India’s geopolitical strategy in the Indo-Pacific increasingly hinges on enhanced connectivity, with the India-Myanmar-Thailand Trilateral Highway (IMT-TH) serving as a key component in strengthening regional ties and boosting trade.
India-Myanmar-Thailand Trilateral Highway (IMT-TH)
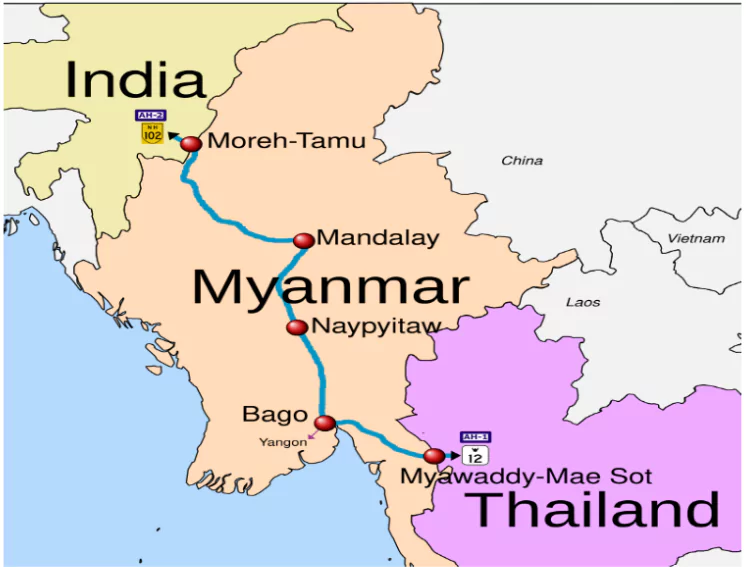
- The India-Myanmar-Thailand Trilateral Highway (IMT-TH) is a key infrastructure project aimed at improving connectivity between India, Myanmar, and Thailand.
- It is a 1,360-km corridor that would connect Kolkata in India to Bangkok in Thailand.
- This route will go through Northeast India and Myanmar, making it an important link between South and Southeast Asia.
- History: Since its inception in 2002, the Trilateral Highway project has encountered a range of delays and challenges that have hindered its progress.
- Key Challenges: Key issues include political instability in Myanmar since February 2021, which has disrupted construction timelines and posed significant logistical hurdles.
- The COVID-19 pandemic has further exacerbated the delays in the Trilateral Highway project.
- Progress: The aim was to finish the highway in 2015, but it was then pushed to 2019.
- The sections in India and Thailand have been completed; however, the highway, which has a major portion in Myanmar, has experienced delays in progress.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Advantages of IMT-TH
- Economic Benefits for Northeast India: The IMT-TH opens direct trade routes to Southeast Asia, creating new markets for agriculture, textiles, and handicrafts, and attracting investments in food processing, logistics, and tourism to spur industrial growth.
- Reducing Insurgency and Unrest in Northeast: When young people are unemployed, they often resort to engaging in insurgent activities and violence.
- By improving infrastructure and creating better commercial opportunities, we could help deter such insurgent activities.
- Access to Low Cost Labour in Myanmar: Indian businesses, particularly in electronics, could use Myanmar as a cost-effective manufacturing hub and transport finished products to Southeast Asian markets.
- Strategic Counterbalance to China:
- BRI: In the face of China’s expansive Belt and Road Initiative, the IMT-TH provides India with an independent route to Southeast Asia.
- Trade Route Diversification: The IMT-TH provides India with a critical overland trade route, bypassing the heavily trafficked Malacca Strait where China exerts significant influence.
- Currently, around 95% of India’s trade by volume is shipped by sea, making it vulnerable to disruptions along maritime routes.
- Regional Coalition: By strengthening ties with Myanmar and Thailand, India builds a coalition of like-minded nations to maintain sovereignty in the face of China’s regional influence.
- Access to ASEAN Markets:
- With the IMT-TH, India gains direct access to the ASEAN region, a combined market with a GDP exceeding $3 trillion.
- Trade with Thailand, a significant ASEAN partner, was $16.04 billion in 2023.
- The highway could increase Indian exports to Southeast Asia in high-demand sectors such as pharmaceuticals, textiles, and automotive components, helping India tap into ASEAN’s growing consumer market and bolstering its role in regional trade networks.
- Strengthened Logistics and Supply Chains: The IMT-TH enhances the logistics network for Indian exporters, allowing them to reduce costs associated with sea and air freight.
- Indian companies can leverage Thailand’s infrastructure, such as its Eastern Economic Corridor, to distribute products across ASEAN markets like Cambodia, Laos, and Vietnam.
- Access to RCEP: The enhanced connectivity will enable India to engage more actively in ASEAN-led initiatives such as the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP).
| Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP)
Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) is a mega-regional economic agreement between ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations) and their FTA (Free Trade Agreement) partners, aiming to boost trade and investment in the region.
India was a founding member of the RCEP. However, in 2019, India announced that it would not join the RCEP. |
Diplomatic Balancing Act in the Region
- US and Quad: While the US views India as critical in countering China’s influence in the Indo-Pacific, particularly through initiatives like the Quad, which it wants to be a military alliance, India has not agreed to this.
- India-China Relations: Recent agreements between India and China on patrolling arrangements along the Line of Actual Control (LAC) could shift the geopolitical dynamics in the region, influencing India’s role in the Indo-Pacific.
- Russia-China-India Alignment: Speculation about a potential Russia-China-India alignment, exemplified by plans for a joint lunar project, underscores India’s strategic autonomy in navigating competing global alliances.
- This balanced diplomacy could support the IMT-TH’s role in enhancing economic integration and reinforcing India’s independent geopolitical role.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Conclusion
The IMT-TH highway is a transformative project that not only boosts economic integration between India, Myanmar, and Thailand but also strengthens India’s strategic position in the Indo-Pacific, reducing reliance on China while fostering regional cooperation and growth.
![]() 14 Nov 2024
14 Nov 2024

