statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Ans: C |
![]() 30 Sep 2023
30 Sep 2023

