In January 2025 wildfires in Los Angeles caused widespread destruction, claiming lives and displacing many. These catastrophic events once again highlighted the urgent need to address and prevent forest fires.
Forest Fires in India
- Situation in India: According to the Forest Survey of India, over 36% of the country’s forest cover is susceptible to fire.
-
- Temperature, precipitation, vegetation and moisture contribute to the scale as well as frequency of forest fires.
- Forest Fire Season in India: November to June is considered to be forest fire season in India.
- Higher fire incidents are reported in March, April and May due to ample availability of dry biomass following the end of winter and amid the prevailing summer season.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
| Forest Fire Situation in 2024: During March 2024, the highest number of forest fires were reported from Mizoram (3,738), Manipur (1,702), Assam (1,652), Meghalaya (1,252), and Maharashtra (1,215), as per FSI data. |
- Reasons: Fuel load, oxygen and temperature are considered three factors that cause the spread of forest fire.
- Dry leaves are the fuel for forest fires.
- States Vulnerable to Forest Fires: According to the biennial India State of Forest Report (ISFR) 2021, northeastern states showed the highest tendency for forest fires.
- Parts of western Maharashtra, southern Chhattisgarh, central Odisha and regions in Andhra Pradesh, Telangana and Karnataka also showed patches of extremely and very highly fire-prone zones.
- According to India State of Forest Report (ISFR) 2019 about 4% of the forest cover was ‘extremely prone’ to fire, and another 6% was ‘very highly’ fire prone.
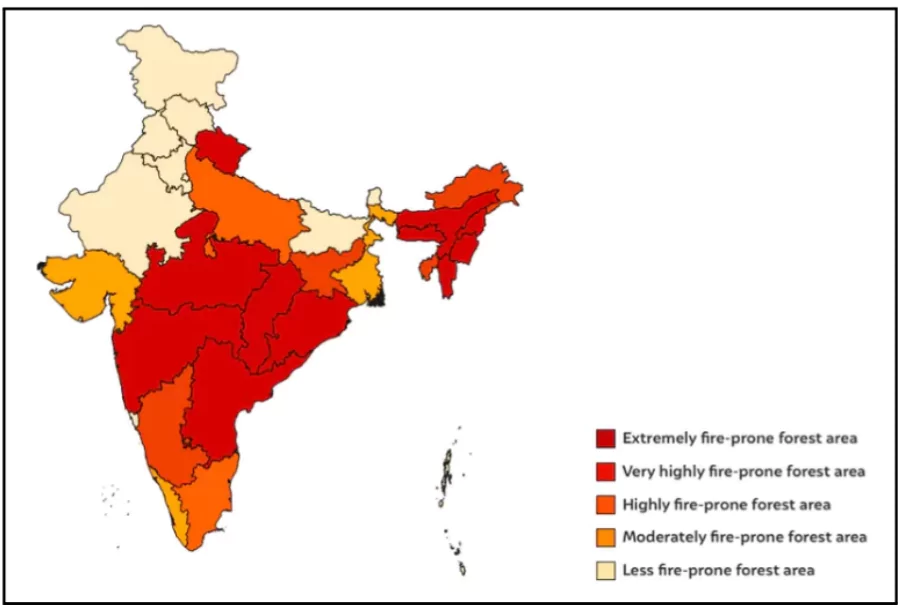
- Forest Fire Vulnerability Across Ecosystems: According to the FSI, severe fires break out in dry deciduous forests, while evergreen, semi-evergreen, and montane temperate forests are comparatively less prone to fires.
Causes and Prevention of Forest Fires
- Causes: Intentional fires by locals, negligence, farming activities, and natural factors.
- A government report highlights that locals set forests on fire to encourage the growth of high-quality grass, cover illegal tree cutting, or facilitate poaching.
- Friction of electricity cables and lighting also trigger wildfires.
| Setting a forest on fire is a punishable offence under the Indian Penal Code. While several cases have been filed, the accused remain unidentified in most of them. |
- Prevention: The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) outlines several measures to prevent and control forest fires, including the construction of watch towers for early detection, deployment of fire watchers, engagement of local communities, and the establishment and maintenance of fire lines.
- Types of Fire Lines: According to the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA), there are two types of fire lines:
- Kachha (covered) fire lines: In Kachha fire lines, undergrowth and shrubs are cleared, while trees are left intact to reduce the fuel load.
- Pucca (open) fire lines: Pucca fire lines are clear-felled areas that separate different forest compartments or blocks to control the spread of potential fires.
- The FSI website states: “Satellite-based remote sensing technology and GIS (Geographic Information System)) tools have proven effective in improving fire prevention and management by creating early warnings for fire-prone areas, monitoring fires in real time, and estimating burnt scars.”
Check Out UPSC Modules From PW Store
Conclusion
By combining policy, technology, and community engagement, India can better protect its forests and the livelihoods dependent on them.
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
![]() 12 Feb 2025
12 Feb 2025


