![]() 22 Feb 2024
22 Feb 2024

This editorial is based on the news “Collapse of the ecological balance and an undeclared war with nature” which was published in the Hindu.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Western Ghats, Human Wildlife Conflict, Environment & Ecology, and Protected Areas In India.
Relevancy for Mains: Rising Human Wildlife Conflicts: Recent Accidents, Statistics, and Impact on Environment & Ecology. |
|---|
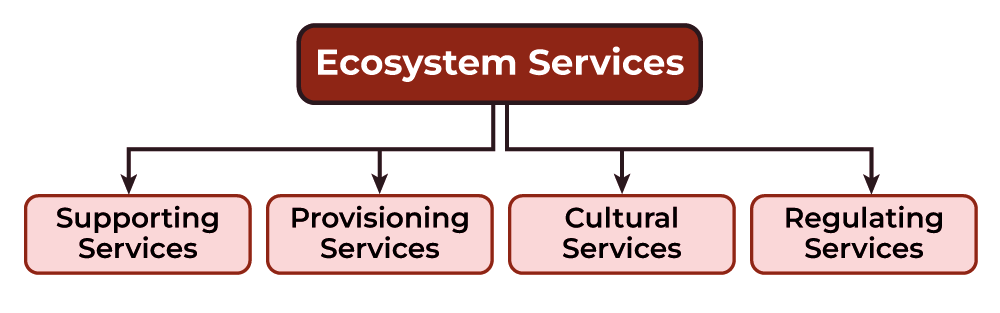
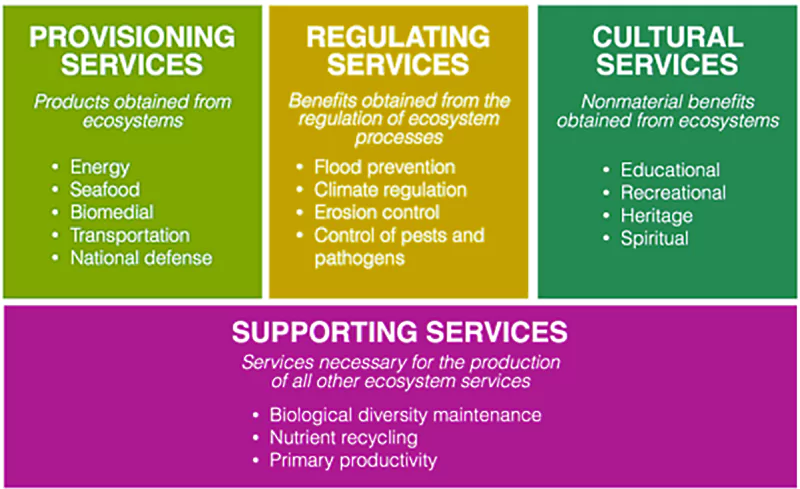
| Prelims PYQ (2023):
Consider the following statements: 1. Amarkantak Hills are at the confluence of Vindhya and Sahyadri Ranges. 2. Biligirirangan Hills constitute the easternmost part of Satpura Range. 3. Seshachalam Hills Constitute the southernmost part of Western Ghats. How many of the statements given above the correct? (a) Only one (b) Only two (c) All three (d) None Ans: (d) |
|---|
| Mains Question: Why is human wildlife conflict on the rise? What solutions are there to help humans and wildlife coexist? (10 marks, 150 words) |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>