![]() 22 Jun 2024
22 Jun 2024
|
Disaster Risk Reduction |
1. Preparedness:
2. Mitigation:
|
|---|
The three key stages of disaster risk management are: Before, During, After Management
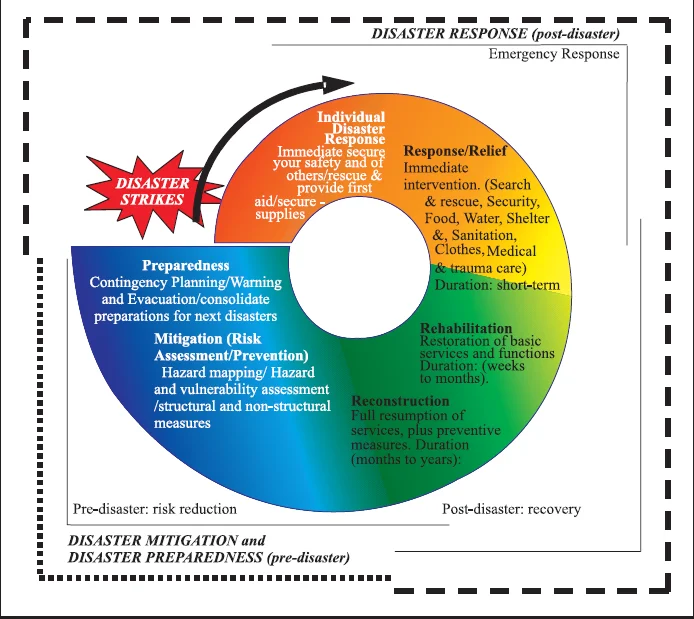
Disaster Management
|
Yokohama Strategy and International Decade for Natural Disaster Reduction (IDNDR) Yokohama Strategy and Plan of Action for a Safer World |
|---|
(a) Human and institutional capacity-building and strengthening. (b) Technology sharing: the collection, dissemination and utilisation of information. (c) Mobilisation of resources.
|
Conclusion
Glossary
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>