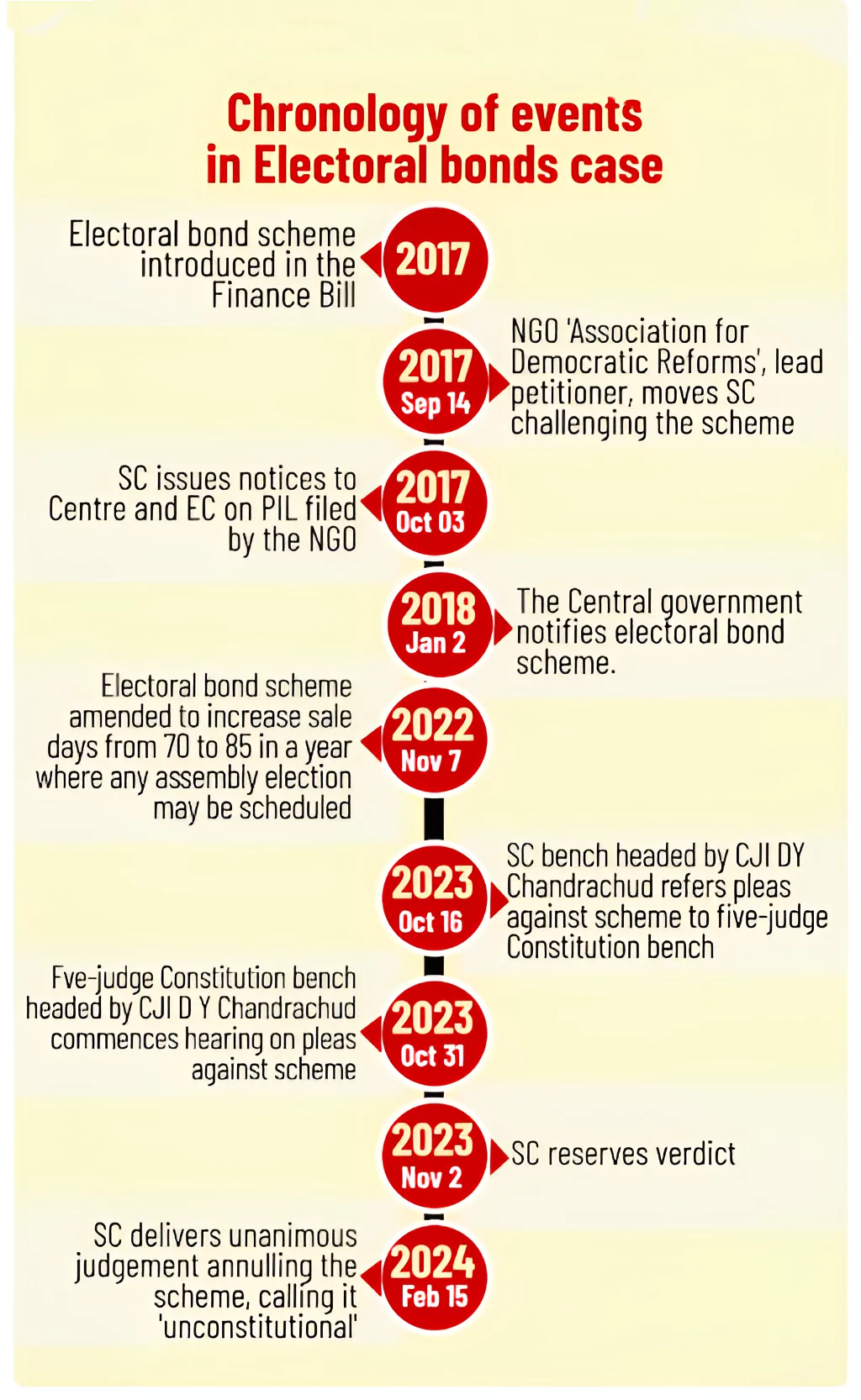
Recently, a constitutional bench of the Supreme Court strike down the electoral bonds scheme and declared it unconstitutional.

Context: Recently, a constitutional bench of the Supreme Court struck down the electoral bonds scheme and declared it unconstitutional.
