On 1 February 2025, Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman unveiled her eighth consecutive Union Budget.
Focus on Four Sectors
- The Finance Minister outlined four primary engines of development:
- Agriculture
- MSMEs (Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises)
- Investments
- Exports
- Many Southeast Asian countries have boosted their economies by prioritizing exports. Similarly, in the coming decades, India must shift from being a consumer economy to focusing more on exports for sustainable growth.
- Objective: The emphasis of such reforms is to attain the goal of the vision of a “Viksit Bharat” in 2047 and have inclusive growth.
- Other Focus Areas of Reforms: Additionally, the Budget aims to drive reforms in six critical areas:
- Taxation
- Power Sector
- Urban Development
- Mining
- Financial Sector
- Regulatory Reforms
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
1. Agriculture
- Promotion of Pulses and Makhana: The government will focus on achieving self-sufficiency in pulses, including toor, urad, and masur.
- Makhana Board: Bihar will receive a Makhana Board (similar to tea board and coffee board) to promote the cultivation and marketing of fox nuts.
- Benefits of Farmer Board Organization: This initiative will benefit the 10 lakh people engaged in Makhana cultivation, contributing about 85% of India’s total Makhana production.

-
- Rural Prosperity and Resilience Program: A multi-sectoral ‘Rural Prosperity and Resilience’ program will be launched in collaboration with state governments.
- Aim/Focus: This program aims to tackle underemployment by promoting skill development, investment, and technology adoption, focusing on rural women, young farmers, small farmers, and landless families.

-
- National Mission on High Yielding Seeds: The government will launch a National Mission on High Yielding Seeds, focusing on research, development, and the availability of pest-resistant and climate-resilient seeds.

-
- Cotton Productivity Mission: A 5-year ‘Mission for Cotton Productivity’ will be introduced to support cotton farmers.
- Fisheries and Rural Logistics: An enabling framework will be introduced for sustainable fisheries from India’s Exclusive Economic Zone and High Seas, with a special focus on Andaman & Nicobar and Lakshadweep Islands.

India’s Exclusive Economic Zones
As per the UN Convention on Laws of the Seas (UNCLOS), countries usually have control over waters up to 200 nautical miles (370 km) from their coastlines, called exclusive economic zones (EEZs).
Waters beyond these zones are known as the high seas or international waters. |
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
-
- Expanding Scope of India Post: India Post and India Post Payments Bank will be repositioned as catalysts for rural economic development and will be transformed into a major logistics organization.
- Agricultural Loan Support: The Modified Interest Subvention Scheme will increase the loan limit from Rs. 3 lakh to Rs. 5 lakh for loans under the Kisan Credit Card (KCC).
- New Agricultural Scheme: PMDDKY: A new scheme, Prime Minister Dhan Dhanya Krishi Yojana (PMDDKY), will be launched across 100 districts to promote agricultural development, aligned with the Aspirational Districts Program.
Aspirational Districts Programme
The Aspirational Districts Programme which was launched in 2018 is an initiative to improve the living standards of people in under-developed districts.
Underdeveloped districts are renamed as Aspirational districts, which are affected by poor socio-economic indicators. |
-
- Urea Plant in Assam: A new urea plant will be set up at Namrup (Assam), with an annual production capacity of 12.7 lakh tonnes, marking the 7th such plant since 2019.
- Other Plants: Gadepan (Rajasthan), Ramagundam (Telangana), Panagarh (West Bengal), Gorakhpur (Uttar Pradesh), Barauni (Bihar), Sindri (Jharkhand) and Talcher (Odisha).
- Support for Cooperative Sector: Financial support will be provided to the National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC) to enhance its lending operations for the cooperative sector.
