Context: This article is based on an Editorial “India’s space economy to soar to $40 billion by 2040: Union Minister” Which was published in the Live Mint. As per Deloitte consultancy, private investments in the Indian Space sector increased by 77% between 2021 and 2022 with the Opening of 190 Indian space start-ups. It was twice as many as a year earlier.
| Relevancy for Mains: Privatization Of Indian Space Sector, its Significance and Associated Challenges. |
What is the potential of the Indian space sector?
- Space Economy: At present, its value is around ₹6,700 crore ($8.4 billion).
- Revenue From Satellite Launch: The Indian SpaceTech sector has received $62 million funding in 2023, registering a 60% increase, compared to the last year, as per data research firm Tracxn.
- Future Prospect: As per IN-SPACe’s projection, India’s space economy has the potential to reach ₹35,200 crore ($44 billion) by 2033 with about 8% of the global share.
- Export Share: At present, the export market share is ₹2,400 crore ($0.3 billion).
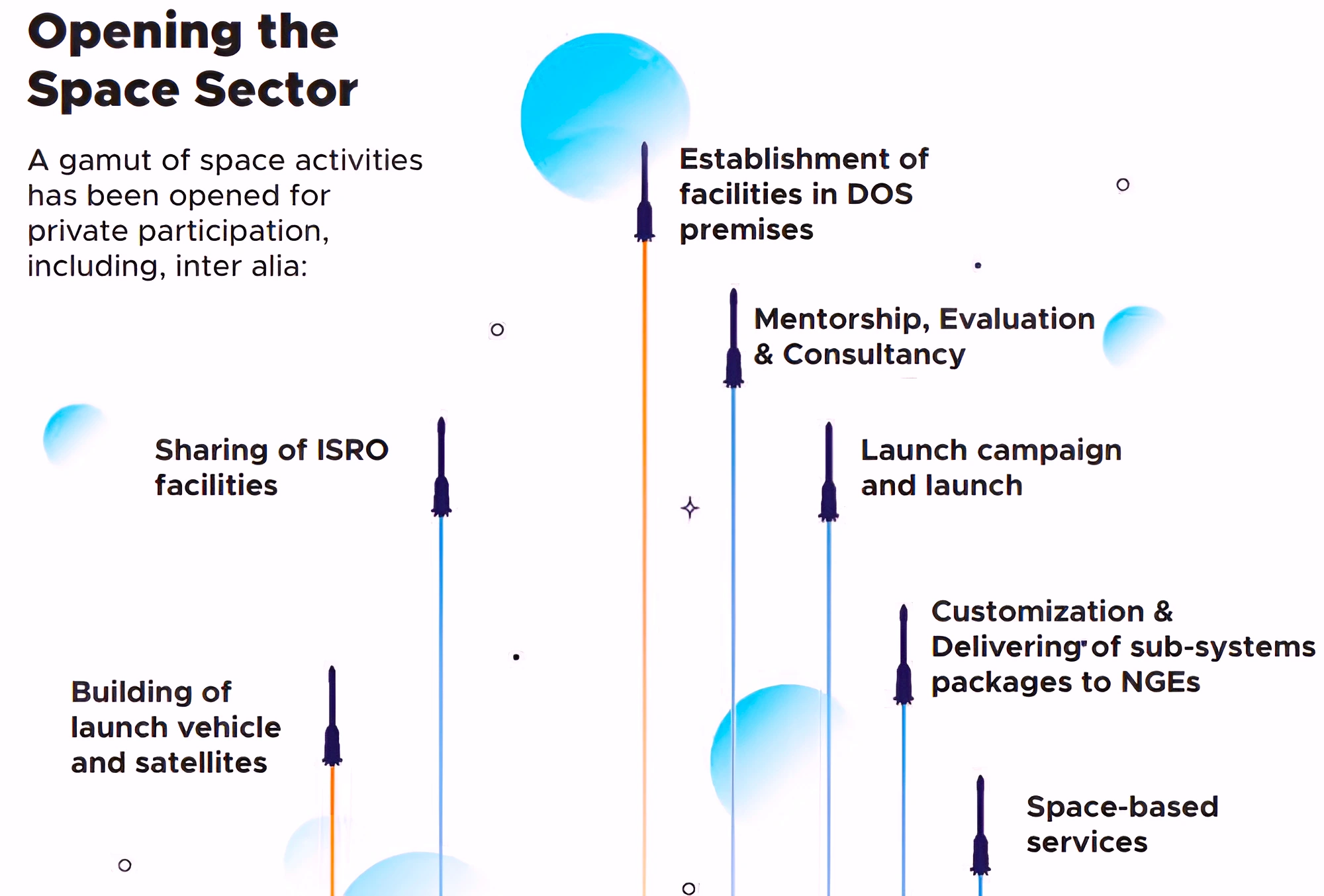
Read more about the Privatisation Of Space Sector here.
What is the current status of the privatization of Indian space sector?
- As per SpaceTech Analytics, India is the sixth-largest player in the industry internationally having 3.6% of the world’s space-tech companies (as of 2021).
- The U.S. is on top spot housing 56.4% of all companies in the space-tech ecosystem.
- As per Economic Survey of India, there have been over 100 active space companies since 2012.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
What is the significance of private sector participation in the Indian space sector?
- Enhancing Foreign Direct Investment: The private sector participation will attract more foreign direct investment for space startups and related technology companies in India.
- Realizing the Vision of ‘’Make in India”: The vision of “Make in India” call for a remodelling of the mostly government-led space sector of the country.
- Policy Framework and Goals: The Private Sector particpation will help India increase its share in the global space economy from about 2 per cent to 9 percent by 2030.
What challenges are associated with the privatization of Indian space sector?
- Access to Capital: Private capital is still not flowing freely and blindly through to space-based enterprises like it is with internet-, digital media- and hardware-related technology businesses.
- Inability to Create Self-Sustaining Markets: As observed in the past, it puts into question the commercial viability of space-based enterprises.
- Access to Insurance: There is also a lack of adequate and secured insurance, due to the inability of insurers to see and test the reliability of space-based technologies in the recent past.
Pros of Privatization of Space Exploration:
- Reduce Exploration Cost: With innovation and advanced technology, the space sector can reduce costs and time. Companies like SpaceX, Blue Origin, etc., have made a revolution.
- Tourism: As proved by Blue Origin, passengers could take on trips beyond Earth’s atmosphere.
- Natural Resources: Countries are establishing a legal framework securing private rights over resources mined in space, such as Luxembourg, Japan, and the United Arab Emirates.
Cons of Privatization of Space Exploration:
- Regulation: The regulation of the private sector is not easy. The time taken for regulatory clearances and unstable political institutions can cause delays and hurdles.
- Spacecraft Emissions: Their participation has led to an enormous increase in the number of launches that will likely continue to grow in spacecraft emissions.
- Growing Orbital Debris: NASA researchers suggested that the increased number of launches are leading to a growing number of collisions and consequently, orbital debris.
Way Forward:
- Demand-driven Approach: Optimizing the utilization of space assets such as satellites and launch capacity by determining accountability amongst various stakeholders.
- Upskilling the Human Power: It would provide a boost to private sector participation in the space sector.
- India is already conducting ISRO Technical Training Programme (ITTP) at various National Skill Training Institutes (NSTIs) across the country for upskilling of ISRO human assets in four to five years in a phased manner.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Conclusion:
The privatization of the Indian space sector holds immense potential, attracting investments and fostering innovation. Despite its potential, challenges like funding and regulatory issues need addressing.
![]() 28 Nov 2023
28 Nov 2023

