IAS Full Form is Indian Administrative Service. IAS is regarded as the most difficult exam in India and provides the most competitive exam position. Cansistates can check out details on IAS Exam, Eligibility, Patterns, Attempts, Salary Structure.

The IAS Full Form 2026 is Indian Administrative Service. IAS is regarded as the most difficult exam in India and provides the most competitive exam position. Every year, UPSC conducts the IAS Exam and selects applicants for a number of roles based on the Government of India’s results. Candidates who pass an exam administered by the Union Public Service Commission are appointed by the Union or State government and given various district-level jobs.
The IAS Full form is the Indian Administrative Service, which is the premier administrative civil service of the Indian government. It is one of the three All-India services and is considered to be the backbone of India’s administrative machinery. The Civil Services Examination is responsible for the entire gamut of operations of the government, including policy formulation, implementation, and evaluation at the district, state, and national levels.
IAS officer full form refers to an officer of the Indian Administrative Service. These officers are selected through the Civil Services Examination conducted by the UPSC and are appointed by the President of India. They hold crucial responsibilities ranging from district administration to policy formulation at the highest levels of government.
| Indian Administrative Service | |
| Aspect | Details |
| Full Form of IAS | Indian Administrative Service (IAS) |
| Founded | 1947 (Post-independence restructuring of ICS) |
| Conducting Authority | Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) |
| Recruitment Exam | Civil Services Examination (CSE) |
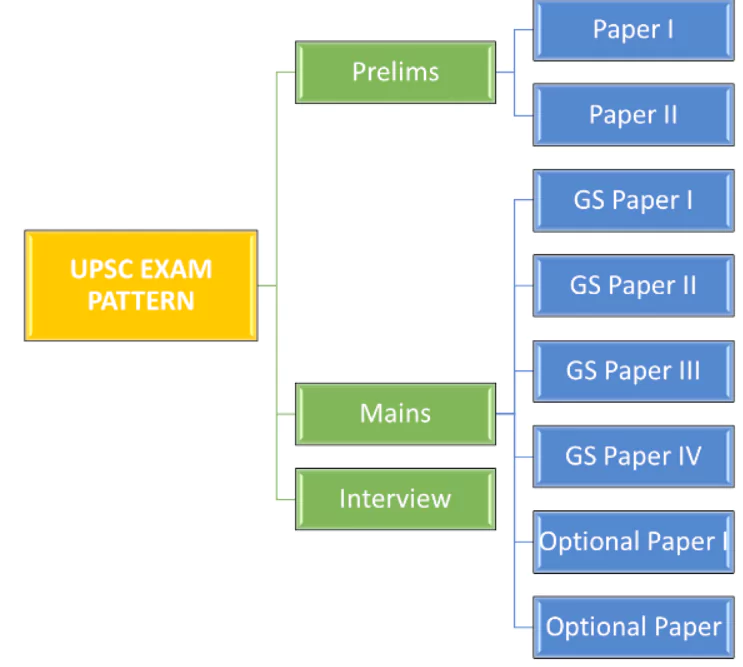
| Exam Stages | Preliminary Exam, Mains Exam, Personality Test (Interview) |
| Eligibility Criteria | Indian nationality, Graduate degree, Age 21–32 years (General category) |
| Number of Attempts | 6 (General), 9 (OBC), Unlimited (SC/ST within age limit) |
| Training Academy | Lal Bahadur Shastri National Academy of Administration (LBSNAA), Mussoorie |
| Initial Posting | Sub-Divisional Magistrate (SDM) |
| Career Progression | SDM → DM/Collector → Secretary → Chief Secretary → Cabinet Secretary |
| Pay Scale (Starting) | ₹56,100 per month (Pay Level 10) |
| Top Pay Scale | ₹2,50,000 per month (Cabinet Secretary, Pay Level 18) |

