Core Demand of the Question
- Highlight that “The India-Middle East-Europe Corridor (IMEC) holds transformative benefits for international maritime trade.”
- Assess the limitations of the (IMEC) in achieving its intended benefits.
- Highlight the strategies that can be implemented by India to maximise its impact on global trade routes.
|
Answer
The India-Middle East-Europe Corridor (IMEC), launched at the 2023 G20 Summit, is a major transcontinental trade route enhancing connectivity from India to Europe via the Middle East. By cutting transit times and costs compared to routes like the Suez Canal, IMEC strengthens the Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment (PGII) initiative.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Transformative Benefits of IMEC for International Maritime Trade
- Reduced Transit Time and Transportation Costs: IMEC promises a 40% reduction in transit time and a 30% decrease in transportation costs as compared to Suez canal.
- Strengthening Economic Ties Across Regions: IMEC enhances India’s trade relations with partner countries, providing structured pathways for increased exports and imports.
For example: India-UAE trade under CEPA observed an annual increase of 14%.
- Strategic Geopolitical Alignment: By bypassing volatile regions, IMEC reduces dependence on the Suez Canal and aligns India with Middle Eastern and European partners, enhancing strategic autonomy in trade routes.
For instance: IMEC will strengthen India’s geopolitical position in West Asia and Europe.
- Enhanced Connectivity and Integration with Global Supply Chains: IMEC links India directly to Europe, facilitating integration into global supply chains, which is essential for sectors like manufacturing and technology.
For example: The National Logistics Policy 2022 identifies improved connectivity as vital for India’s goal of becoming a global manufacturing hub.
- Boost for Energy Infrastructure: IMEC’s inclusion of clean energy projects aims to transform regional energy networks, promoting sustainable growth and energy security by fostering cleaner, renewable energy sources.
For example: India’s National Green Hydrogen Mission and One Sun One World One Grid (OSOWOG) aligns with IMEC’s energy corridor vision, promoting green energy trade.
- Expansion of Digital Infrastructure: India’s Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) boosts financial inclusion via mobile-accessible payment networks like RuPay and UPI, enabling faster cross-border transactions with nations like Dubai(UAE) and France.
| The IMEC will comprise two separate corridors, the east corridor connecting India to the Gulf and northern corridor connecting Gulf to Europe.
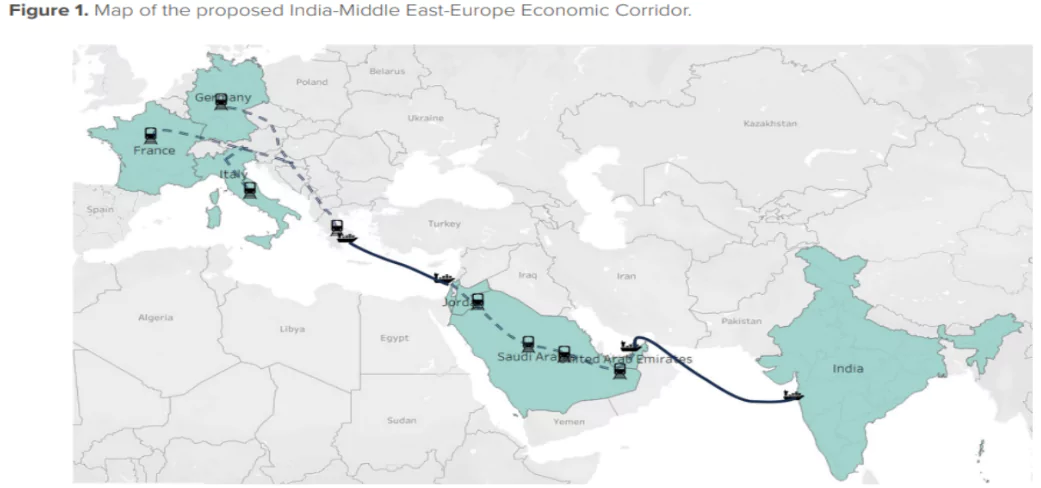
|
Limitations of IMEC in Achieving Intended Benefits
- Geopolitical Tensions in West Asia: Ongoing conflicts, particularly the Israel-Palestine situation, pose serious delays and affect regional cooperation, limiting IMEC’s operational efficiency.
- Dependence on Infrastructure Development: The corridor’s success hinges on rapid port and rail infrastructure development in all participating countries, which may face funding and logistical delays.
For example: The National Infrastructure Pipeline highlights a need for $1.4 trillion for infrastructure, indicating financing challenges for IMEC.(NIP Task force 2019-25)
- Complex Regulatory and Customs Procedures: Divergent customs and trade regulations among participating nations could hinder smooth cargo movement, impacting the corridor’s efficiency.
- Limited Digital and Technological Infrastructure: Digital integration is essential for IMEC’s success, but limited IT infrastructure in some regions may affect logistics coordination, delaying benefits realisation.
- Uncertain Regional Partnerships and Political Commitment: Sustained commitment from all countries is vital; however, political changes or shifts in regional policies may weaken IMEC’s foundation and stall progress.
Strategies for India to Maximise IMEC’s Impact on Global Trade Routes
- Strengthening Domestic Port and Logistics Infrastructure: Enhancing port facilities and logistics infrastructure, particularly at IMEC nodes, will boost India’s capacity to handle increased trade volumes efficiently.
For example: Sagarmala Project focuses on port modernization and Port-led development, enhancing India’s alignment with IMEC.
- Digital Integration and Upgrading Supply Chains: Investing in digital logistics and supply chain management systems can reduce costs and improve reliability.
- Diplomatic Engagement for Regional Stability: India must play a proactive diplomatic role in fostering regional peace, particularly in the Middle East, to ensure the corridor’s long-term stability and reliability.
For example: India’s engagement in I2U2 and the Abraham Accords reflects its efforts to promote cooperation and peace in West Asia.
- Establishing an IMEC Secretariat: A dedicated IMEC Secretariat can coordinate among stakeholders, streamline operations, and monitor progress, ensuring consistent alignment with strategic objectives.
- Aligning Policies with Global Standards for Trade Facilitation: Harmonising trade laws, customs procedures, and standards with international norms can facilitate seamless goods movement, enhancing IMEC’s attractiveness for global partners.
For example: India’s National Logistics Policy 2022 promotes standardisation, which is essential for IMEC’s smooth functioning.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
The India-Middle East-Europe Corridor (IMEC) has the potential to reshape global trade. Along with the INSTC project, IMEC holds great significance for India to boost regional connectivity and increase its trade with partner countries as well.
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.


https://uploads.disquscdn.com/images/29ba58d3397a45d2d61727eede03bb25959232153091ef21969bf92cec7c71a5.jpg https://uploads.disquscdn.com/images/01e6a097f06f6b371677adf58bed56a1a73c45b2bcf096f6b376cdfb79f4b07e.jpg