![]() November 23, 2023
November 23, 2023
![]() 1058
1058
![]() 0
0
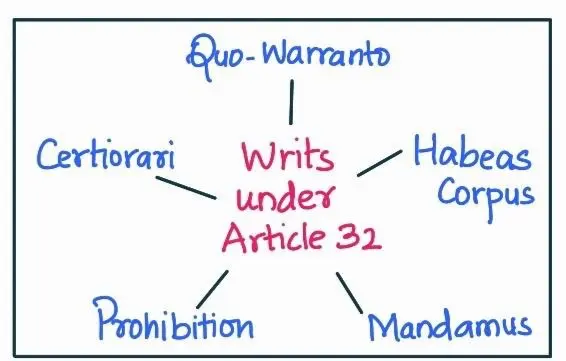
Fundamental Rights ensure that ‘All are equal before the law’ which means that all citizens have equal right to freedom of religion, assembly, association, and movement. No person is to be deprived of his life, liberty or property, except in accordance with the law.
Right to Property: A Protracted Struggle and Constitutional Remedies
| National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) |
|
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
Latest Comments