To become an IAS Officer in India which is the topmost coveted service of the Government of India. To be recruited in the IAS, one has to clear the Civil services Exam conducted by UPSC (Union Public Service Commission). Due to the popularity of the भारतीय प्रशासनिक सेवा विवरण (IAS Full Form in Hindi) as the most preferred service, this exam is sometimes also referred to as the IAS Exam in India.
This Civil Services/IAS Exam is conducted annually by UPSC. The IAS is a part of the executive branch of the Government of India and is regarded as the permanent bureaucracy. Lakhs of aspiring candidates belonging to different levels and categories of society, attempt the exam each year.
Although many of you would have not fully known about this Civil Services exam or even the full form of IAS, however, it is always fair to relearn about this All India Exam. In this article we will be covering every segment of the Indian Administrative Services (IAS Full Form) profile and IAS exam which will be beneficial for your upcoming preparation of this exam.
Every year UPSC releases notification for Civil Services/IAS exam there is clear mention of eligibility for the aspiring candidates. Here we are putting essential and important required eligibility that one has to fulfill in order to qualify for the IAS exam are as follows:
1. Nationality- The aspiring candidate has to be an Indian national in order to try and attempt the Indian Civil Service Exam.
| OBC | 3 years |
| Defence Service Personnel | 3 years |
| SC/ST | 5 years |
| Ex-Servicemen | 5 years |
| Deaf/Mute/Blind/Orthopedically Handicapped | 10 years |
3. Educational Qualification – The aspiring candidate should graduate from a university registered under or recognised by the Government. Candidates who are in their final year of their graduation can also apply for the examination.
4. Number of Attempts – There is a distinct number of attempts that are assigned to the following categories.
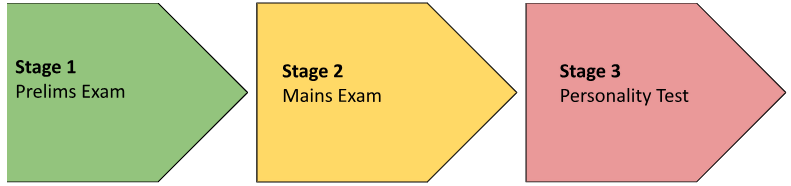
UPSC IAS Exam Pattern: The Civil Services Examination (CSE) examination is conducted by the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC). It is one of the toughest competitive exams in India. It is conducted in three stages: Preliminary Examination, Mains Examination, and Personality Test.
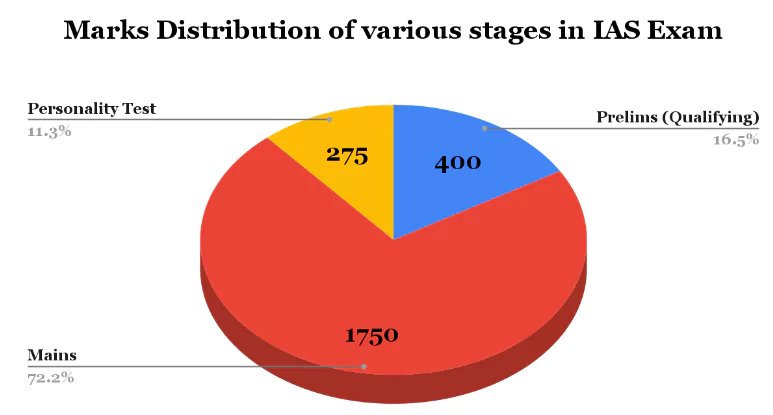
| Stage of Exam | Specification | Total Marks Allotted |
| Prelims |
|
400 marks |
| Mains |
|
1750 marks |
| Personality Test |
|
275 marks |
|
Also Read- UPSC Optional Subjects |
|---|
| Also Read: | |
| NCERT Notes | Daily Current Affairs |
| Daily Editorial Analysis | CSAT Strategy |
| UPSC Blogs | Prelims 2024 Strategy |
Once a candidate clears all stages of the exam and achieves a good rank so that he/she gets selected for IAS officer after that IAS officers undergo rigorous training to prepare them for the responsibilities they will be shouldering.

