Context:
| Relevancy for Prelims: Indian Port Sector, Major Ports in India, Ancient Indian Ports, Special Economic Zones, Sagarmala scheme,
Relevancy for Mains: Indian Ports and Economic Development, Historical Significance of Indian Ports, Multifaceted Role of Ports, Government Reforms. |
Indian Ports – Historical Significance
- Indian Ports have played a pivotal role throughout Indian history, connecting the country to distant lands.
- They facilitated trade, cultural exchange, and economic prosperity in ancient times.
- Indus Valley Civilization: The ancient city of Lothal, part of the Indus Valley Civilization connected the Indus Valley Mesopotamia, Oman, and the Persian Gulf.
- Mauryan Era: Pataliputra, located near the confluence of the Ganges and Son rivers served as a natural route for transportation, facilitating trade within the Indian subcontinent.
- Gupta Period: The port of Broach (modern-day Bharuch) on the west coast of India became a significant center for maritime trade.
- Chola Dynasty: The Cholas developed the port of Nagapattinam on the southeast coast of India as a major center for trade and maritime activities.
- Medieval Period: The port of Calicut (Kozhikode) on the Malabar Coast gained prominence during the medieval period. It became a key center for the spice trade, attracting traders from the Middle East and Europe.
Indian Ports – Growth in the Modern Era
- Over the past three decades, the Indian ports sector has experienced significant growth due to rapid economic development and government policies.
- As of 2022, India had 12 major and over 210 non-major ports.
- Public and Private Sector Involvement: While most ports are government-controlled, the private sector has made substantial contributions to port infrastructure development.
- The Mundra port and the Adani Group’s seaport in Vizhinjam are notable private sector examples.
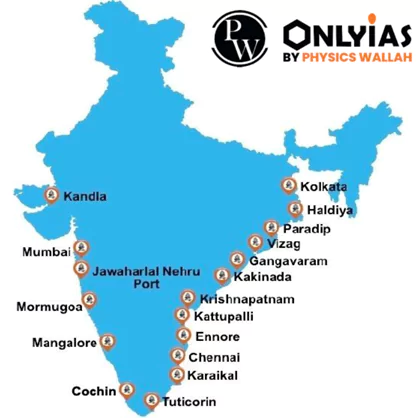
Indian Ports – Multifaceted Role
- Economic Contribution: Indian ports are essential for international trade, industrial growth, energy imports, tourism, and employment generation.
- Approximately 95% of India’s trade by volume and 68% by value relies on maritime transport.
- India’s extensive coastline (over 7,500 km) supports rapid economic development and diversification.
- As India targets exports worth $900 billion in FY24, Indian ports serve as the crucial gateway to becoming a $5 trillion economy.
Indian Ports and Economic Development
- SEZs and Industrial Clusters: The Special Economic Zones Act in 2006 paved the way for port-connected SEZs, promoting industrial and commercial development around ports.
- Energy Imports: Indian ports on the western coast, including Mundra and Kandla, handle significant volumes of crude oil and energy imports crucial for the nation’s needs.
- Eastern Coast Trade and Tourism: Indian ports on the eastern coast, like Chennai, Visakhapatnam, Kolkata, Paradip, and Haldia, support trade with countries in Asia, Europe, and the Americas.
Government Reforms and Infrastructure Schemes
- The Sagarmala scheme aims to provide holistic development to ports, with 802 projects worth ₹5.40 lakh crore by 2035.
- This support leads to increased revenues for the government, substantial employment generation, and an overall significant contribution to the Indian economy.
Also read: MISSION SAGAR: Indian Ocean Diplomacy and India’s Strategic Outreach
Conclusion:
Indian ports, with their rich historical legacy and modern strategic importance, serve as vital catalysts for economic growth, global trade, and extensive employment opportunities. Thus, the Indian port sector has the potential to play an important role in India’s journey toward becoming a $5 trillion economy.
| Prelims Question (2022)
Which one of the following statements best describes the ‘Polar Code’?
(a) It is the international code of safety for ships operating in polar waters.
(b) It is the agreement of the countries around the North Pole regarding the demarcation of their territories in the polar region.
(c) It is a set of norms to be followed by the countries whose scientists undertake research studies in the North Pole and South Pole.
(d) It is a trade and security agreement of the member countries of the Arctic Council.
Ans: (a) |
![]() 27 Oct 2023
27 Oct 2023

