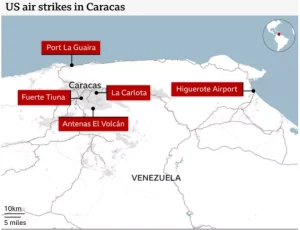
On 3 January 2026, the USA launched Operation Absolute Resolve and carried out extensive airstrikes as well as coordinated assaults targeting Venezuelan military sites and the capture of Venezuelan President Nicolás Maduro and his wife, Cilia Flores.
Historical Precedents

- Manuel Noriega (Panama, 1989): The United States invaded Panama (Operation Just Cause), captured Noriega, and tried him in U.S. courts on drug-trafficking charges.
Reasons Behind Operation Absolute Resolve
- Narco Terrorism: The US government officially justified this action by labelling Maduro a “drug lord” rather than a legitimate head of state. The key allegations included:
- Cartels of the Suns: The US claims this is a gang formed by senior Venezuelan military officers, with Maduro as its leader.
- Tren de Aragua Gang: This group is accused of sending drugs into the US that resulted in the deaths of 800,000 Americans.
- Bounty and Indictment: Maduro was previously indicted for cocaine trafficking in 2020, and the reward for information leading to him was increased to $50 million in August 2025.
- Counter-argument: However, experts argue that Venezuela’s role in drug trafficking is limited; most narcotics originate from Colombia, and despite the U.S. destroying over 35 boats, no conclusive drug evidence was presented.
- Self Defence: The US invoked Article 51 of the UN Charter, claiming they acted in “self-defence” against an “armed attack” in the form of drug trafficking, which they viewed as a national security threat.
- Counter-Argument: Critics argue this violates Article 2(4) of the UN Charter, which protects a nation’s sovereignty and territorial integrity.
 The Legal Tests: The operation failed the three critical tests for justified force: Necessity, Proportionality, and Imminence.
The Legal Tests: The operation failed the three critical tests for justified force: Necessity, Proportionality, and Imminence. - ICJ Precedent- Nicaragua Case, 1986: An International Court of Justice ruling explicitly stated that drug trafficking does not constitute an “armed attack”.
- Regime Change: The confrontation between the United States and Nicolás Maduro is not sudden but the outcome of a prolonged and escalating standoff. The Timeline of Escalation is as follows:
- Leadership Transition (2013): Nicolás Maduro assumed power after the death of Hugo Chávez, inheriting strained relations with the United States.
- Diplomatic Rupture (2019): The United States formally recognised Juan Guaidó as Venezuela’s legitimate leader, rejecting Maduro’s presidency.
- Electoral Dispute (2024): Venezuela’s elections were widely disputed, and the United States refused to recognise the results.
- Military Action (2026): The prolonged political conflict culminated in a direct U.S. military attack.
- Venezuela’s Oil Wealth: Venezuela possesses over 300 billion barrels of proven oil reserves, the largest in the world.
- Its reserves exceed those of Saudi Arabia.
- Despite this, current production is around 800,000 barrels per day, far below its peak of 3.5 million barrels per day, indicating untapped potential.
Resource Curse Theory
- About Resource Curse Theory: The Resource Curse Theory argues that countries rich in natural resources (oil, gas, and minerals) often experience slower economic growth, weaker institutions, authoritarianism, corruption, and conflict, external intervention, instability, and regime change rather than broad-based development.
- Historical Examples: Iraq, Libya, Venezuela.
|
- Monroe Doctrine 2.0: The Western Hemisphere was declared a U.S. sphere of influence. It prevents any European colonial intervention in the Americas.
- “Donroe Doctrine: The “Donroe Doctrine” is a term used to describe a revived, more aggressive interpretation of the Monroe Doctrine under Donald Trump.
- It justifies direct intervention—political, economic, or military—against regimes seen as hostile to U.S. interests.
- Strategic Focus: Control of energy resources (e.g., Venezuela), Securing strategic chokepoints (e.g., the Panama Canal), Countering rivals (China, Russia, Iran) in the U.S.’s immediate strategic western hemisphere neighbourhood.
Conclusion
The 2026 capture of Nicolás Maduro sets a perilous precedent for unilateral intervention. For India, sovereignty, dialogue, and multilateralism are strategic imperatives, while inclusive transition and civilian protection remain key to restoring Venezuela’s legitimacy and stability.
![]() 5 Jan 2026
5 Jan 2026


 The Legal Tests: The operation failed the three critical tests for justified force: Necessity, Proportionality, and Imminence.
The Legal Tests: The operation failed the three critical tests for justified force: Necessity, Proportionality, and Imminence. 