![]() 7 Dec 2023
7 Dec 2023
Economic activities, which generate income, fall into primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary sectors. Primary activities are directly dependent on Earth’s resources like land, water, vegetation, and minerals. This includes hunting, pastoralism, fishing, forestry, agriculture, mining and quarrying.
This article emphasizes primary activities with special focus on land use patterns and agriculture in India.
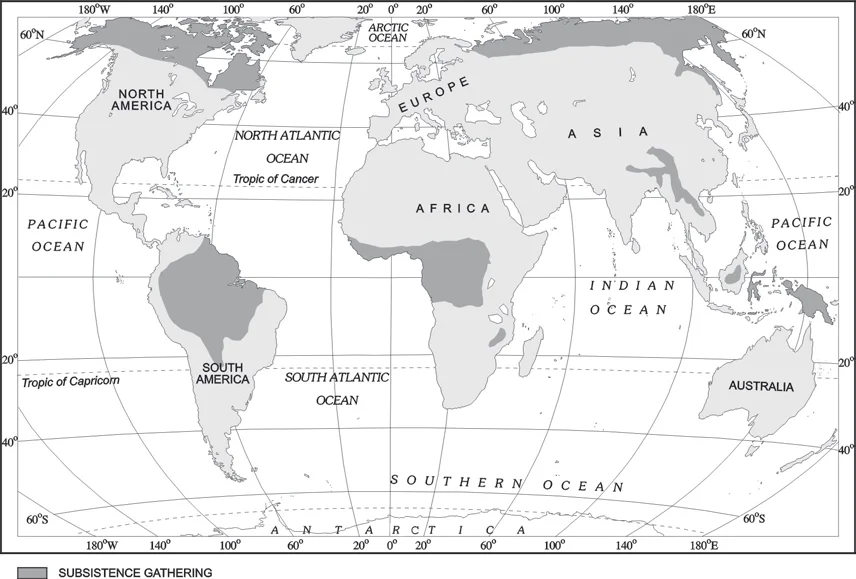
Areas of Subsistence Gathering
Pastoralism is a practice of domesticating animals. People in different climatic conditions selected and raised local animals. Animal rearing today is practiced at subsistence or commercial levels, influenced by geography and technology.It is also called as Pastoral Nomadism
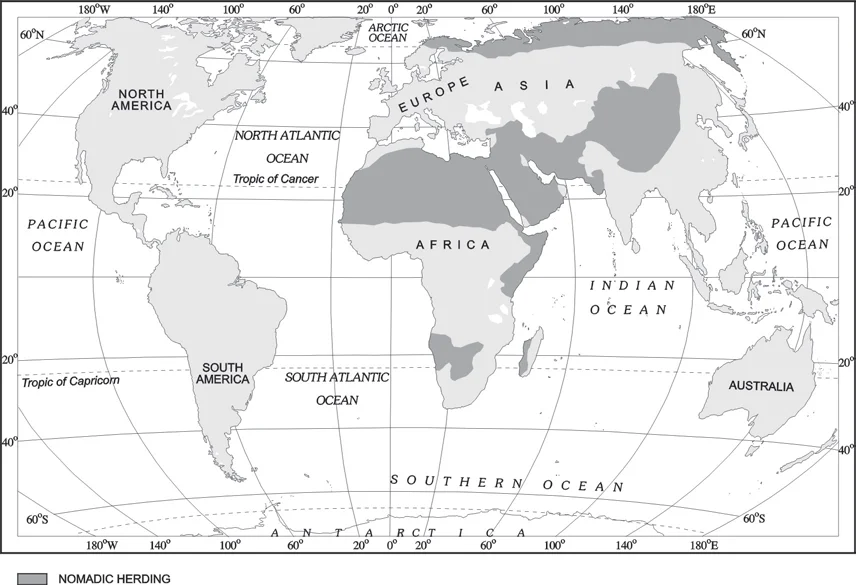
Areas of Nomadic Herding

Nomadic Herders
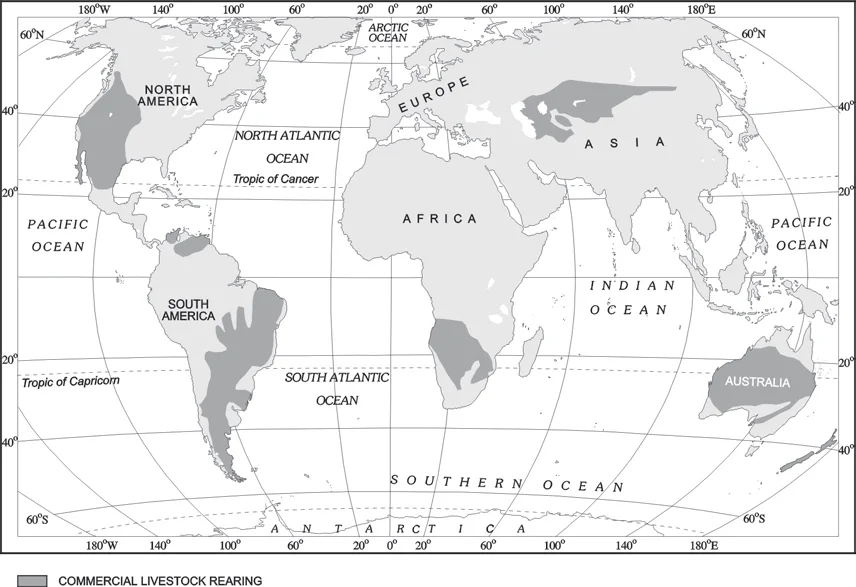
Areas of Commercial Livestock Rearing

Commercial Livestock Rearing
Also Read: Land Resources and Agriculture in India: Dynamic, changes and Relationships
<div class="new-fform">
</div>