Understanding inflation in India with a clear breakdown of its key causes, economic impact on households and businesses, and practical policy solutions aimed at ensuring price stability and sustainable growth.

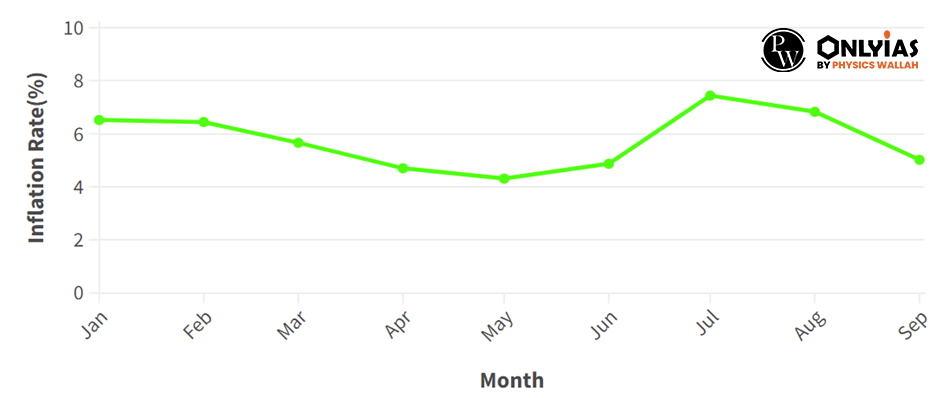
Understanding Inflation in India: Inflation in India, measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI), has remained subdued at around 0.71% in November 2025, driven by falling food prices amid favorable monsoons and supply chain stability. Persistent pressures from volatile oil imports and wage growth challenge the Reserve Bank of India’s 4% target, influencing monetary policy and economic growth projected at 7.4% for FY26. Understanding its causes like demand-pull factors and supply shocks, alongside impacts on purchasing power and investments, is crucial for policymakers and citizens alike.
| Parameters | CPI | WPI |
| Base Year |
|
|
| Scope |
|
|
| Released by |
|
|
| Major components |
|
|
| Purpose |
|
|
| Uses |
|
|
| Relevance |
|
|
A moderate amount of inflation in India is generally considered to be a sign of a healthy economy because as the economy grows, demand for stuff increases. However persistent high inflation can have many negative consequences like the following:
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Urijit Panel Committee
Consumer Price Index
It attempts to remove the volatile, transitory movements from the CPI
They better encapsulate the demand side pressures in the economy; monetary policy cannot control food or fuel inflation in India.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>