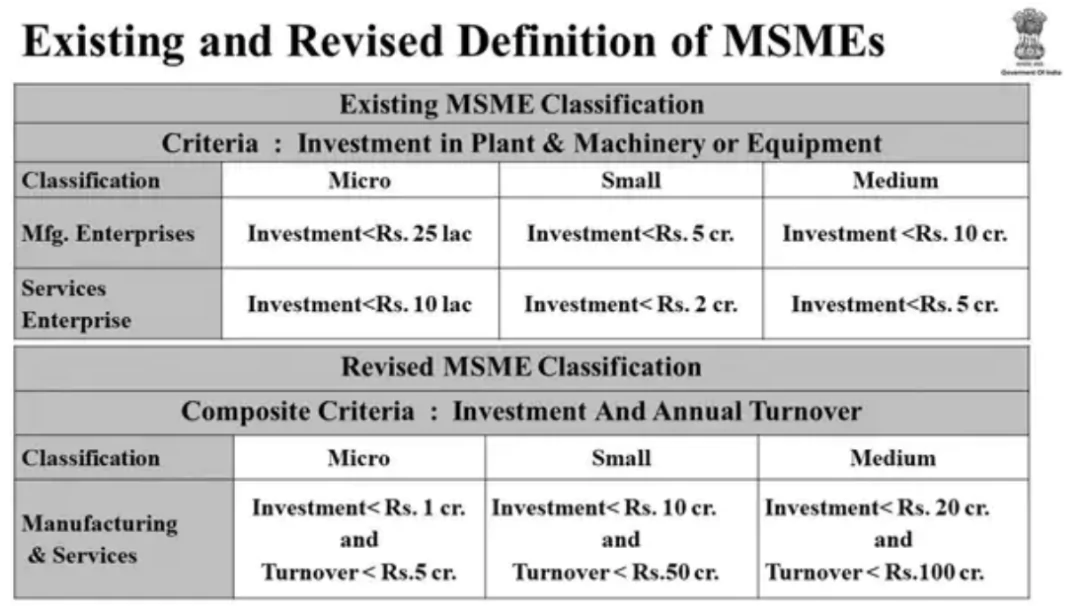
2. MSMEs (Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises)
- Enhancements to MSME Classification: Investment and turnover limits for MSMEs will be increased to encourage higher efficiencies and better access to capital.
- Enhanced Credit Guarantee Scheme: Credit guarantee cover will be increased for MSMEs, startups, and well-established exporter MSMEs:
- Micro and Small Enterprises: Cover increased from Rs. 5 crore to Rs. 10 crore, facilitating an additional credit of Rs. 1.5 lakh crore over the next 5 years.
- Startups: Credit cover increased from Rs. 10 crore to Rs. 20 crore, with a reduced guarantee fee of 1% for loans in 27 focus sectors important for Atmanirbhar Bharat.
- Exporter MSMEs: Term loans up to Rs. 20 crore will be covered.
- Customized Credit Cards for Micro Industries: The government will issue customized credit cards with a limit of Rs. 5 lakh under the Udyam portal. In the first year, 10 lakh cards will be issued.
- New Fund of Funds for Startups: A new Fund of Funds for startups will be launched, with an additional contribution of Rs. 10,000 crore. The Fund of Funds will be expanded to support Alternate Investment Funds (AIFs) for startups.
-
- It’s important to note that Alternative Investment Funds (AIFs) for startups have received over Rs. 91,000 crore in commitments. These funds are backed by a Fund of Funds, which has a government contribution of Rs. 10,000 crore.
Fund of Funds
A “fund of funds” (FoF) is an investment strategy where a fund invests in other investment funds rather than directly in stocks, bonds, or other securities. |
- Scheme for First-Time Entrepreneurs: A new scheme will offer term loans of up to Rs. 2 crore to first-time women entrepreneurs and those from Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes.
- Global Toy Hub: Building on the National Action Plan for Toys, the government will launch a scheme to make India a global toy manufacturing hub, promoting the ‘Make in India’ brand.
- National Institute of Food Technology: A National Institute of Food Technology, Entrepreneurship, and Management will be set up in Bihar to further the ‘Purvodaya’ initiative.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Purvodaya Scheme
The Purvodaya Plan encompasses the following regions: Andhra Pradesh, West Bengal, Jharkhand, Bihar, and Odisha.
Emphasis: Economic opportunity, human resource development, and infrastructure.
Goal: Transform the eastern area into a growth engine. |
- National Manufacturing Mission: A National Manufacturing Mission will be launched to promote Make in India, offering policy support, execution roadmaps, and frameworks for governance and monitoring.
- The mission will support clean-tech manufacturing in sectors such as solar PV cells, EV batteries, wind turbines, very high voltage transmission equipment and grid-scale batteries.
3. Investments

- Extension of Jal Jeevan Mission: The Jal Jeevan Mission will be extended until 2028 with the goal of achieving 100% coverage of household tap water connections across the country.
