The earth is the only planet which has life. The surface of the earth is a complex zone which has three main components of the environment viz. Lithosphere, Hydrosphere and Atmosphere. These 3 meet, overlap and interact and form a narrow zone called a Biosphere which sustains life. Along with land and water, air pressure is a main part of this biosphere which plays a major role in regulating atmospheric activities. In this chapter, we will deal primarily with this atmosphere and its major components.
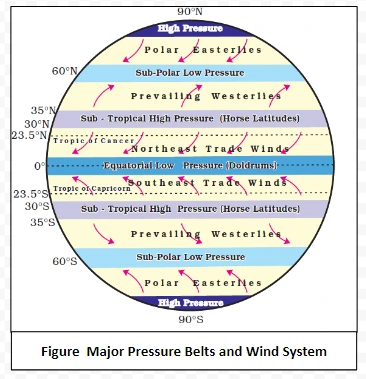
Wind is named after the direction from which it blows, e.g. the wind blowing from the west is called westerly.
Odisha, located on India’s eastern seacoast, is prone to cyclones originating in the Bay of Bengal. In October 1999, a cyclone hit five districts of Odisha, followed by a super cyclone on October 29, 1999. The damages were primarily caused by three factors viz. high wind velocity (up to 260 km/h for over 36 hours), heavy rain lasting for three days, and a tidal surge. The cyclonic winds caused heavy damage in Odisha. The cyclone originated as a depression in the Gulf of Thailand and intensified into a supercyclone, hitting Odisha on October 29, 1999. The super cyclone affected the entire Odisha coast, including cities like Bhubaneswar and Cuttack, impacting around 13 million people.
Earth’s harmony depends on the balance of its land, water, and air. Humans need to take care of our planet by making responsible choices to ensure a healthy and stable environment for us and future generations. The Earth’s atmosphere is a complex and vital part of our planet, supporting life and influencing weather and climate. Understanding the atmosphere’s layers, composition, and interactions is crucial for environmental preservation and climate management.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