After the application of the 7th Pay Commission salary of IAS Officers has been revised now there are new salary rates for IAS officers in India. At the entry level when an IAS Officer just joins his/her department ,receives a basic pay of Rs. 56,100 (excluding additional allowances such as TA, DA, and HRA). Additionally, there is a grade pay of Rs. 16,500. The maximum salary for a senior IAS officer like Cabinet Secretary, can reach up to Rs. 2,50,000.
| Continue To Read: IAS Officer Salary Per Month In India [Post Wise] |
|---|
| Pay Level | Basic Pay (INR) | Service Tenure | Designation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| District Administration | State Secretariat | Central Secretariat | |||
| 10 | 56100 | 1-4 | Sub-Divisional Magistrate | Undersecretary | Assistant Secretary |
| 11 | 67,700 | 5-8 | Additional District Magistrate | Deputy Secretary | Undersecretary |
| 12 | 78,800 | 9-12 | District Magistrate | Joint Secretary | Deputy Secretary |
| 13 | 1,18,500 | 13-16 | District Magistrate | Special Secretary-cum-Director | Director |
| 14 | 1,44,200 | 16-24 | Divisional Commissioner | Secretary-cum-Commissioner | Joint Secretary |
| 15 | 1,82,200 | 25-30 | Divisional Commissioner | Principal Secretary | Additional Secretary |
| 16 | 2,05,400 | 30-33 | No Equivalent Rank | Additional Chief Secretary | No Equivalent Rank |
| 17 | 2,25,000 | 34-36 | No Equivalent Rank | Chief Secretary | Secretary |
| 18 | 2,50,000 | 37+ years | No Equivalent Rank | No Equivalent Rank | Cabinet Secretary of India |
IAS Officers enjoy various perks during his/her tenure as an IAS officer. These perks can be categorized as an advantage of being an Indian IAS officer. Let us see the various perks and facilities given to Indian Administrative Services during his/her tenure and after that:
The IAS officer service involves many duties. To be chosen for this job, a person needs to be sincere, patient, and have unique skills. IAS officers are vital for running the country. They work in different areas like the central government, state government, public companies, and international organizations.
IAS officers are responsible for managing various administrative functions at both the central and state levels of the government. Their roles encompass implementing government policies, handling public affairs, and ensuring the smooth functioning of government departments.
IAS officers are involved in policy making, developmental activities, and public service, working closely with other government agencies and stakeholders. With immense power and influence, IAS officers play a vital role in shaping the nation’s governance and development.

The roles and responsibilities that are assigned to an IAS officer vary through different stages of their career.
Indian Administrative Services (full form of ias) officers selected by UPSC possess significant power, roles and responsibilities which set them apart from other professions and services. Let us see some significant power governed by an IAS Officer during his/her role at various positions.
Facts you should know
|
|---|
Becoming an IAS Officer requires clearing the UPSC CSE Exam, which consists of three stages: UPSC Prelims, Mains, and Interview. To start the journey, it’s essential to thoroughly review and comprehend the UPSC Syllabus. While the Prelims Syllabus and the UPSC Mains Syllabus are interconnected, they demand different preparation strategies.
It’s important to understand each stage’s requirements and prepare accordingly for a successful attempt at achieving your goal of becoming an IAS Officer.
To become an IAS officer, one needs to have a graduation degree from a recognized university. The Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) is responsible for recruiting IAS officers through the Civil Service Exam. Alternatively, one can also become an IAS officer through promotion from state civil services.

| Also Read: | |
| NCERT Notes | Daily Current Affairs |
| Daily Editorial Analysis | CSAT Strategy |
| UPSC Blogs | Prelims 2024 Strategy |
| Challenges | Rewards |
|
|
Overall, being an IAS officer is a challenging but rewarding career. IAS officers have the opportunity to make a real difference in the lives of the people they serve. They are respected and held in high esteem by the people of India.
Ready to boost your UPSC 2026 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
Check Out UPSC CSE Books
Visit PW Store
No, Top rankers candidates who topped the list are entitled to get IAS services for reserved candidates they can get IAS rank if their rank vary.
No, not completely true every service under civil services exam have their own importance and have their unique role in nation building. IAS covers a wide range of spheres that is why it is generally considered as the most influential service.
If this happens you will get Indian Police Service, Indian Revenue Service and many other Group A services
IAS stands for the Indian Administrative Service (full form of ias). It is a premier administrative civil service in India, considered the backbone of the country's administrative machinery.
To become an IAS officer, one needs to clear the Civil Services Exam conducted by the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC). The exam consists of three stages: Prelims, Mains, and Interview.
The aspiring candidate should be an Indian national, aged between 21 and 32, with certain age relaxations for various categories. Educational qualification requires a graduate degree from a recognized university.
Yes, candidates can attempt the IAS exam multiple times. The attempts are limited to six for general candidates, nine for OBC, and unlimited attempts for SC/ST candidates.
IAS officers enjoy perks like government-provided accommodation, transportation, security, and various allowances. After retirement, they receive lifetime pensions and may be appointed to commissions or international organizations.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>