- ₹1 Lakh Crore Urban Challenge Fund: A ₹1 lakh crore Urban Challenge Fund will be established to support urban development projects under initiatives such as ‘Cities as Growth Hubs,’ ‘Creative Redevelopment,’ and ‘Water & Sanitation.’
- Viable Gap Funding: The fund will cover up to 25% of project costs, with at least 50% of the funding to come from bonds, bank loans, or Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs).
- ₹10,000 crore has been allocated for 2025-26.
Part 2
- Nuclear Energy Mission: A new Nuclear Energy Mission for the research and development of Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) will be launched, with an outlay of ₹20,000 crore.
- At least five indigenously developed small modular reactors will be operationalized by 2033.
Small Modular Reactors (SMRs)
Small Modular Reactors are small nuclear reactors that offer a power output of 30-300 MWe per unit. They harness nuclear fission to generate heat to produce energy.
SMRs have the potential to provide a reliable and low-carbon source of electricity, complementing renewable energy sources.
Why is it Called Modular?: All the systems and assembled factory products are sent and transported on the site. |
- Revamped Shipbuilding Financial Assistance Policy: The Shipbuilding Financial Assistance Policy will be revised to address cost disadvantages. This includes providing credit notes for shipbreaking in Indian yards to promote the circular economy.
- Large ships above a specified size will be added to the Infrastructure Harmonized Master List (HML).
- Additionally, Shipbuilding Clusters will be developed with enhanced infrastructure, skill-building, and technology to expand ship categories and capacity.
Harmonized Master List of Infrastructure (HML)
- A Commission was set up under the National Statistical Commission in January 2000 under the Chairmanship of Dr. C. Rangarajan reviewed the statistical system and the entire gamut of Official Statistics in the country.
- The Rangarajan Commission submitted its report to the Government in August 2001. Based on the Rangarajan framework, the Harmonized Master List of Infrastructure (HML) list was created in 2012.
- Inclusion in the HML allows investors to access infrastructure lending on more favorable terms, with higher limits, larger funds through External Commercial Borrowings (ECB), longer-term financing from insurance and pension funds, and eligibility for loans from the India Infrastructure Financing Company Limited (IIFCL).
Circular Economy
‘Circular Economy’ refers to all the activities of reduce, reuse, and recycle in production, circulation, and consumption.
As an important route to achieving a resource-saving and environmentally friendly society. |
- Maritime Development Fund: A Maritime Development Fund with a corpus of ₹25,000 crore will be established to support the development of India’s maritime infrastructure.
-
- The government will contribute up to 49% to the fund and mobilize the rest from the private sector.
Check Out UPSC Modules From PW Store
Bihar-Specific Investments
- Greenfield Airports: New greenfield airports will be developed in Bihar to meet future demand, complementing the expansion of Patna Airport and the development of a brownfield airport at Bihta.
- Western Koshi Canal Project: Financial support will be provided for the Western Koshi Canal ERM (extension, renovation and modernization) Project, benefiting farmers in the Mithilanchal region by improving irrigation across over 50,000 hectares of land.
Fog: Koshi River
- SWAMIH Fund 2: SWAMIH Fund 2, a blended finance facility, will be established with contributions from the government, banks, and private investors. This fund will support the completion of 1 lakh unfinished housing units.
- SWAMIH stands for Special Window for Affordable and Mid-Income Housing.
- Tourism Development Initiatives: The government plans to develop the top 50 tourist destinations in collaboration with state governments, with states providing land for key infrastructure.
- Initiatives include:
- Skill development programs in Institutes of Hospitality Management.
- MUDRA loans for homestays.
- Improved travel connectivity to tourist sites.
- Performance-linked incentives for states to manage tourism destinations, amenities, cleanliness, and marketing.
- Streamlined e-visa facilities and visa-fee waivers for some tourist groups.
- Focus on destinations tied to Lord Buddha’s life and promotion of medical tourism through easier visa norms and private sector collaboration.
- Modified UDAN Scheme: A modified UDAN scheme will be launched to enhance regional connectivity, adding 120 new destinations and aiming to carry 4 crore passengers over the next 10 years.
- The scheme will also support helipads and smaller airports in hilly, aspirational, and North Eastern region districts.
