The India-Middle East-Europe Corridor (IMEC) was launched at the G20 Summit in September 2023. Despite its potential, progress has been uneven due to geopolitical challenges.
India-Middle East-Europe Corridor (IMEC)
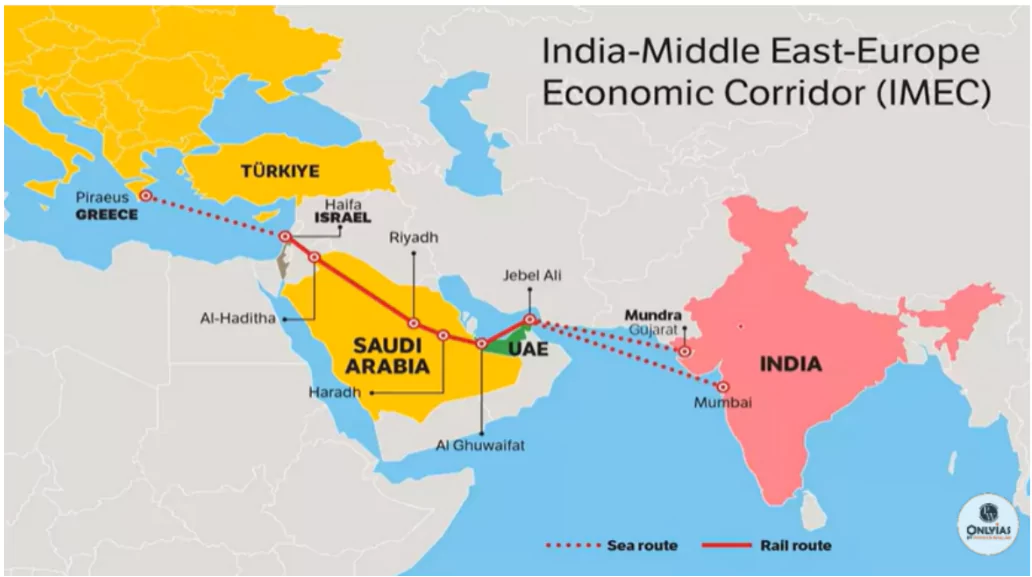
- The IMEC is an ambitious transcontinental trade corridor designed to reduce transit time by 40% and transportation costs by 30%, compared to traditional routes like the Suez Canal.
- The corridor connects India’s ports with the Middle East and Europe, facilitating the smooth flow of goods and enhancing trade relations across these regions.
- The corridor will begin with a sea route from India, connecting to the UAE (specifically Jebel Ali Port), which is a major hub for trade in the region.
- From the UAE, the corridor will extend through rail and road networks, passing through West Asia (including countries like Saudi Arabia, Jordan, and potentially Israel) and eventually reaching Greece in Europe.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Current Status and Challenges of the IMEC Corridor
1. Eastern Leg of the Corridor
- The eastern leg connecting India and the UAE is advancing rapidly, supported by strong bilateral trade and the Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA), signed in 2022.
- Bilateral trade has surged by 93%, from $43.30 billion in 2020-21 to $83.64 billion in 2023-24.
- Non-oil trade between India and the UAE has grown substantially, signalling positive momentum for the IMEC’s trade aspects.
- A key development includes the launch of the Virtual Trade Corridor, which aims to streamline trade processes, reduce logistics costs, and enhance trade efficiency between India and the UAE.
2. Western Leg of the Corridor
- The western part of the corridor, especially in the Middle East, faces significant challenges due to the ongoing Israel-Palestine conflict.
- This crisis has delayed progress, particularly affecting Saudi Arabia and Jordan’s involvement in the project.
- While ground-level implementation may not be directly impacted by the political situation, the geopolitical dimension affects cooperation between Arab countries and Israel, slowing progress.
3. Progress on Other Elements of the Corridor
- The full scope of the IMEC, including clean energy exports, fiber-optic cables, energy grids, and telecommunications, remains on hold due to the ongoing conflict in West Asia. Until the situation stabilises, progress on these elements will be delayed.
Way Forward
- Infrastructure and Port Development: India must use this time to strengthen its port infrastructure, develop Special Economic Zones (SEZs) along connectivity nodes, and enhance domestic logistics to support seamless integration with the IMEC.
- Improving Digital Logistics: Upgrading India’s digital infrastructure in the domestic logistic landscape can reduce transport costs and increase export competitiveness, critical to leveraging the IMEC.
- Supply Chain Integration: India seeks to establish itself as a global supply chain hub, and the IMEC provides a key opportunity for integration into international value chains.
- However, this potential can only be realised by improving India’s manufacturing and trade competitiveness, particularly in competition with nations like China.
- Establishment of IMEC Secretariat: Establishing an IMEC Secretariat could ensure better coordination among stakeholders, systematic implementation, and clarity on progress.
- The Secretariat could conduct empirical research on the corridor’s benefits and develop frameworks for cross-border trade facilitation, enhancing transparency and attracting new partner countries.
- Focus on Geopolitical Stability: Efforts should focus on navigating Middle East geopolitical tensions, and once stabilised, the broader IMEC elements, including energy and technology cooperation, should be pursued to unlock its full potential.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Conclusion
The India-Middle East-Europe Corridor has great potential to transform global trade, with progress in the eastern leg between India and the UAE. However, resolving geopolitical tensions in West Asia is key to unlocking the full potential of the corridor. Focused efforts on infrastructure, digital integration, and diplomacy will drive its success.
![]() 13 Nov 2024
13 Nov 2024

