![]() 30 Nov 2023
30 Nov 2023
The lithosphere, composed of rigid plates known as lithospheric plates, undergoes slow movement driven by circulating molten magma beneath the Earth’s surface. These movements , classified as endogenic and exogenic forces, give rise to transformative phenomena like earthquakes and volcanoes. It emphasizes that the Earth’s surface, vital for all life, is a complex system influenced by these intricate forces. Grasping these mechanisms is essential for the responsible care of our planet, enabling us to harmonize utilization and preservation for the well-being of generations to come.
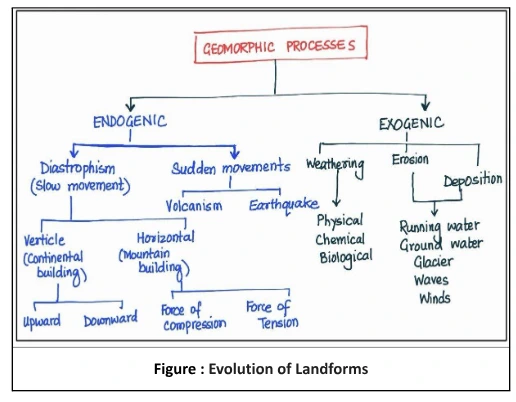
Endogenic forces occur due to the energy emanating from within the earth surface which can result in either diastrophism or sudden movements such as earthquakes and volcanoes.
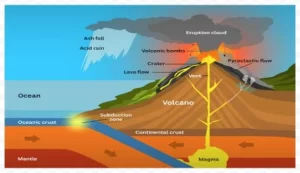
A Volcano Epicentre
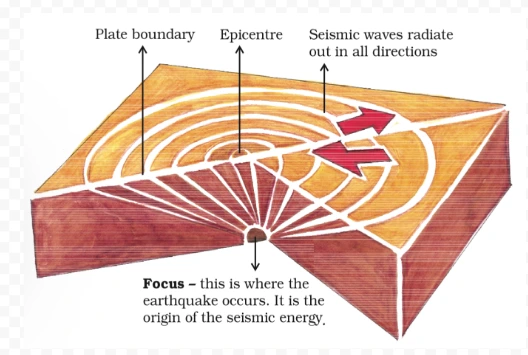
Origin of an Earthquake
There are three types of earthquake waves:
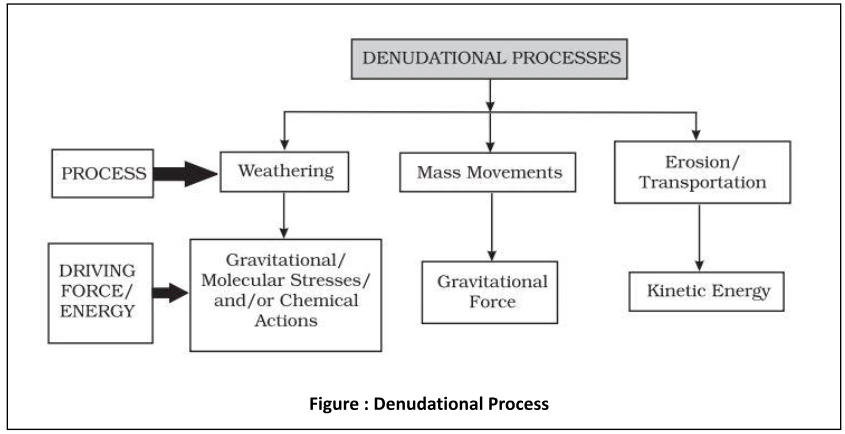
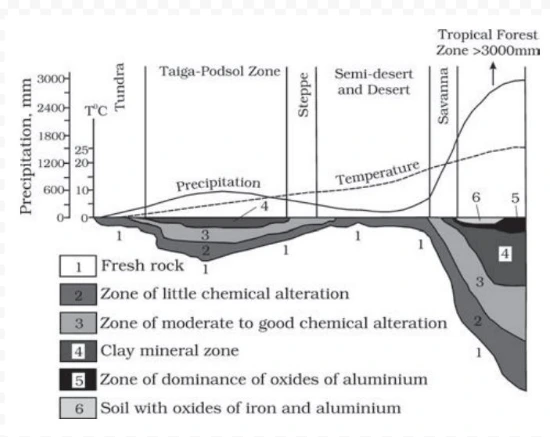
Climatic regimes and depth of weathering mantles (adapted and modified from Strakhov, 1967)
Weathering Processes are classified into the following categories:

Exfoliation (Flacking) and granular disintegration
<div class="new-fform">
</div>