4. Exports
- Export Promotion Mission: The government will establish an Export Promotion Mission to improve export credit access and provide greater support for MSMEs in global markets.
- BharatTradeNet: A BharatTradeNet platform will be developed as a unified digital system for international trade documentation and financing solutions, streamlining processes for exporters.
- Global Supply Chain Integration: The government will support domestic manufacturing to better integrate India’s economy into global supply chains, focusing on Industry 4.0 and leveraging the talent of Indian youth.
- National Framework for GCC: A framework will be established to promote Global Capability Centres (GCC) in tier 2 cities, focusing on talent development and infrastructure to attract global business.
- Improving Air Cargo and Customs for Perishables: Efforts will be made to enhance air cargo infrastructure and streamline customs procedures for perishable goods to reduce logistical bottlenecks and improve export efficiency.
Education
- 50,000 Atal Tinkering Labs in govt schools over 5 years
- Broadband for all government secondary schools under BharatNet
- Bharatiya Bhasha Pustak Scheme for digital Indian language books in schools & higher education
- 5 National Centres of Excellence for skilling to equip youth for “Make for India, Make for the World”
- Infrastructure boost in 5 IITs for 6,500 more student seats
- Centre of Excellence in Al for education with ₹500 crore investment
- 10,000 additional seats in medical colleges next year, aiming for 75,000 over 5 years
Health
- Increase in health Budget:
- Health Budget in 2014-15 was ₹34,286 Cr
- Health Budget in 2025-26 is said to be ₹99,858.56 Cr i.e. 191 percent of increase.
- Cheaper Medicines: 36 lifesaving drugs are fully exempted from Basic Customs Duty.
- 6 life-saving drugs will receive a 5% concessional duty.
- 37 additional medicines and 13 patient assistance programs are fully exempted from duty.
- Day Care Cancer Centres: 200 centres to be set up in district hospitals by 2025-26.
- Gig Workers’ Healthcare: Government to register gig workers on the e-Shram portal.
- 1 crore gig workers to receive coverage under PM Jan Arogya Yojana.
- Heal in India: Medical Tourism: Government to promote medical tourism through public-private partnerships.
- Simplified visa norms for medical patients.
- Strengthening India as a global healthcare hub.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Financial Sector Reforms
- FDI in Insurance Sector: The FDI limit in the insurance sector will be increased from 74% to 100% for companies investing entirely in India, opening the door to greater foreign capital and competition.
- Expanding India Post Payment Bank Services: India Post Payment Bank will deepen and expand its services, particularly in rural areas, to improve financial inclusion.
- Credit Enhancement Facility by NaBFID: The introduction of a ‘Partial Credit Enhancement Facility’ for corporate bonds in infrastructure will support more accessible credit for infrastructure projects.
- NaBFID stands for National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development.
- Grameen Credit Score: Public Sector Banks will develop a framework for serving rural areas and Self-Help Group (SHG) members, leveraging a Grameen Credit Score to facilitate credit access in these regions.
- Pension Sector Reforms: A forum will be created for regulatory coordination and pension product development, improving the pension sector’s efficiency and reach.
- KYC Simplification: A revamped Central KYC Registry will be rolled out in 2025, simplifying the Know Your Customer (KYC) process and ensuring streamlined periodic updates.
- Merger of Companies: The approval procedures for company mergers will be rationalized, expanding the fast-track merger process to enhance business efficiency.
- Bilateral Investment Treaties (BITs): Two BITs with other countries will be signed in 2024, with a revamp of the BIT model to make it more investor-friendly.
- Regulatory Reforms: ‘Ease of Doing Business’ initiatives will be emphasized, with a focus on light-touch regulatory frameworks, updating old regulations to keep pace with technological and global policy changes.
- High-Level Committee for Regulatory Reforms
- A high-level committee will review non-financial sector regulations, licenses, and compliance procedures, providing recommendations within a year to improve governance and ease of doing business.
- Investment Friendliness Index of States: An Investment Friendliness Index will be launched in 2025 to promote competitive cooperative federalism among states.
- Jan Vishwas Bill 2.0: Decriminalization of over 100 provisions across various laws will be enacted through the new Jan Vishwas Bill 2.0.
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
![]() 3 Feb 2025
3 Feb 2025