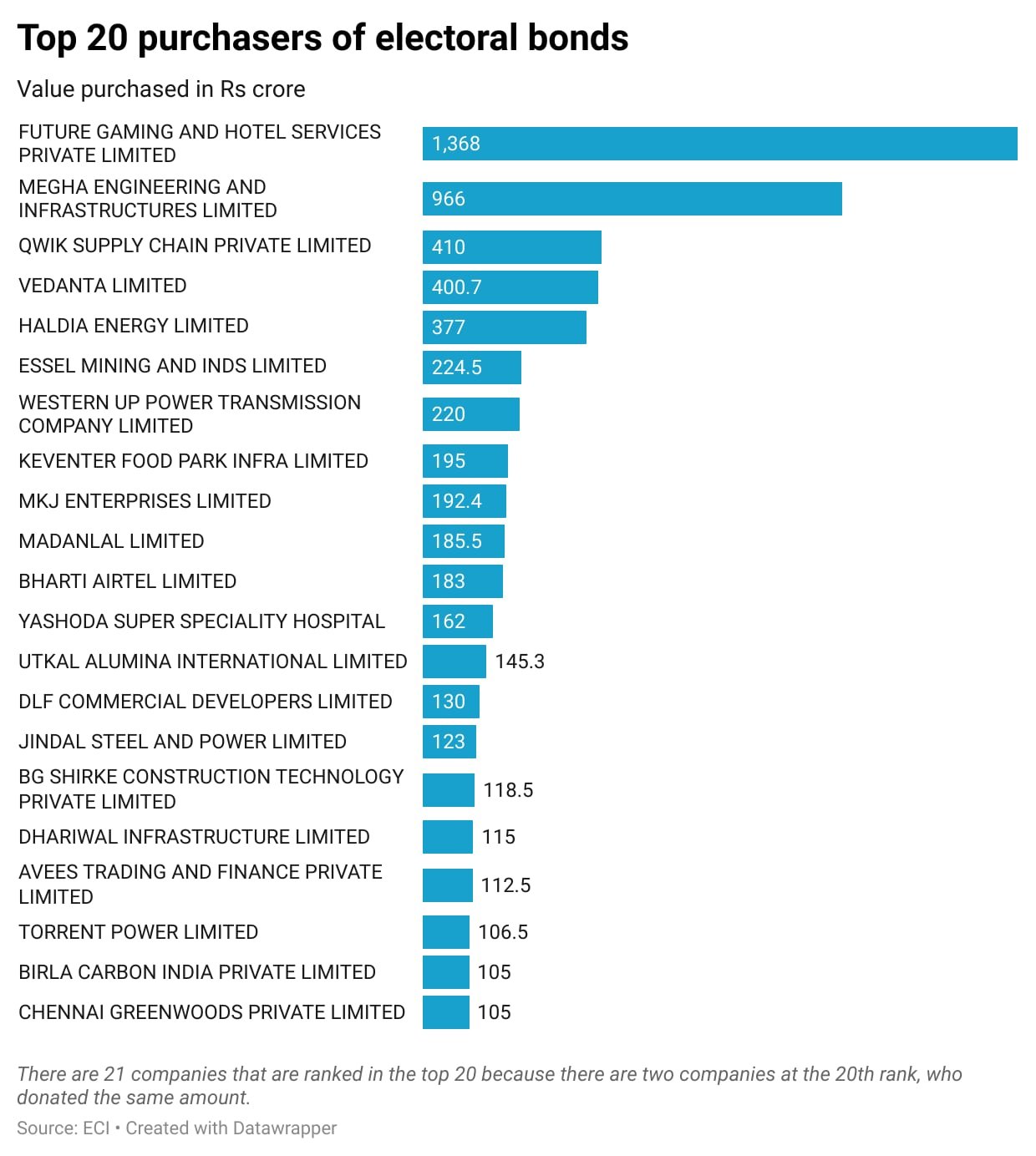
Election Commission of India (ECI) recently, publishes details of electoral bond data. On March 12, Supreme Court’s directed SBI to share the electoral bond data with the ECI.
Supreme Court struck down several amendments made through The Finance Act, 2016, and The Finance Act, 2017, to facilitate corporate donations to political parties.

