Core Demand of the Question
- Discuss the strategic significance of the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) in the current Eurasian geopolitical scenario.
- Highlight the current challenges of the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) .
- Suggest a suitable way forward.
|
Answer
Introduction
The India–Middle East–Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC), launched during the G20 Summit in New Delhi in September 2023, is a transformative initiative connecting India, the Gulf, Israel, and Europe through a multimodal network of railways, shipping lanes, energy pipelines, and digital infrastructure. Designed to bolster connectivity, trade efficiency, and strategic autonomy across Eurasia, IMEC emerges as a compelling alternative to existing China-led trade corridors.
Body
Strategic Significance of IMEC
- Diversifies Trade Routes: IMEC provides an alternative to the Suez Canal and China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
Eg. It can cut transit time by 40% and logistics costs by 30%, thereby enhancing the global competitiveness of Indian exports.
- Enhances India’s Eurasian Presence: It deepens India’s integration with Central Asia and Europe, bypassing China-dominated routes.
Eg. India’s engagement with Kazakhstan’s Middle Corridor facilitates alternate overland access to Europe.
- Strengthens Energy Security: IMEC will support green energy transport, connecting energy-rich Gulf nations with energy-hungry India and Europe.
Eg. Undersea cables between Cyprus and Israel are part of renewable power and hydrogen supply chains.
- Deepens Geopolitical Alliances: The corridor enhances ties with the UAE, EU, and USA, counterbalancing China’s strategic influence.
Eg. Nations like France, Italy, and Germany are already partnering, sending dedicated envoys to support the project.
- Boosts Regional Integration: It fosters economic cooperation through integrated rail, port, and digital infrastructure across regions.
Eg. The ongoing India–UAE MAITRI portal negotiations aim to ensure smoother multimodal connectivity and cargo movement.
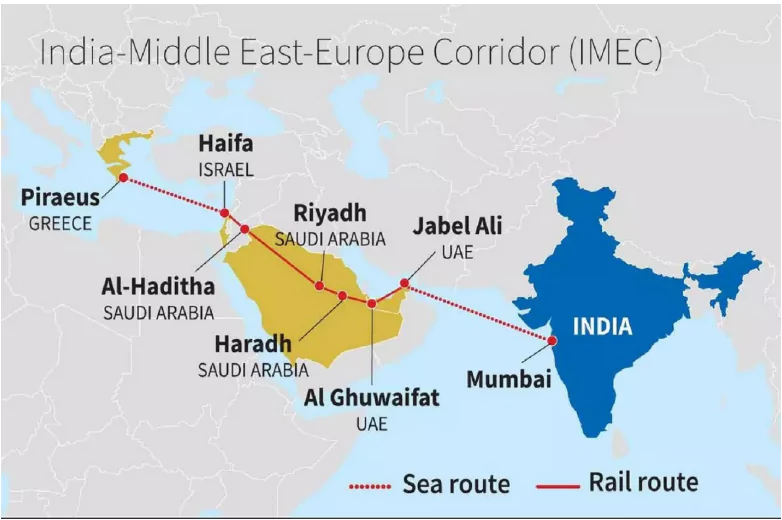
Challenges Facing IMEC
- Geopolitical Instability: Conflicts in the Middle East disrupt planning, financing, and construction timelines.
Eg. The Israel–Gaza conflict stalled corridor diplomacy and postponed infrastructure discussions.
- Funding Gaps: The corridor lacks comprehensive financial backing for large-scale infrastructure.
Eg. Only US$20 billion has been pledged so far, against the estimated need of US$600 billion by 2027.
- Complex Multilateral Coordination: Aligning policies across multiple nations with different legal and logistical standards is difficult.
Eg. Lack of harmonized systems in customs, rail gauge, and digital protocols hampers timely progress.
- Competition from China’s BRI: IMEC must compete with already established and well-funded BRI corridors.
Eg. BRI-controlled hubs like Piraeus Port in Greece and the Suez Canal remain dominant trade routes.
- Strategic Exclusion of Key States: Current framework excludes important transit states, risking geopolitical friction.
Eg. Turkey has objected to its exclusion and demanded inclusion to maintain corridor viability and regional balance.
Way Forward
- Settle Regional Conflicts: Active diplomacy is essential to maintain corridor stability.
Eg. India’s Foreign Minister S. Jaishankar has engaged the UAE, Oman, and Greece to restore confidence in the corridor.
- Create Robust Funding Models: Leverage the G7’s PGII (Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment) and private capital.
- Expand Membership Inclusivity: Inclusion of Turkey, Egypt, and Oman can ensure broader connectivity and stability.
Eg. The Greek Foreign Minister labelled IMEC a “project for peace” and emphasized the need for regional expansion.
- Harmonize Regulatory Frameworks: Establish uniform standards for rail, port logistics, and data flow.
Eg. Agreements via the MAITRI digital platform aim to align India–UAE customs and logistics systems.
Conclusion
The IMEC offers India a transformative corridor to enhance connectivity, energy security, and Eurasian integration. By resolving regional conflicts, securing funding, broadening membership, and harmonizing regulations, India can position IMEC as a durable alternative to China’s BRI and reinforce its global strategic footprint.
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.



Latest Comments