Context:
- This article is based on an Editorial “Reform can address India’s kidney transplant deficit” which was published in the Hindu. India’s organ shortage for kidneys is alarming. In 2022, over two lakh patients needed a transplant, but there were only about 7,500 transplants (about 3.4%).
- In contrast to India, the United States and other developed countries could carry out about 20% transplants.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD), difference between Kidney Chains and Swap Transplants, and New National Organ Transplantation Guidelines.
Relevancy for Mains: Chronic Kidney Disease, India’s policies for organ transplantation, associated challenges and its tackling. |
India: A High Prevalence of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Country
- Affected Population: About 17% of the population in India.
- Reason: Due to the prevalence of diabetes, malnourishment, overcrowding and poor sanitation.
- Severity: CKD often leads to end-stage renal disease (ESRD).
- Remedy: A kidney transplant is often the best treatment for ESRD.
- Why is Transplant a Better Option?
-
- Better quality of life, patient convenience, life expectancy, as well as cost-effectiveness.
- Reason for Gap in India: On account of more stringent regulations in India than a lack of medical facilities.
Ways to obtain a Kidney & Associated Concerns
- From a Deceased Person: This is constrained due to a lack of donations, the particular conditions required on the nature of death, and the infrastructure needed to collect and store kidneys.
- Request a Relative or Friend to donate: Donor and recipient have to be compatible in terms of blood type and tissue type; such relative/friend donors are often incompatible.
Also read: Ayushman Bharat – Pradhan Mantri Jan Aarogya Yojana (PMJAY)
What Challenges are associated with the trans
- Less Use of Technologies: Very less swap transplants and almost no chain transplants in India because of legal roadblocks.
- Differences in Rules for Swap Transplants: Swap transplants are legally allowed in India with due permission, but only near-relatives are allowed as donor-recipient pairs. While Kerala, Punjab and Haryana are exceptions by allowing non-near-relative donor-recipient pairs after verification.
- Almost no Kidney Chains: In all States except Kerala, it is illegal to donate a kidney out of altruism.
- Kidneys from the deceased or brain dead are only used for direct transplants, not for chains or cycles.
- The lack of kidney chains is possibly an even bigger opportunity missed than swaps as chains, compared to swaps, involve significantly lower hospital resources and uncertainty for participants.
- Lack of a Coordinating Authority: Unlike national, regional, and State lists for direct transplant from cadavers, there is no national coordinating authority for swaps.
- This is also a huge lost opportunity, since larger and more diverse pools make it easier to find compatible swaps.
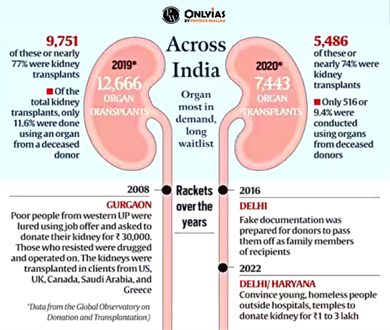
- Proliferation of Black Markets: Harsh laws regulating swaps and chains have contributed to a proliferation of black markets for kidneys. These black markets endanger all, since these operations are conducted without due legal and medical safeguards.
- Missing out Fundamental issue of Inadequate Kidney Supply: The government’s recent reforms i.e., New National Organ Transplantation Guidelines (February 2023) allow more flexibility in age and domicile requirements while registering to obtain an organ. But these reforms leave the fundamental issue of inadequate kidney supply largely unaddressed.
Wayforward
- Regulations for kidney exchange are needed as kidney exchange must often occur across family members.
- These regulations need urgent reforms to liberate innovative kidney exchange methods: kidney ‘swaps’ and kidney ‘chains’.
- Need to allow and encourage altruistic donation, non-near relative donation for swaps, and to improve the kidney-exchange infrastructure.
- Learn from Others: India does not need to innovate in order to reform chains and swaps. India needs to learn from others and implement such regulations to overcome organ shortage for kidneys.
- Allow Altruistic Donations like Australia, Canada, Israel, the Netherlands and the U.S. (among others).
- Maintain National-Level Registries for kidney chains and swaps like Spain and the United Kingdom.
- The U.S. has especially made progress in facilitating thousands of swaps and chains.
- Reach out for international collaborations for kidney exchange like Spain.
- Easing the laws for swaps to make them on a par with direct donations is necessary.
Conclusion
The unveiled kidney transplant crisis in India demands urgent attention and comprehensive reforms. By learning from international practices, implementing regulatory changes, and fostering collaborations, India can bridge the gap in organ transplantation.
| Attempt the PY Prelims Question:
Q. Consider the following statements in the context of interventions being undertaken under Anaemia Mukt Bharat Strategy: (2023)
- It provides prophylactic calcium supplementation for pre-school children, adolescents and pregnant women.
- It runs a campaign for delayed cord clamping at the time of childbirth.
- It provides for periodic deworming. to children and adolescents.
- It addresses non-nutritional causes of anaemia in endemic pockets with special focus on malaria, hemoglobinopathies and fluorosis.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Ans: C |
![]() 30 Sep 2023
30 Sep 2023