| Arguments in favour | Arguments against |
|
|
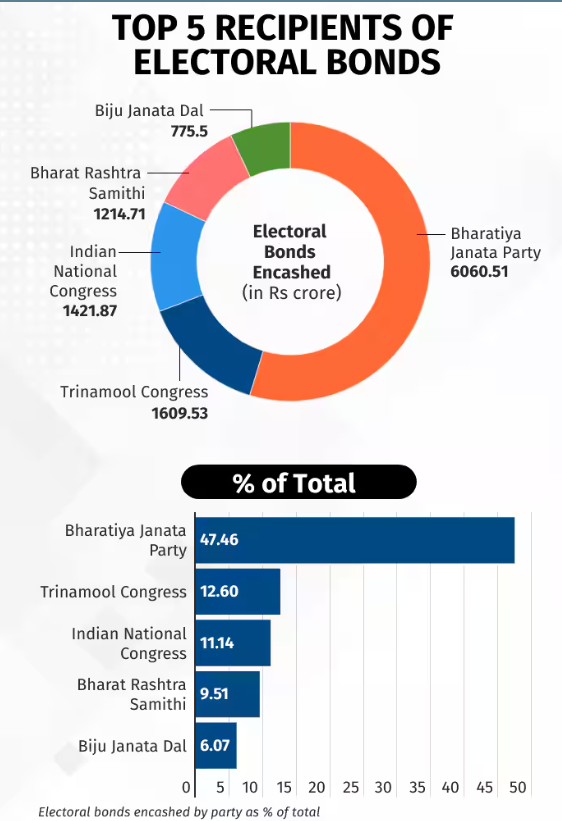
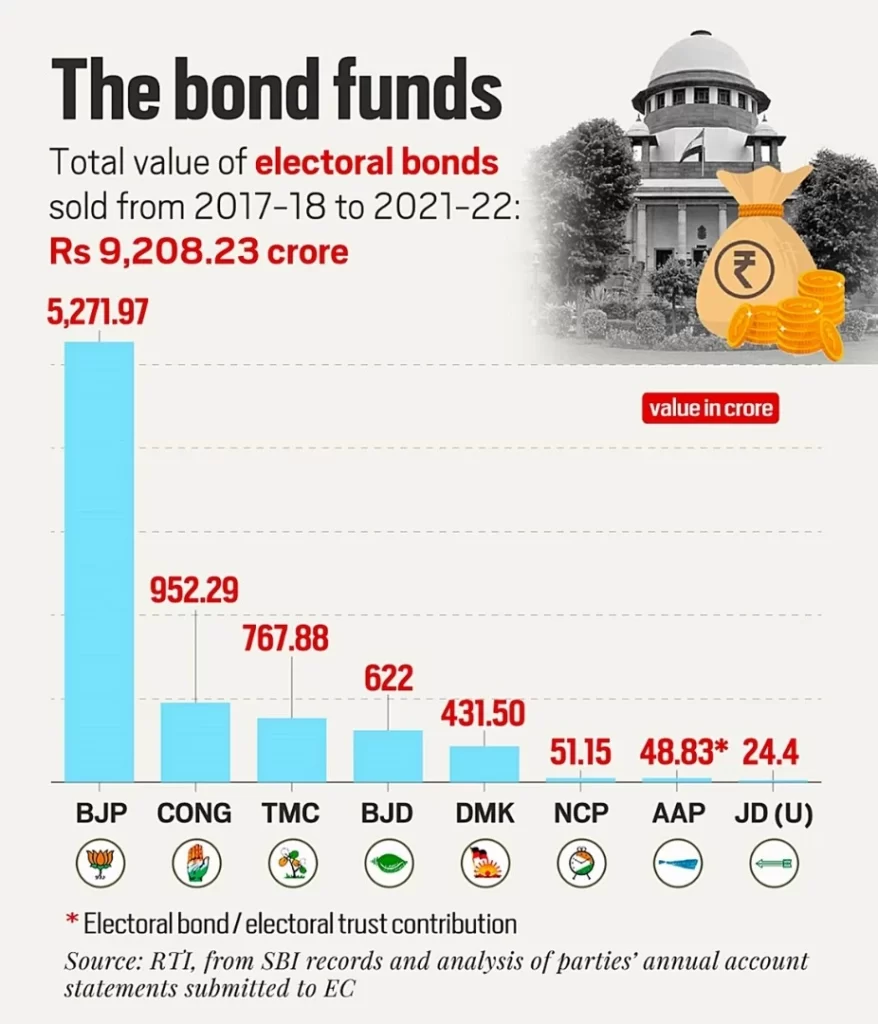
The Association of Democratic Reforms (ADR), a Delhi-based NGO, has published a report on electoral bonds and political party donations between 2016-17 and 2021-22. Key highlights of the report:
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Electoral bonds are interest-free bearer instruments that are essentially used to donate money anonymously to political parties. The scheme was first announced in the 2017 Union Budget speech.
It promotes transparency by requiring donors to provide KYC details while keeping their names confidential, ensuring accountability in political funding.
It may be purchased by Indian citizens or entities incorporated in India.
Only political parties registered under Section 29A of the Representation of the People Act, 1951, and meeting the criteria of having secured not less than one per cent of the votes polled in the last General Election to the House of the People or the Legislative Assembly of the State are eligible to receive electoral bonds.
These are issued in denominations of Rs 1,000, Rs 10,000, Rs 1 lakh, Rs 10 lakh, and Rs 1 crore.
These are valid for fifteen calendar days from the date of issue.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>