Context:
| Relevancy for Prelims: Southern States of India, Finance Commission, Tax Collections, Distribution of taxes in India.
Relevancy for Mains: What Southern states of India are expressing worries about the allocation of Central taxes and as upcoming constituency delimitation. |
Are Southern States of India being punished for their success? – Raised Concerns
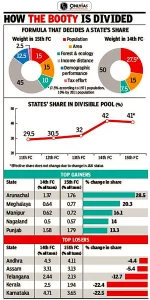
- Distribution of Taxes: The Finance Commission (FC) decides the devotion of taxes from the Centre to the States and distribution of these proceeds among the States.
- Inter-State distribution is based on two factors i.e., State’s share in the total population and the income distance ratio (means how far the State’s per capita income is higher or lower than the national average).
- Certain criteria against the Southern States of India: On both of the above counts, the south loses out. For example, in the case of Kerala, the share of resource distribution was 3.8% during the 10th Finance commission and now it is 1.9%. This decline has been accelerating over time.
- The Equity Principle: The richer States and regions will have to contribute to the development of the States which are backward because every citizen has a right to certain minimum uniform services. But the re-distributive transfers must be within certain limits.
- Since, this transfer does not produce the expected improvement, now there is a need to find the exact reason for backwardness of these states.
- Impact of shift in the Population Base Year: There is a high correlation between the decline in population growth and the growth rate of the economy. Example, Kerala, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu saw a drastic reduction. However, the final outcome has been negative.
- Recently, Kerala’s Finance Minister stated in the Assembly that the State gets ₹35 paise, while Uttar Pradesh gets ₹1.6 for every rupee collected from the State.
- Following Norms & Schemes: The southern States have complied with population norms and schemes that have been promoted by the Central government, which has resulted in their population share going down.
- Hence, the delimitation of constituencies would lead to a decline in their representation in Parliament and the States feel penalized for their success
The Path Ahead
- There should be a strong effort to ensure that the next Finance Commission has terms of reference which take cognisance of the problems that the federal policy is facing.
- For example, if the population basis is being shifted, the weightage of the population can be adjusted.
- A reasonable solution would be to freeze the seats of the Rajya Sabha at the level at which they are, rather than adjusting them in terms of population.
- After the proposed delimitation, there would be different populous constituencies because of the demographic disparities. It is necessary to provide effective representation to all the regions of India.
Also read: FRBM – Objectives, Features, Full Form, FRBM Act UPSC
Conclusion:
The objective of all the Indian institutions should be to build a better economy, a better polity, and a better society. Hence, there is a need for a more proactive attitude by identifying the points where intervention is required to prevent any unbalanced and fragmentation results.
| Prelims Question (2015)
The Government of India has established NITI Aayog to replace the
(a) Human Rights Commission
(b) Finance Commission
(c) Law Commission
(d) Planning Commission
Ans: (d) |
![]() 20 Oct 2023
20 Oct 2023

